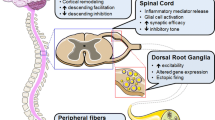
Abstract
Electroacupuncture (EA) is an effective treatment to relieve pain in patients with postherpetic neuralgia. However, the mechanisms of EA involved therein are still unknown. We first injected resiniferatoxin (RTX) into Sprague Dawley rats to construct the neuralgia model. One week after injection, the rats were treated with EA at the “Huantiao” (GB30) and “Yanglingquan” (GB34) acupoints for 5 weeks. Nociceptive behavioral tests were performed to analyze the changes in thermal sensitivity and mechanical allodynia after RTX induction and EA treatment. Deep sequencing was performed to identify differentially expressed miRNAs in the spinal cord of RTX-induced rats in response to EA treatment. The nociceptive behavioral tests showed that EA at the left GB30 and GB34 acupoints significantly reduced RTX-induced tactile sensitivity and increased RTX-inhibited thermal sensitivity. The sequencing data indicated that RTX resulted in one upregulated and five downregulated miRNAs, and EA treatment resulted in two upregulated miRNAs. Furthermore, seven upregulated and two downregulated miRNAs were found between rats subjected to EA and sham operation. Functional analysis suggested that the targets of differentially expressed miRNAs were enriched in many nervous system–related pathways. The pathway-gene-miRNA net analysis showed that miR-7a-5p had the most target genes. Moreover, miR-233-3p was downregulated after RTX injection and upregulated by EA treatment. We speculated that the upregulation of miR-7a-5p and miR-233-3p is involved in the analgesic effects of EA. Our analysis on the EA-induced differential expression of miRNAs provides novel insights into the mechanisms of EA analgesia in postherpetic neuralgia.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baron R, Saguer M (1993) Postherpetic neuralgia. Are C-nociceptors involved in signalling and maintenance of tactile allodynia? Brain 116(Pt 6):1477–1496
Berman BM, Lao L, Langenberg P, Lee WL, Gilpin AM, Hochberg MC (2004) Effectiveness of acupuncture as adjunctive therapy in osteoarthritis of the knee: a randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med 141:901–910
Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM, Yaksh TL (1994) Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods 53:55–63
Chen SR, Pan HL (2005) Effect of systemic and intrathecal gabapentin on allodynia in a new rat model of postherpetic neuralgia. Brain Res 1042:108–113
Chen L, Zhang J, Li F, Qiu Y, Wang L, Li YH, Shi J, Pan HL, Li M (2009) Endogenous anandamide and cannabinoid receptor-2 contribute to electroacupuncture analgesia in rats. J Pain 10:732–739
de Chevigny A, Core N, Follert P, Gaudin M, Barbry P, Beclin C, Cremer H (2012) miR-7a regulation of Pax6 controls spatial origin of forebrain dopaminergic neurons. Nat Neurosci 15:1120–1126
Grachev Iu V, Kukushkin ML, Sudarikov AP, Zhuravlev VF, Gerasimenko M (1998) Clinical course and treatment of herpetic trigeminal ganglionic neuropathy. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im SS Korsakova 98:4–8
Hargreaves K, Dubner R, Brown F, Flores C, Joris J (1988) A new and sensitive method for measuring thermal nociception in cutaneous hyperalgesia. Pain 32:77–88
Khan GM, Chen SR, Pan HL (2002) Role of primary afferent nerves in allodynia caused by diabetic neuropathy in rats. Neuroscience 114:291–299
Klompas M, Kulldorff M, Vilk Y, Bialek SR, Harpaz R (2011) Herpes zoster and postherpetic neuralgia surveillance using structured electronic data. Mayo Clin Proc 86:1146–1153
Laszlo K, Dorothy CB, Andrew JM, Stephen TC, Jacob B, Michael G, Ofer MW, John KN, Zoltan O, Michael JI (2004) Deletion of vanilloid receptor 1_expressing primary afferent neurons for pain control. J Clin Invest 113(9):1344–1352
Levin MJ, Smith JG, Kaufhold RM, Barber D, Hayward AR, Chan CY, Chan IS, Li DJ, Wang W, Keller PM, Shaw A, Silber JL, Schlienger K, Chalikonda I, Vessey SJ, Caulfield MJ (2003) Decline in varicella-zoster virus (VZV)-specific cell-mediated immunity with increasing age and boosting with a high-dose VZV vaccine. J Infect Dis 188:1336–1344
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Lopez-Gonzalez MJ, Landry M, Favereaux A (2017) MicroRNA and chronic pain: from mechanisms to therapeutic potential. Pharmacol Ther 180:1–15
Ma C, Li CX, Yi JL, Yan LP (2008) Effects of electroacupuncture on glutamate and aspartic acid contents in the dorsal root ganglion and spinal cord in rats with neuropathic pain. Zhen ci yan jiu 33:250–254
Pan HL, Khan GM, Alloway KD, Chen SR (2003) Resiniferatoxin induces paradoxical changes in thermal and mechanical sensitivities in rats: mechanism of action. J Neurosci 23:2911–2919
Park JH, Han JB, Kim SK, Park JH, Go DH, Sun B, Min BI (2010) Spinal GABA receptors mediate the suppressive effect of electroacupuncture on cold allodynia in rats. Brain Res 1322:24–29
Sakai A, Saitow F, Miyake N, Miyake K, Shimada T, Suzuki H (2013) miR-7a alleviates the maintenance of neuropathic pain through regulation of neuronal excitability. Brain 136:2738–2750
Shukla GC, Singh J, Barik S (2011) MicroRNAs: processing, maturation, target recognition and regulatory functions. Mol Cell Pharmacol 3:83–92
Tanaka N, Yamaga M, Tateyama S, Uno T, Tsuneyoshi I, Takasaki M (2010) The effect of pulsed radiofrequency current on mechanical allodynia induced with resiniferatoxin in rats. Anesth Analg 111:784–790
Vickers AJ, Cronin AM, Maschino AC, Lewith G, MacPherson H, Foster NE, Sherman KJ, Witt CM, Linde K, Acupuncture Trialists C (2012) Acupuncture for chronic pain: individual patient data meta-analysis. Arch Intern Med 172:1444–1453
Virgin HW, Wherry EJ, Ahmed R (2009) Redefining chronic viral infection. Cell 138:30–50
Wang CY, Fang JQ (2012) Analysis on therapeutic effect of variable-frequency electroacupuncture combined with herbal-moxa moxibustion for post-zoster neuralgia. Zhen ci yan jiu 37:64–66
Wang L, Zhang Y, Dai J, Yang J, Gang S (2006) Electroacupuncture (EA) modulates the expression of NMDA receptors in primary sensory neurons in relation to hyperalgesia in rats. Brain Res 1120:46–53
Wu CH, Lv ZT, Zhao Y, Gao Y, Li JQ, Gao F, Meng XF, Tian B, Shi J, Pan HL, Li M (2013) Electroacupuncture improves thermal and mechanical sensitivities in a rat model of postherpetic neuralgia. Mol Pain 9:18
Xie XJ, Ma LG, Xi K, Fan DM, Li JG, Zhang Q, Zhang W (2017) Effects of microRNA-223 on morphine analgesic tolerance by targeting NLRP3 in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Mol Pain 13:1744806917706582
Yan LP, Wu XT, Yin ZY, Ma C (2011) Effect of electroacupuncture on the levels of amino acid neurotransmitters in the spinal cord in rats with chronic constrictive injury. Zhen ci yan jiu 353–356(379):36
Yawn BP, Saddier P, Wollan PC, St Sauver JL, Kurland MJ, Sy LS (2007) A population-based study of the incidence and complication rates of herpes zoster before zoster vaccine introduction. Mayo Clin Proc 82:1341–1349
Yu-Lin H, Chiang H, Lue J-H, Hsieh S-T (2012) P2X3-mediated peripheral sensitization of neuropathic pain in resiniferatoxin-induced neuropathy. Exp Neurol 235(1):316–325
Zhang R, Lao L, Ren K, Berman BM (2014) Mechanisms of acupuncture-electroacupuncture on persistent pain. Anesthesiology 120:482–503
Zhao ZQ (2008) Neural mechanism underlying acupuncture analgesia. Prog Neurobiol 85:355–375
Zimmermann M (1983) Ethical guidelines for investigations of experimental pain in conscious animals. Pain 16:109–110
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jing Zou and Guofu Huang designed the experiments. Xueyang Dong and Yanling Li drafted and revised the manuscript. Siqi Tong and Jingwen Wang assisted with data analysis and interpretation. Mingxuan Liao was a major contributor to the writing of the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All experimental procedures were approved by the Animal Care Committee at Huazhong University of Science and Technology and conformed to the ethical guidelines of the International Association for the Study of Pain.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Significance
The present study identified changes in miRNA expression induced by electroacupuncture in the spinal cord in a rat model of postherpetic neuralgia. The results elucidate the potential role of miRNAs in electroacupuncture-mediated analgesia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, J., Dong, X., Li, Y. et al. Deep Sequencing Identification of Differentially Expressed miRNAs in the Spinal Cord of Resiniferatoxin-Treated Rats in Response to Electroacupuncture. Neurotox Res 36, 387–395 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-019-00052-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-019-00052-8