Abstract
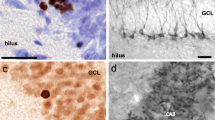
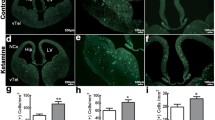
Depression is a leading cause of disability which at its worst leads to suicide. Its treatment relies on psychotherapy in combination with certain antidepressants (AD(s)) from various classes such as tricyclics, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, or serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs). Among SNRIs, venlafaxine (VEN) is one such most commonly prescribed AD which is recently reported to be in the top 50 most prescribed drugs in the USA. Depression during pregnancy is a common condition, where prescribing an AD becomes necessary as untreated depression during pregnancy has its own complications for both mother and the child. This, probably, is why an incredible rise has been reported in prescribing ADs like VEN to pregnant women in the recent past, despite some studies, including the one from our own group, having reported the in-utero VEN-induced apoptotic neurodegeneration in the fetal neocortex and the consequent neurobehavioral anomalies in adulthood. However, there still exists a lack of insight into the effects of intrauterine exposures of VEN on other fetal brain regions like the hippocampus (HPC) and striatum (STR) and the consequent effects on their cognitive and emotional wellbeing in later life. Hence, this study has been conducted where pregnant Charles-Foster (CF) rats were oral gavaged with VEN (25, 40, and 50 mg/kg bw) from gestation day (GD) 05–19. On GD-19, half of the control and treated dams were euthanized to collect their fetuses. Fetal brains were dissected and processed for reactive oxygen species (ROS) estimation neurohistopathology and confocal microscopic studies. The remaining dams were allowed to deliver naturally, and litters were reared for up to 8 weeks then tested for their cognitive abilities by the Morris water maze test and for their emotionality by the Forced swimming test. Our results showed substantial neurocytoarchitectural deficits in both HPC and STR, along with enhanced ROS levels and apoptotic neurodegenerations. Furthermore, VEN-treated young rat offsprings displayed cognitive impairments and depressive behavior as the long-lasting impact of VEN in a dose-dependent manner. So it may be inferred that prenatal VEN-induced oxidative stress causes apoptotic neurodegeneration leading to neuronal loss in HPC and STR which consequently affects the development of the said brain areas resulting in impaired cognitive and emotional abilities of young adult offsprings. Therefore, extrapolating these findings in animal models, caution may be taken before prescribing VEN to pregnant women, especially during the sensitive phase of pregnancy.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altman J, Bayer SA (1995) Atlas of prenatal rat brain development. Trends in Neurosciences
Anderson KN, Lind JN, Simeone RM, Bobo WV, Mitchell AA, Riehle-Colarusso T, Polen KN, Reefhuis J (2020) Maternal use of specific antidepressant medications during early pregnancy and the risk of selected birth defects. JAMA Psychiat 77(12):1246–1255
Andrews JM, Ninan PT, Nemeroff CB (1996) Venlafaxine: a novel antidepressant that has a dual mechanism of action. Depression 4(2):48–56
Arias N, Fidalgo C, Vallejo G, Arias JL (2014) Brain network function during shifts in learning strategies in portal hypertension animals. Brain Res Bull 104:52–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2014.04.004
Arvind BA, Gururaj G, Loganathan S, Amudhan S, Varghese M, Benegal V, Rao GN, Kokane AM, Chavan BS, Dalal PK, Ram D (2019) Prevalence and socioeconomic impact of depressive disorders in India: multisite population-based cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 9(6):e027250. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2018-027250
Bakker MK, Kölling P, Van Den Berg PB, De Walle HE, Jong De, van den Berg LT (2008) Increase in use of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in pregnancy during the last decade, a population-based cohort study from the Netherlands. Br J Clin Pharmacol 65(4):600–606
Bayer SA, Altman J, Russo RJ, Zhang X (1993) Timetables of neurogenesis in the human brain based on experimentally determined patterns in the rat. Neurotoxicology 14(1):83–144
Benkert O, GRUeNDER G, WETZEL H (1997) Is there an advantage to venlafaxine in comparison with other antidepressants? Hum Psychopharmacol Clin Exp 12(1):53–64
Bennett HA, Einarson A, Taddio A, Koren G, Einarson TR (2004) Prevalence of depression during pregnancy: systematic review. Obstet Gynecol 103(4):698–709. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.AOG.0000116689.75396.5f
Bittigau P, Sifringer M, Genz K, Reith E, Pospischil D, Govindarajalu S, Dzietko M, Pesditschek S, Mai I, Dikranian K, Olney JW, Ikonomidou C (2002) Antiepileptic drugs and apoptotic neurodegeneration in the developing brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99(23):15089–15094. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.222550499
Bogi E, Belovicová K, Ujhazy E, Mach M, Koprdova R, Zilava L, Garafová A, Jezova D, Dubovicky M (2018) Perinatal exposure to venlafaxine leads to lower anxiety and depression-like behavior in the adult rat offspring. Behav Pharmacol 29(5):445–452
Bondi DS, Khan OA, Hageman J (2016) Pharmacology review: maternal selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor use and neurologic effects on the neonate. NeoReviews 17(7):e356–e366
Bot P, Semmekrot BA, van der Stappen J (2006) Neonatal effects of exposure to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors during pregnancy. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 91(2):F153. https://doi.org/10.1136/adc.2004.066431
Brigitta B (2002) Pathophysiology of depression and mechanisms of treatment. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 4(1):7–20
Casper RC, Fleisher BE, Lee-Ancajas JC, Gilles A, Gaylor E, DeBattista A, Hoyme HE (2003) Follow-up of children of depressed mothers exposed or not exposed to antidepressant drugs during pregnancy. J Pediatr 142(4):402–408
Coppen A (1967) The biochemistry of affective disorders. Br J Psychiatry 113(504):1237–1264. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.113.504.1237
Costa LG, Steardo L, Cuomo V (2004) Structural effects and neurofunctional sequelae of developmental exposure to psychotherapeutic drugs: experimental and clinical aspects. Pharmacol Rev 56(1):103–147. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.56.1.5
D’Hooge R, De Deyn PP (2001) Applications of the Morris water maze in the study of learning and memory. Brain Res Rev 36(1):60–90
Dobbing J, Sands J (1979) Comparative aspects of the brain growth spurt. Early Human Dev 3(1):79–83
Dowlatshahi K, Marosek SH (2019) An analysis of major depressive disorder and the effectivity of effexor XR®(Venlafaxine Hydrochloride) in its treatment
Dubovický M, Császárová E, Brnoliaková Z, Ujházy E, Navarová J, Mach M (2012) Effect of prenatal administration of venlafaxine on postnatal development of rat offspring. Interdiscip Toxicol 5(2):92
Dunlop BW (2016) Evidence-based applications of combination psychotherapy and pharmacotherapy for depression. Focus 14(2):156–173
Fryer JD, Lukas RJ (1999) Antidepressants noncompetitively inhibit nicotinic acetylcholine receptor function. J Neurochem 72(3):1117–1124
Gabbay V, Ely BA, Li Q, Bangaru SD, Panzer AM, Alonso CM, Castellanos FX, Milham MP (2013) Striatum-based circuitry of adolescent depression and anhedonia. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 52(6):628–641 e613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2013.04.003
Gilbert M, MacPhail R, Baldwin J, Moser V, Chernoff N (2010) Moderate developmental undernutrition: impact on growth and cognitive function in youth and old age. Neurotoxicol Teratol 32(3):362–372
Goodman J, Packard MG (2018) The role of the dorsal striatum in extinction: a memory systems perspective. Neurobiol Learn Mem 150:48–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2018.02.028
Green FJ (1990) Sigma-Aldrich handbook of stains, dyes, and indicators. Aldrich Chemical Co
Gururaj G, Girish N, Isaac M (2005) Mental, neurological and substance abuse disorders: strategies towards a systems approach. Burden of Disease in India 226
Hackley B (2010) Antidepressant medication use in pregnancy. J Midwifery Womens Health 55(2):90–100
Holson RR, Webb PJ, Grafton TF, Hansen DK (1994) Prenatal neuroleptic exposure and growth stunting in the rat: an in vivo and in vitro examination of sensitive periods and possible mechanisms. Teratology 50(2):125–136
Hoppenbrouwers CJ, Bosma J, Wennink HJ, Hilgevoord AA, Heres M, Honig A (2010) Neonatal seizures on EEG after in utero exposure to venlafaxine. Br J Clin Pharmacol 70(3):454–456. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2125.2010.03714.x
Ikonomidou C, Kaindl AM (2011) Neuronal death and oxidative stress in the developing brain. Antioxid Redox Signal 14(8):1535–1550. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2010.3581
Ikonomidou C, Turski L (2010) Antiepileptic drugs and brain development. Epilepsy Res 88(1):11–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2009.09.019
Jefferies AL, Canadian Paediatric Society F, Newborn C (2011) Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in pregnancy and infant outcomes. Paediatr Child Health 16(9):562–563. https://doi.org/10.1093/pch/16.9.562
Jimenez-Solem E, Andersen JT, Petersen M, Broedbaek K, Lander AR, Afzal S, Torp-Pedersen C, Poulsen HE (2013) SSRI use during pregnancy and risk of stillbirth and neonatal mortality. Am J Psychiatry 170(3):299–304
Kessler RC, Berglund P, Demler O, Jin R, Koretz D, Merikangas KR, Rush AJ, Walters EE, Wang PS, National Comorbidity Survey R (2003) The epidemiology of major depressive disorder: results from the National Comorbidity Survey Replication (NCS-R). JAMA 289(23):3095–3105. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.289.23.3095
Kessler RC, Merikangas KR, Wang PS (2008) The prevalence and correlates of workplace depression in the national comorbidity survey replication. J Occup Environ Med 50(4):381–390. https://doi.org/10.1097/JOM.0b013e31816ba9b8
Latt SA, Stetten G, Juergens LA, Willard HF, Scher CD (1975) Recent developments in the detection of deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis by 33258 Hoechst fluorescence. J Histochem Cytochem 23(7):493–505. https://doi.org/10.1177/23.7.1095650
Lecoeur H (2002) Nuclear apoptosis detection by flow cytometry: influence of endogenous endonucleases. Exp Cell Res 277(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1006/excr.2002.5537
Lee T, Lee A, Luo L (1999) Development of the Drosophila mushroom bodies: sequential generation of three distinct types of neurons from a neuroblast. Development 126(18):4065–4076
Levitt P (1998) Prenatal effects of drugs of abuse on brain development. Drug Alcohol Depend 51(1–2):109–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0376-8716(98)00070-2
Maciag D, Simpson KL, Coppinger D, Lu Y, Wang Y, Lin RC, Paul IA (2006) Neonatal antidepressant exposure has lasting effects on behavior and serotonin circuitry. Neuropsychopharmacology 31(1):47–57
Magalhães P, Alves G, Llerena A, Falcão A (2014) Venlafaxine pharmacokinetics focused on drug metabolism and potential biomarkers. Drug Metab Drug Interact 29(3):129–141
Manent J-B, Jorquera I, Franco V, Ben-Ari Y, Perucca E, Represa A (2008) Antiepileptic drugs and brain maturation: fetal exposure to lamotrigine generates cortical malformations in rats. Epilepsy Res 78(2–3):131–139
McDonald RJ, White NM (1994) Parallel information processing in the water maze: evidence for independent memory systems involving dorsal striatum and hippocampus. Behav Neural Biol 61(3):260–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0163-1047(05)80009-3
Mishra SK, Singh S, Shukla S, Shukla R (2018) Intracerebroventricular streptozotocin impairs adult neurogenesis and cognitive functions via regulating neuroinflammation and insulin signaling in adult rats. Neurochem Int 113:56–68
Morris R (1984) Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J Neurosci Methods 11(1):47–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-0270(84)90007-4
Moser EI, Kropff E, Moser MB (2008) Place cells, grid cells, and the brain’s spatial representation system. Annu Rev Neurosci 31:69–89. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.neuro.31.061307.090723
Murphy BL, Arnsten AF, Goldman-Rakic PS, Roth RH (1996) Increased dopamine turnover in the prefrontal cortex impairs spatial working memory performance in rats and monkeys. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93(3):1325–1329. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.93.3.1325
Muth EA, Haskins JT, Moyer JA, Husbands GE, Nielsen ST, Sigg EB (1986) Antidepressant biochemical profile of the novel bicyclic compound Wy-45,030, an ethyl cyclohexanol derivative. Biochem Pharmacol 35(24):4493–4497
Muth EA, Moyer JA, Haskins JT, Andree TH, Husbands GM (1991) Biochemical, neurophysiological, and behavioral effects of Wy-45,233 and other identified metabolites of the antidepressant venlafaxine. Drug Dev Res 23(2):191–199
Nair AB, Jacob S (2016) A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. Journal of Basic and Clinical Pharmacy 7(2):27
Nakhai-Pour HR, Broy P, Bérard A (2010) Use of antidepressants during pregnancy and the risk of spontaneous abortion. CMAJ 182(10):1031–1037
Nguyen L, Rigo J-M, Rocher V, Belachew S, Malgrange B, Rogister B, Leprince P, Moonen G (2001) Neurotransmitters as early signals for central nervous system development. Cell Tissue Res 305(2):187–202
Noisin EL, Thomas WE (1988) Ontogeny of dopaminergic function in the rat midbrain tegmentum, corpus striatum and frontal cortex. Dev Brain Res 41(1–2):241–252
Nörby U, Forsberg L, Wide K, Sjörs G, Winbladh B, Källén K (2016) Neonatal morbidity after maternal use of antidepressant drugs during pregnancy. Pediatrics 138(5)
Nulman I, Koren G, Rovet J, Barrera M, Pulver A, Streiner D, Feldman B (2012) Neurodevelopment of children following prenatal exposure to venlafaxine, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, or untreated maternal depression. Am J Psychiatry 169(11):1165–1174
Packard MG, Knowlton BJ (2002) Learning and memory functions of the basal ganglia. Annu Rev Neurosci 25(1):563–593. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.neuro.25.112701.142937
Packard MG, McGaugh JL (1996) Inactivation of hippocampus or caudate nucleus with lidocaine differentially affects expression of place and response learning. Neurobiol Learn Mem 65(1):65–72. https://doi.org/10.1006/nlme.1996.0007
Pakalapati RK, Bolisetty S, Austin MP, Oei J (2006) Neonatal seizures from in utero venlafaxine exposure. J Paediatr Child Health 42(11):737–738. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1754.2006.00962.x
Petit-Demouliere B, Chenu F, Bourin M (2005) Forced swimming test in mice: a review of antidepressant activity. Psychopharmacology 177(3):245–255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-2048-7
Porsolt RD, Bertin A, Jalfre M (1977) Behavioral despair in mice: a primary screening test for antidepressants. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 229(2):327–336
Preskorn SH (1999) Two in one: the venlafaxine story. J Pract Psychiatry Behav Health 5(6):346–350
Rice D, Barone S, Jr (2000) Critical periods of vulnerability for the developing nervous system: evidence from humans and animal models. Environ Health Perspect 108 Suppl 3(suppl 3):511–533 https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.00108s3511
Salk RH, Hyde JS, Abramson LY (2017) Gender differences in depression in representative national samples: meta-analyses of diagnoses and symptoms. Psychol Bull 143(8):783
Sasváriová M, Tyukos-Kaprinay B, Salvaras L, Belovičová K, Bögi E, Knezl V, Barteková M, Stankovičová T, Dubovický M (2018) Effect of pre-gestational stress and prenatal venlafaxine administration on cardiovascular system of rat offspring. Acta Facultatis Pharmaceuticae 65(2):17–22
Sawaguchi T, Goldman-Rakic PS (1991) D1 dopamine receptors in prefrontal cortex: involvement in working memory. Science 251(4996):947–950
Schotte A, Janssen PF, Gommeren W, Luyten WH, Van Gompel P, Lesage AS, De Loore K, Leysen JE (1996) Risperidone compared with new and reference antipsychotic drugs: in vitro and in vivo receptor binding. Psychopharmacology 124(1–2):57–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245606
Shalaby NM, Sarhan NI (2008) Light and electron microscopic study on the effect of valproic acid on cerebellar cortex of adult male albino rats and the possible protective effect of L-carnitine. Egypt J Histol 31:256–265
Sharma M, Tiwari V, Shukla S, Panda JJ (2020) Fluorescent dopamine–tryptophan nanocomposites as dual-imaging and antiaggregation agents: new generation of amyloid theranostics with trimeric effects. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12(39):44180–44194
Singh D, Saadabadi A (2021) Venlafaxine. StatPearls, StatPearls Publishing Copyright © 2021, StatPearls Publishing LLC., Treasure Island (FL)
Singh KP, Singh M (2001) Effect of single prenatal haloperidol exposure on hippocampus and striatum of developing rat brain. Indian J Exp Biol 39(3):223–229
Singh KP, Singh M (2002) Effect of prenatal haloperidol exposure on behavioral alterations in rats. Neurotoxicol Teratol 24(4):497–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0892-0362(02)00189-7
Singh KP, Singh MK (2017) In utero exposure to atypical antipsychotic drug, risperidone: effects on fetal neurotoxicity in hippocampal region and cognitive impairment in rat offspring. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 75:35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2016.12.006
Singh KP, Singh MK, Singh M (2016) Effects of prenatal exposure to antipsychotic risperidone on developmental neurotoxicity, apoptotic neurodegeneration and neurobehavioral sequelae in rat offspring. Int J Dev Neurosci 52:13–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2016.05.006
Singh KP, Tripathi N (2015) Prenatal exposure to a novel antipsychotic quetiapine: impact on neuro-architecture, apoptotic neurodegeneration in fetal hippocampus and cognitive impairment in young rats. Int J Dev Neurosci 42:59–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2015.02.011
Singh M, Singh K (2013) In utero exposure of venlafaxine: impact on maternal, fetal, neonatal weight and postnatal growth in rat offspring. National Academy Science Letters 36(1):35–40
Singh M, Singh K, Shukla S, Dikshit M (2015) Assessment of in-utero venlafaxine induced, ROS-mediated, apoptotic neurodegeneration in fetal neocortex and neurobehavioral sequelae in rat offspring. Int J Dev Neurosci 40:60–69
Swerts CA, Costa AM, Esteves A, Borato CE, Swerts MS (2010) Effects of fluoxetine and imipramine in rat fetuses treated during a critical gestational period: a macro and microscopic study. Braz J Psychiatry 32(2):152–158. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1516-44462009005000015
Thurston JH, Hauhart RE, Schulz DW, Naccarato EF, Dodson WE, Carroll JE (1981) Chronic valproate administration produces hepatic dysfunction and may delay brain maturation in infant mice. Neurology 31(9):1063–1063
Tota S, Kamat PK, Awasthi H, Singh N, Raghubir R, Nath C, Hanif K (2009) Candesartan improves memory decline in mice: involvement of AT1 receptors in memory deficit induced by intracerebral streptozotocin. Behav Brain Res 199(2):235–240
Verhoven B, Schlegel RA, Williamson P (1995) Mechanisms of phosphatidylserine exposure, a phagocyte recognition signal, on apoptotic T lymphocytes. J Exp Med 182(5):1597–1601. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.182.5.1597
Ververs T, Kaasenbrood H, Visser G, Schobben F, de Jong-van den Berg L, Egberts T (2006) Prevalence and patterns of antidepressant drug use during pregnancy. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 62(10):863–870
Vorhees CV, Williams MT (2006) Morris water maze: procedures for assessing spatial and related forms of learning and memory. Nat Protoc 1(2):848–858
Vorhees CV, Williams MT (2014) Assessing spatial learning and memory in rodents. ILAR J 55(2):310–332
WHO (2017) Depression and other common mental disorders. In: Global Health Estimates.
Williams R, Ali S, Scalzo F, Soliman K, Holson R (1992) Prenatal haloperidol exposure: effects on brain weights and caudate neurotransmitter levels in rats. Brain Res Bull 29(3–4):449–458
Wisner KL, Zarin DA, Holmboe ES, Appelbaum PS, Gelenberg AJ, Leonard HL, Frank E (2000) Risk-benefit decision making for treatment of depression during pregnancy. Am J Psychiatry 157(12):1933–1940. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.157.12.1933
Zhu Y, Gao H, Tong L, Li Z, Wang L, Zhang C, Yang Q, Yan B (2019) Emotion regulation of hippocampus using real-time fMRI neurofeedback in healthy human. Front Hum Neurosci 13:242
Acknowledgements
Manish Singh thankfully acknowledges INST Mohali, for providing necessary infrastructure and lab facilities. HOD, Department of Zoology, UP, Allahabad, India, is thankfully acknowledged for providing laboratory facilities.
Funding
Prashant Sharma is thankful to University Grants Commission (UGC) for fellowship 1013/[CSIR-UGC NET, JUNE 2019].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Prashant Sharma contributed to data analysis and manuscript writing. Manish Singh carried out all experiments and interpretation and contributed to manuscript writing. KP Singh conceived, planned, and supervised the entire study.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
All the animal studies have been performed in accordance with the CPCSEA-approved guidelines.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, K.P., Sharma, P. & Singh, M. Prenatal Venlafaxine Exposure–Induced Neurocytoarchitectural and Neuroapoptotic Degeneration in Striatum and Hippocampus of Developing Fetal Brain, Manifesting Long-term Neurocognitive Impairments in Rat Offspring. Neurotox Res 40, 1174–1190 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-022-00541-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-022-00541-3