Abstract
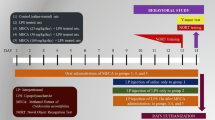
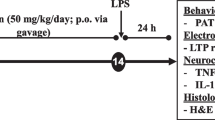
Inflammation can cause memory impairment. In the present study, the effect of carvacrol on brain tissue inflammation and oxidative stress as well as learning and memory in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-challenged rats was evaluated. The animals were grouped and treated: (1) control which received vehicle instead of LPS and carvacrol, (2) LPS (1 mg/kg; i.p. 120 min before behavioral tests), and (3–5) in these groups, 25, 50, or 100 mg/kg of carvacrol (i.p.) was administered 30 min prior to LPS. In a Morris water maze test, compared to LPS group, administration of all three doses of carvacrol shortened the elapsed time and the traveled distance to find the platform, while it prolonged the traveled time in the target area. In a passive avoidance test, administration of all 25, 50, and 100 mg/kg carvacrol significantly increased the latency at the 3 h, 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h after the shock compared to the LPS group. Interleukin (IL)-6, malondialdehyde (MDA), and NO (nitric oxide) metabolites were increased in the brain by LPS injection, while thiol, superoxide dismutase (SOD), and catalase (CAT) were decreased. Pretreatment with carvacrol reduced IL-6, NO metabolites, and MDA, while it improved thiol content, CAT, and SOD. The results indicated that carvacrol protected from learning and memory impairment and the brain tissue inflammation and oxidative stress in LPS-challenged rats.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abareshi A, Anaeigoudari A, Norouzi F et al (2016a) Lipopolysaccharide-induced spatial memory and synaptic plasticity impairment is preventable by captopril. Adv Med 2016:7676512
Abareshi A, Hosseini M, Beheshti F et al (2016b) The effects of captopril on lipopolysaccharide induced learning and memory impairments and the brain cytokine levels and oxidative damage in rats. Life Sci 167:46–56
Aebi H (1984) [13] catalase in vitro Methods in Enzymology, vol 105. Academic Press, Cambridge, pp 121–126
Aeschbach R, Löliger J, Scott B, Murcia A, Butler J, Halliwell B, Aruoma OI (1994) Antioxidant actions of thymol, carvacrol, 6-gingerol, zingerone and hydroxytyrosol. Food Chem Toxicol 32:31–36
Bargi R, Asgharzadeh F, Beheshti F, Hosseini M, Sadeghnia HR, Khazaei M (2017) The effects of thymoquinone on hippocampal cytokine level, brain oxidative stress status and memory deficits induced by lipopolysaccharide in rats. Cytokine 96:173–184
Barrientos RM, Higgins EA, Biedenkapp JC et al (2006) Peripheral infection and aging interact to impair hippocampal memory consolidation. Neurobiol Aging 27:723–732
Benveniste EN (1992) Inflammatory cytokines within the central nervous system: sources, function, and mechanism of action. Am J Phys Cell Phys 263:C1–C16
Chenet AL, Duarte AR, de Almeida FJS, Andrade CMB, de Oliveira MR (2019) Carvacrol depends on Heme Oxygenase-1 (HO-1) to exert antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and mitochondria-related protection in the human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells line exposed to hydrogen peroxide. Neurochem Res 44:884–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02724-5
da Silva Lima M, Quintans-Júnior LJ, de Santana WA et al (2013) Anti-inflammatory effects of carvacrol: evidence for a key role of interleukin-10. Eur J Pharmacol 699:112–117
Dati LM, Ulrich H, Real CC, Feng ZP, Sun HS, Britto LR (2017) Carvacrol promotes neuroprotection in the mouse hemiparkinsonian model. Neuroscience 356:176–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.05.013
Deng W, Lu H, Teng J (2013) Carvacrol attenuates diabetes-associated cognitive deficits in rats. J Mol Neurosci 51:813–819
Ferrero-Miliani L, Nielsen O, Andersen P, Girardin SE (2007) Chronic inflammation: importance of NOD2 and NALP3 in interleukin-1β generation. Clin Exp Immunol 147:227–235
Gilroy DW, Newson J, Sawmynaden P et al (2004) A novel role for phospholipase A2 isoforms in the checkpoint control of acute inflammation. FASEB J 18:489–498
González H, Elgueta D, Montoya A, Pacheco R (2014) Neuroimmune regulation of microglial activity involved in neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. J Neuroimmunol 274:1–13
Haddadi H, Rajaei Z, Alaei H, Shahidani S (2018) Chronic treatment with carvacrol improves passive avoidance memory in a rat model of Parkinson's disease. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 76:71–77
Hamzehloei L, Rezvani ME, Rajaei Z (2019) Effects of carvacrol and physical exercise on motor and memory impairments associated with Parkinson's disease. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 77:493–500
Karkabounas S, Kostoula O, Daskalou T, Veltsistas P, Karamouzis M, Zelovitis I, Metsios A, Lekkas P, Evangelou AM, Kotsis N, Skoufos I (2006) Anticarcinogenic and antiplatelet effects of carvacrol. Exp Oncol 28:121–125
Khalil A, Kovac S, Morris G, Walker MC (2017) Carvacrol after status epilepticus (SE) prevents recurrent SE, early seizures, cell death, and cognitive decline. Epilepsia 58:263–273
Khazdair MR, Boskabady MH (2019) The effect of carvacrol on inflammatory mediators and respiratory symptoms in veterans exposed to sulfur mustard, a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Respir Med 150:21–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2019.01.020
Khazdair MR, Anaeigoudari A, Hashemzehi M, Mohebbati R (2019) Neuroprotective potency of some spice herbs, a literature review. J Tradit Complement Med 9:98–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcme.2018.01.002
Kianmehr M, Rezaei A, Boskabady MH (2016) Effect of carvacrol on various cytokines genes expression in splenocytes of asthmatic mice. Iran J Basic Med Sci 19:402–410
Landa P, Kokoska L, Pribylova M, Vanek T, Marsik P (2009) In vitro anti-inflammatory activity of carvacrol: inhibitory effect on COX-2 catalyzed prostaglandin E 2 biosynthesisb. Arch Pharm Res 32:75–78
Lee JW, Lee YK, Yuk DY et al (2008) Neuro-inflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide causes cognitive impairment through enhancement of beta-amyloid generation. J Neuroinflammation 5:37
Madesh M, Balasubramanian K (1998) Microtiter plate assay for superoxide dismutase using MTT reduction by superoxide. Indian J Biochem Biophys 35:184–188
McGeer P, Itagaki S, Boyes B et al (1988) Reactive microglia are positive for HLA-DR in the substantia nigra of Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease brains. Neurology 38:1285–1285
Mehri S, Abnous K, Khooei A et al (2015) Crocin reduced acrylamide-induced neurotoxicity in Wistar rat through inhibition of oxidative stress. Iran J Basic Med Sci 18:902
Nakagawa Y, Chiba K (2014) Role of microglial m1/m2 polarization in relapse and remission of psychiatric disorders and diseases. Pharmaceuticals 7:1028–1048
Paik YH, Schwabe RF, Bataller R, Russo MP, Jobin C, Brenner DA (2003) Toll-like receptor 4 mediates inflammatory signaling by bacterial lipopolysaccharide in human hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology 37:1043–1055
Papandreou MA, Tsachaki M, Efthimiopoulos S, Cordopatis P, Lamari FN, Margarity M (2011) Memory enhancing effects of saffron in aged mice are correlated with antioxidant protection. Behav Brain Res 219:197–204
Pohl F, Kong Thoo Lin P (2018) The potential use of plant natural products and plant extracts with antioxidant properties for the prevention/treatment of neurodegenerative diseases: in vitro, In Vivo and Clinical Trials. Molecules 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123283
Pourganji M, Hosseini M, Soukhtanloo M et al (2014) Protective role of endogenous ovarian hormones against learning and memory impairments and brain tissues oxidative damage induced by lipopolysaccharide. Iran Red Crescent Med J 16:e13954
Richardson JS (1993) Free radicals in the genesis of Alzheimer's disease a. Ann N Y Acad Sci 695:73–76
Sadegh M, Sakhaie MH (2018) Carvacrol mitigates proconvulsive effects of lipopolysaccharide, possibly through the hippocampal cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition. Metab Brain Dis 33:2045–2050. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-018-0314-3
Saito T, Saido TC (2018) Neuroinflammation in mouse models of Alzheimer's disease. Clin Exp Neuroimmunol 9:211–218. https://doi.org/10.1111/cen3.12475
Salmani H, Hosseini M, Beheshti F, Baghcheghi Y, Sadeghnia HR, Soukhtanloo M, Shafei MN, Khazaei M (2018) Angiotensin receptor blocker, losartan ameliorates neuroinflammation and behavioral consequences of lipopolysaccharide injection. Life Sci 203:161–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2018.04.033
Samarghandian S, Farkhondeh T, Samini F et al (2016) Protective effects of carvacrol against oxidative stress induced by chronic stress in rat’s brain, liver, and kidney. Biochem Res Int 2016:2645237
Sharifi-Rad M, Varoni EM, Iriti M, Martorell M, Setzer WN, del Mar Contreras M, Salehi B, Soltani-Nejad A, Rajabi S, Tajbakhsh M, Sharifi-Rad J (2018) Carvacrol and human health: a comprehensive review. Phytother Res 32:1675–1687
Vegeto E, Bonincontro C, Pollio G, Sala A, Viappiani S, Nardi F, Brusadelli A, Viviani B, Ciana P, Maggi A (2001) Estrogen prevents the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in microglia. J Neurosci 21:1809–1818
Wang P, Luo Q, Qiao H, Ding H, Cao Y, Yu J, Liu R, Zhang Q, Zhu H, Qu L (2017) The Neuroprotective effects of Carvacrol on ethanol-induced hippocampal neurons impairment via the Antioxidative and Antiapoptotic pathways. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2017:4079425. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4079425
Acknowledgments
The results described in this article were part of a MSc. thesis (Zahra Hakimi).
Funding
The Vice Chancellor for Research and Technology of Mashhad University of Medical Sciences financially supported this work (970981).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hakimi, Z., Salmani, H., Marefati, N. et al. Protective Effects of Carvacrol on Brain Tissue Inflammation and Oxidative Stress as well as Learning and Memory in Lipopolysaccharide-Challenged Rats. Neurotox Res 37, 965–976 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-019-00144-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-019-00144-5