Abstract
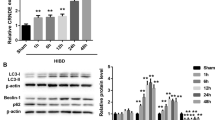
Delayed encephalopathy after acute carbon monoxide poisoning (DEACMP) is the most serious sequel of acute CO poisoning, with structure or function injury of the brain. LncRNA colorectal neoplasia differentially expressed (CRNDE) aberrant expression was involved in nerve cell injury; however, the mechanism of CRNDE in DEACMP remains elusive. CO poisoning model of Sprague–Dawley rats was established. Neurological function was measured by Morris water maze (MWM) testing. Histopathological condition of brain and hippocampus tissues was observed by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E), Nissl, and TUNEL staining. Pro-inflammatory cytokine levels were evaluated by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Oxidative damage and apoptosis markers were determined by related detection assays. Cell apoptosis were evaluated by flow cytometry analysis. Luciferase report and RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assays were employed to identify the binding relationship of CRNDE and miR-212-5p. CRNDE was significantly increased in CO poisoning animal model and oxygen–glucose deprivation (OGD) group, while that of miR-212-5p was decreased. CRNDE knockdown repressed the histopathological damage and apoptosis of brain and hippocampus tissues. Besides, CRNDE suppressed the AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin signaling pathway via targeting miR-212-5p. Furthermore, the protective effects of CRNDE silencing on brain tissue injury and apoptosis and AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin signaling pathway were reversed by inhibition of miR-212-5p in CO poisoning model. Collectively, CRNDE, serving as a sponge of miR-212-5p, aggravated the injury and apoptosis of brain and hippocampus tissues through regulating AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin signaling pathway under the CO-poisoning and OGD-treated model, suggesting a selected therapeutic target of DEACMP.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Barnhart CD, Yang D, Lein PJ (2015) Using the morris water maze to assess spatial learning and memory in weanling mice. PLoS ONE 10(4):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0124521
Brunet A, Datta SR, Greenberg ME (2001) Transcription-dependent and -independent control of neuronal survival by the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Curr Opin Neurobiol 11(3):297–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0959-4388(00)00211-7
Canene-Adams K (2013) Preparation of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue for immunohistochemistry. Methods Enzymol 533:225–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-420067-8.00015-5
Chang HL, Wang HC, Chunag YT, Chou CW, Lin IL, Lai CS, Chang LL, Cheng KI (2017) MiRNA expression change in dorsal root ganglia after peripheral nerve injury. J Mol Neurosci 61(2):169–177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-016-0876-7
Di C, Zeng Y, Mao J, Shen Z, Gu W (2018) Dynamic changes and clinical significance of serum S100B protein and glial fibrillary acidic protein in patients with delayed encephalopathy after acute carbon monoxide poisoning. Pak J Med Sci 34(4):945–949. https://doi.org/10.12669/pjms.344.15363
Dindar Badem N, Comertpay E, Coskun F (2019) How much apoptosis does carbon monoxide poisoning cause? Primary clinical soluble TWEAK protein level study. Hum Exp Toxicol 38(8):974–982. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327119845038
Fu CH, Zhang BH, Fang CZ, Yan CX, Lai FF, Chen S, Wang GH (2020) Long non-coding RNA CRNDE deteriorates intrauterine infection-induced neonatal brain injury. Mol Cell Probes 52:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcp.2020.101565
Han P, Li JW, Zhang BM, Lv JC, Li YM, Gu XY, Yu ZW, Jia YH, Bai XF, Li L, Liu YL, Cui BB (2017) The lncRNA CRNDE promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation and chemoresistance via miR-181a-5p-mediated regulation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Mol Cancer 16(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-017-0583-1
Hsiao CL, Kuo HC, Huang CC (2004) Delayed encephalopathy after carbon monoxide intoxication–long-term prognosis and correlation of clinical manifestations and neuroimages. Acta Neurol Taiwan 13(2):64–70
Huang YQ, Peng ZR, Huang FL, Yang AL (2020) Mechanism of delayed encephalopathy after acute carbon monoxide poisoning. Neural Regen Res 15(12):2286–2295. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.284995
Kavakli HS, Erel O, Delice O, Gormez G, Isikoglu S, Tanriverdi F (2011) Oxidative stress increases in carbon monoxide poisoning patients. Hum Exp Toxicol 30(2):160–164. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327110388539
Li D, Yang T, Shao C, Cao Z, Zhang H (2021) LncRNA MIAT activates vascular endothelial growth factor A through RAD21 to promote nerve injury repair in acute spinal cord injury. Mol Cell Endocrinol 528:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2021.111244
Li Z, Wu G, Li J, Wang Y, Ju X, Jiang W (2020) lncRNA CRNDE promotes the proliferation and metastasis by acting as sponge miR-539-5p to regulate POU2F1 expression in HCC. BMC Cancer 20(1):282. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-020-06771-y
Liu J, Si Z, Liu J, Lin Y, Yuan J, Xu S, He Y, Zhang T, Wang A (2020a) Clinical and imaging prognosis in patients with delayed encephalopathy after acute carbon monoxide poisoning. Behav Neurol 2020:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/1719360
Liu R, Li F, Zhao W (2020b) Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 knockdown inhibits MPP(+)-induced apoptosis, inflammation and cytotoxicity in SK-N-SH cells by regulating miR-212-5p/RAB3IP axis. Neurosci Lett 731:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2020.135060
Mori K, Beppu T, Fujisawa Y, Onodera M, Ogasawara K, Sasaki M, Ehara S, Sakai A, Endo S (2015) Effect of free radical scavenger, edaravone, for patients with carbon monoxide poisoning. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 139:56–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2015.09.003
Park EJ, Min YG, Kim GW, Cho JP, Maeng WJ, Choi SC (2014) Pathophysiology of brain injuries in acute carbon monoxide poisoning: a novel hypothesis. Med Hypotheses 83(2):186–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2014.04.032
Peng WX, Koirala P, Mo YY (2017) LncRNA-mediated regulation of cell signaling in cancer. Oncogene 36(41):5661–5667. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.184
Shen M, Zheng Y, Zhu K, Cai Z, Liu W, Sun X, Liu J, Zhu D (2020) Hydrogen gas protects against delayed encephalopathy after acute carbon monoxide poisoning in a rat model. Neurol Res 42(1):22–30. https://doi.org/10.1080/01616412.2019.1685064
Sommer C, Leinders M, Uceyler N (2018) Inflammation in the pathophysiology of neuropathic pain. Pain 159(3):595–602. https://doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001122
Song T, Zheng Y, Wang Y, Katz Z, Liu X, Chen S, Singer RH, Gu W (2015) Specific interaction of KIF11 with ZBP1 regulates the transport of beta-actin mRNA and cell motility. J Cell Sci 128(5):1001–1010. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.161679
Weaver LK, Oliver LC, Deru K, Stemmer-Rachamimov AO (2019) Myositis associated with carbon monoxide poisoning. Undersea Hyperb Med 46(1):63–67
Xiao X, Jiang Y, Liang W, Wang Y, Cao S, Yan H, Gao L, Zhang L (2019a) MiR-212-5p attenuates ferroptotic neuronal death after traumatic brain injury by targeting Ptgs2. Mol Brain 12(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13041-019-0501-0
Xiao Z, Qiu Y, Lin Y, Medina R, Zhuang S, Rosenblum JS, Cui J, Li Z, Zhang X, Guo L (2019b) Blocking lncRNA H19-miR-19a-Id2 axis attenuates hypoxia/ischemia induced neuronal injury. Aging (Albany NY) 11(11):3585–3600. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.101999
Xu XM, Luo H, Rong BB, Zheng XM, Wang FT, Zhang SJ, Li ZX (2019) Management of delayed encephalopathy after CO poisoning: an evidence-based narrative review. Medicine (Baltimore) 98(49):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000018199
Yao Y, Wang X, Gao J (2020) LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 Sponges miR-206 to ameliorate neural injury induced by anesthesia via up-regulating BDNF. Drug Des Devel Ther 14:4789–4800. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S256319
Yi M, Dai X, Li Q, Xu X, Chen Y, Wang D (2019) Downregulated lncRNA CRNDE contributes to the enhancement of nerve repair after traumatic brain injury in rats. Cell Cycle 18(18):2332–2343. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2019.1647024
Yu B, Zhou S, Yi S, Gu X (2015) The regulatory roles of non-coding RNAs in nerve injury and regeneration. Prog Neurobiol 134:122–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2015.09.006
Yu T, Zhao C, Hou S, Zhou W, Wang B, Chen Y (2019) Exosomes secreted from miRNA-29b-modified mesenchymal stem cells repaired spinal cord injury in rats. Braz J Med Biol Res 52(12):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1590/1414-431X20198735
Yuan J, Yankner BA (2000) Apoptosis in the nervous system. Nature 407(6805):802–809. https://doi.org/10.1038/35037739
Zhang H, Li D, Zhang Y, Li J, Ma S, Zhang J, Xiong Y, Wang W, Li N, Xia L (2018a) Knockdown of lncRNA BDNF-AS suppresses neuronal cell apoptosis via downregulating miR-130b-5p target gene PRDM5 in acute spinal cord injury. RNA Biol 15(8):1071–1080. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2018.1493333
Zhang J, Yin M, Peng G, Zhao Y (2018b) CRNDE: an important oncogenic long non-coding RNA in human cancers. Cell Prolif 51(3):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.12440
Zhang Y, Zhang Y (2020) lncRNA ZFAS1 improves neuronal injury and inhibits inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis by sponging miR-582 and upregulating NOS3 expression in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Inflammation 43(4):1337–1350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-020-01212-1
Zhao N, Liang P, Zhuo X, Su C, Zong X, Guo B, Han D, Yan X, Hu S, Zhang Q, Tie X (2018) After treatment with methylene blue is effective against delayed encephalopathy after acute carbon monoxide poisoning. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 122(5):470–480. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcpt.12940
Zhao S, Fu J, Liu X, Wang T, Zhang J, Zhao Y (2012) Activation of Akt/GSK-3beta/beta-catenin signaling pathway is involved in survival of neurons after traumatic brain injury in rats. Neurol Res 34(4):400–407. https://doi.org/10.1179/1743132812Y.0000000025
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81974286) and Natural Science Foundation of Jilin Province (20200201339JC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
All animal experimental procedures were approved and carried in keeping with the ethical standards of the Ethics Committee of the First Hospital of Jilin University.
Consent for Publication
Not Applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, ZL., Bian, M. & Pang, L. LncRNA CRNDE Deteriorates Delayed Encephalopathy After Acute Carbon Monoxide Poisoning to Inactivate AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin Pathway via miR-212-5p. Neurotox Res 40, 1208–1222 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-022-00518-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-022-00518-2