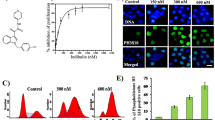
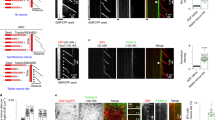
Abstract
In this study, we investigated the role of adducts formation between aminochrome and tubulin and its interference in microtubules assembly and stability in aminochrome-induced toxicity in SH-SY5Y cells. We also investigated whether changes in the microtubules structures are an early event that could affect tubulin expression. We demonstrated in vitro that aminochrome tubulin adducts inhibit tubulin polymerization and that aminochrome induces microtubules disassembly. Moreover, when the SH-SY5Y cells were incubated with aminochrome, we observed an increase in soluble tubulin, indicating depolymerization of microtubules. Aminochrome generates disruption of the microtubules network, leading to changes in the morphology of the cells inducing cell death, in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Interestingly, these changes preceded cell death and were partly inhibited by paclitaxel, a microtubule-stabilizing agent. Furthermore, we observed that aminochrome increased early tubulin expression before significant cell death occurred. Consequently, all these antecedents suggest that aminochrome toxicity is mediated by early disruption of microtubules network, where the adduct formation between aminochrome and tubulin could be responsible for the inhibition in the assembly microtubules and the loss of microtubules stability. Possibly, the early changes in tubulin expression could correspond to compensatory mechanisms against the toxic effects of aminochrome.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguirre P, Urrutia P, Tapia V, Villa M, Paris I, Segura-Aguilar J, Núñez MT (2012) The dopamine metabolite aminochrome inhibits mitochondrial complex I and modifies the expression of iron transporters DMT1 and FPN1. Biometals 25:795–803
Alberts B, Bray D, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K, Hopkin K, Johnson A, Walter P (2014) Essential cell biology. Garland science. New York, Taylor and Francis Group
Arriagada C, Paris I, Sanchez de las Matas MJ, Martinez-Alvarado P, Cardenas S, Castañeda P, Graumann R, Perez-Pastene C, Olea-Azar C, Couve E, Herrero MT, Caviedes P, Segura-Aguilar J (2004) On the neurotoxicity mechanism of leukoaminochrome o-semiquinone radical derived from dopamine oxidation: mitochondria damage, necrosis, and hydroxyl radical formation. Neurobiol Dis 16:468–477
Baas PW, Ahmad FJ (2013) Beyond taxol: microtubule-based treatment of disease and injury of the nervous system. Brain 136:2937–2951
Blesa J, Trigo-Damas I, Quiroga-Varela A, Jackson-Lewis VR (2015) Oxidative stress and Parkinson’s disease. Front Neuroanat 9:91
Breuss M, Keays DA (2014) Microtubules and neurodevelopmental disease: the movers and the makers. Adv Exp Med Biol 800:75–96
Brunden KR, Trojanowski JQ, Smith AB 3rd, Lee VM, Ballatore C (2014) Microtubule-stabilizing agents as potential therapeutics for neurodegenerative disease. Bioorg Med Chem 22:5040–5049
Cappelletti G, Casagrande F, Calogero A, De Gregorio C, Pezzoli G, Cartelli D (2015) Linking microtubules to Parkinson’s disease: the case of parkin. Biochem Soc Trans 43:292–296
Cartelli D, Ronchi C, Maggioni MG, Rodighiero S, Giavini E, Cappelletti G (2010) Microtubule dysfunction precedes transport impairment and mitochondria damage in MPP + -induced neurodegeneration. J Neurochem 115:247–258
Cartelli D, Goldwurm S, Casagrande F, Pezzoli G, Cappelletti G (2012) Microtubule destabilization is shared by genetic and idiopathic Parkinson’s disease patient fibroblasts. PLoS One 7:e37467
Cartelli D, Casagrande F, Busceti CL, Bucci D, Molinaro G, Traficante A, Passarella D, Giavini E, Pezzoli G, Battaglia G, Cappelletti G (2013) Microtubule alterations occur early in experimental parkinsonism and the microtubule stabilizer epothilone D is neuroprotective. Sci Rep 3:1837
Choi WS, Palmiter RD, Xia Z (2011) Loss of mitochondrial complex I activity potentiates dopamine neuron death induced by microtubule dysfunction in a Parkinson’s disease model. J Cell Biol 192:873–882
Choi BH, Chattopadhaya S, le Thanh N, Feng L, Nguyen QT, Lim CB, Harikishore A, Nanga RP, Bharatham N, Zhao Y, Liu X, Yoon HS (2014) Suprafenacine, an indazole-hydrazide agent, targets cancer cells through microtubule destabilization. PLoS One 9:e110955
Chu Y, Morfini GA, Langhamer LB, He Y, Brady ST, Kordower JH (2012) Alterations in axonal transport motor proteins in sporadic and experimental Parkinson’s disease. Brain 135:2058–2073
Cuevas C, Huenchuguala S, Muñoz P, Villa M, Paris I, Mannervik B, Segura-Aguilar J (2015) Glutathione transferase-M2-2 secreted from glioblastoma cell protects SH-SY5Y cells from aminochrome neurotoxicity. Neurotox Res 27:217–228
de Forges H, Bouissou A, Perez F (2012) Interplay between microtubule dynamics and intracellular organization. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 44:266–274
Dehmelt L, Halpain S (2005) The MAP2/Tau family of microtubule-associated proteins. Genome Biol 6:204
Dráber P, Dráberová E (2012) Microtubules. In: Kavallaris M (ed) Cytoskeleton and human disease, 1st edn. Springer, New York, pp 29–53
Esteves AR, Gozes I, Cardoso SM (2014) The rescue of microtubule-dependent traffic recovers mitochondrial function in Parkinson’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1842:7–21
Feinstein SC, Wilson L (2005) Inability of tau to properly regulate neuronal microtubule dynamics: a loss-of-function mechanism by which tau might mediate neuronal cell death. Biochim Biophys Acta 1739:268–279
Ferrer I, Martinez A, Blanco R (2011) Dalfó E (2011) Neuropathology of sporadic Parkinson disease before the appearance of parkinsonism: preclinical Parkinson disease. J Neural Transm 118:821–839
Franco-Iborra S, Vila M, Perier C (2015) The Parkinson disease mitochondrial hypothesis: where are we at? Neuroscientist. doi:10.1177/1073858415574600
Gan-Or Z, Dion PA, Rouleau GA (2015) Genetic perspective on the role of the Autophagy-Lysosome Pathway in Parkinson disease. Autophagy. doi:10.1080/15548627.2015.1067364
Gardner MK, Zanic M, Howard J (2013) Microtubule catastrophe and rescue. Curr Opin Cell Biol 25:14–22
Gąssowska M, Czapski GA, Pająk B, Cieślik M, Lenkiewicz AM, Adamczyk A (2014) Extracellular α-synuclein leads to microtubule destabilization via GSK-3β-dependent Tau phosphorylation in PC12 cells. PLoS One 9:e94259
Gigant B, Cormier A, Dorléans A, Ravelli RB, Knossow M (2009) Microtubule-destabilizing agents: structural and mechanistic insights from the interaction of colchicine and vinblastine with tubulin. Top Curr Chem 286:259–278
Gornstein E, Schwarz TL (2014) The paradox of paclitaxel neurotoxicity: mechanisms and unanswered questions. Neuropharmacology 76:175–183
Hang L, Thundyil J, Lim KL (2015) Mitochondrial dysfunction and Parkinson disease: a Parkin-AMPK alliance in neuroprotection. Ann N Y Acad Sci. doi:10.1111/nyas.12820
Herrero MT, Hirsch EC, Kastner A, Ruberg M, Luquin MR, Laguna J, Javoy-Agid F, Obeso JA, Agid Y (1993) Does neuromelanin contribute to the vulnerability of catecholaminergic neurons in monkeys intoxicated with MPTP? Neuroscience 56:499–511
Hirsch E, Graybiel AM, Agid YA (1988) Melanized dopaminergic neurons are differentially susceptible to degeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Nature 334:345–348
Hongo H, Kihara T, Kume T, Izumi Y, Niidome T, Sugimoto H, Akaike A (2012) Glycogen synthase kinase-3β activation mediates rotenone-induced cytotoxicity with the involvement of microtubule destabilization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 426:94–99
Huenchuguala S, Muñoz P, Zavala P, Villa M, Cuevas C, Ahumada U, Graumann R, Nore BF, Couve E, Mannervik B, Paris I, Segura-Aguilar J (2014) Glutathione transferase mu 2 protects glioblastoma cells against aminochrome toxicity by preventing autophagy and lysosome dysfunction. Autophagy 10:618–630
Janezic S, Threlfella S, Dodsona PD, Dowiea MJ, Taylora TN, Potgietera D, Parkkinena L, Seniora SL, Anwara S, Ryana B, Deltheila T, Kosilloa P, Ciorocha M, Wagnera K, Ansorgea O, Bannermana DM, Bolama JP, Magilla PJ, Cragga SJ, Wade-Martinsa R (2013) Deficits in dopaminergic transmission precede neuron loss and dysfunction in a new Parkinson model. PNAS 110:E4016–E4025. doi:10.1073/pnas.1309143110
Jordan MA, Kamath K (2007) How do microtubule-targeted drugs work? An overview. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 7:730–742
Kamal A, Balakrishna M, Nayak VL, Shaik TB, Faazil S, Nimbarte VD (2014) Design and synthesis of imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole-chalcone conjugates: microtubule-destabilizing agents. Chem Med Chem 9:2766–2780
Kamath K, Oroudjev E, Jordan MA (2010) Determination of microtubule dynamic instability in living cells. Methods Cell Biol 97:1–14
Kanaan NM, Pigino GF, Brady ST, Lazarov O, Binder LI, Morfini GA (2013) Axonal degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease: when signaling abnormalities meet the axonal transport system. Exp Neurol 246:44–45
Kaur R, Kaur G, Gill RK, Soni R, Bariwal J (2014) Recent developments in tubulin polymerization inhibitors: an overview. Eur J Med Chem 87:89–124
Kiris E, Ventimiglia D, Feinstein SC (2010) Quantitative analysis of MAP-mediated regulation of microtubule dynamic instability in vitro focus on Tau. Methods Cell Biol 95:481–503
Lancaster OM, Baum B (2014) Shaping up to divide: coordinating actin and microtubule cytoskeletal remodelling during mitosis. Semin Cell Dev Biol 34:109–115
LaVoie MJ, Ostaszewski BL, Weihofen A, Schlossmacher MG, Selkoe DJ (2005) Dopamine covalently modifies and functionally inactivates parkin. Nat Med 11:1214–1221
Law BM, Spain VA, Leinster VH, Chia R, Beilina A, Cho HJ, Taymans JM, Urban MK, Sancho RM, Blanca Ramírez M, Biskup S, Baekelandt V, Cai H, Cookson MR, Berwick DC, Harvey K (2014) A direct interaction between leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 and specific β-tubulin isoforms regulates tubulin acetylation. J Biol Chem 289:895–908
Lee JC, Timasheff SN (1977) In vitro reconstitution of calf brain microtubules: effects of solution variable. Biochemistry 16:1754–1762
Lees AJ, Hardy J, Revesz T (2009) Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 373:2055–2066
Li G, Faibushevich A, Turunen BJ, Yoon SO, Georg G, Michaelis ML, Dobrowsky RT (2003) Stabilization of the cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activator, p35, by paclitaxel decreases beta-amyloid toxicity in cortical neurons. J Neurochem 84:347–362
Lou K, Yao Y, Hoye AT, James MJ, Cornec AS, Hyde E, Gay B, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Smith AB 3rd, Brunden KR, Ballatore C (2014) Brain-penetrant, orally bioavailable microtubule-stabilizing small molecules are potential candidate therapeutics for Alzheimer’s disease and related tauopathies. J Med Chem 57:6116–6127
Lu X, Kim-Han JS, Harmon S, Sakiyama-Elbert SE, O’Malley KL (2014) The Parkinsonian mimetic, 6-OHDA, impairs axonal transport in dopaminergic axons. Mol Neurodegener 9:17
Masliah E, Dumaop W, Galasko D, Desplats P (2013) Distinctive patterns of DNA methylation associated with Parkinson disease: identification of concordant epigenetic changes in brain and peripheral blood leukocytes. Epigenetics 8:1030–1038
Muñoz P, Cardenas S, Huenchuguala S, Briceño A, Couve E, Paris I, Segura-Aguilar J (2015) DT-diaphorase prevents aminochrome-induced alpha-synuclein oligomer formation and neurotoxicity. Toxicol Sci 145:37–47
Neely MD, Boutte A, Milatovic D, Montine TJ (2005) Mechanisms of 4-hydroxynonenal-induced neuronal microtubule dysfunction. Brain Res 1037:90–98
Paris I, Cardenas S, Lozano J, Perez-Pastene C, Graumann R, Riveros A, Caviedes P, Segura-Aguilar J (2007) Aminochrome as a preclinical experimental model to study degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease. Neurotox Res 12:125–134
Paris I, Perez-Pastene C, Couve E, Caviedes P, Ledoux S, Segura-Aguilar J (2009) Copper dopamine complex induces mitochondrial autophagy preceding caspase-independent apoptotic cell death. J Biol Chem 284:13306–13315
Paris I, Perez-Pastene C, Cardenas S, Iturriaga-Vasquez P, Muñoz P, Couve E, Caviedes P, Segura-Aguilar J (2010) Aminochrome induces disruption of actin, alpha-, and beta-tubulin cytoskeleton networks in substantia-nigra-derived cell line. Neurotox Res 18:82–92
Paris I, Muñoz P, Huenchuguala S, Couve E, Sanders LH, Greenamyre JT, Caviedes P, Segura-Aguilar J (2011) Autophagy protects against aminochrome-induced cell death in substantia nigra-derived cell line. Toxicol Sci 121:376–388
Paz MA, Flückiger R, Boak A, Kagan HM, Gallop PM (1991) Specific detection of quinoproteins by redox-cycling staining. J Biol Chem 266:689–692
Ren Y, Liu W, Jiang H, Jiang Q, Feng J (2005) Selective vulnerability of dopaminergic neurons to microtubule depolymerization. J Biol Chem 280:34105–34112
Risinger AL, Mooberry SL (2012) Microtubules as a target in cancer therapy. In: Kavallaris M (ed) Cytoskeleton and human disease, 1st edn. Springer, New York, pp 203–221
Samii A, Nutt JG, Ransom BR (2004) Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 363:1783–1793
Sayas CL, Avila J (2014) Regulation of EB1/3 proteins by classical MAPs in neurons. Bioarchitecture 4:1–5
Segura-Aguilar J, Kostrzewa RM (2015) Neurotoxin mechanisms and processes relevant to Parkinson’s disease: an update. Neurotox Res 27:328–354
Segura-Aguilar J, Lind C (1989) On the mechanism of the Mn3(+)-induced neurotoxicity of dopamine:prevention of quinone-derived oxygen toxicity by DT diaphorase and superoxide dismutase. Chem Biol Interact 72:309–324
Segura-Aguilar J, Paris I, Muñoz P, Ferrari E, Zecca L, Zucca FA (2014) Protective and toxic roles of dopamine in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 129:898–915
Shelanski ML, Gaskin F, Cantor CR (1973) Microtube assembly in the absence of added nucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci 70:765–768
Sirajuddin M, Rice LM, Vale RD (2014) Regulation of microtubule motors by tubulin isotypes and post-translational modifications. Nat Cell Biol 16:335–344
Srivastava P, Panda D (2007) Rotenone inhibits mammalian cell proliferation by inhibiting microtubule assembly through tubulin binding. FEBS J 274:4788–4801
Törnqvist M, Fred C, Haglund J, Helleberg H, Paulsson B, Rydberg P (2002) Protein adducts: quantitative and qualitative aspects of their formation, analysis and applications. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 778:279–308
Van Laar VS, Mishizen AJ, Cascio M, Hastings TG (2009) Proteomic identification of dopamine-conjugated proteins from isolated rat brain mitochondria and SH-SY5Y cells. Neurobiol Dis 34:487–500
Xu Y, Deng Y, Qing H (2015) The phosphorylation of α-synuclein: development and implication for the mechanism and therapy of the Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem. doi:10.1111/jnc.13234
Zajkowski T, Nieznanska H, Nieznanski K (2015) Stabilization of microtubular cytoskeleton protects neurons from toxicity of N-terminal fragment of cytosolic prion protein. Biochim Biophys Acta 1853:2228–2239
Zecca L, Tampellini D, Gatti A, Crippa R, Eisner M, Sulzer D, Ito S, Fariello R, Gallorini M (2002) The neuromelanin of human substantia nigra and its interaction with metals. J Neural Transm 109:663–672
Zecca L, Bellei C, Costi P, Albertini A, Monzani E, Casella L, Gallorini M, Bergamaschi L, Moscatelli A, Turro NJ, Eisner M, Crippa PR, Ito S, Wakamatsu K, Bush WD, Ward WC, Simon JD, Zucca FA (2008) New melanic pigments in the human brain that accumulate in aging and block environmental toxic metals. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:17567–17572
Acknowledgments
This study was supported through funding from FONDECYT 1120337 and Project University Santo Tomás N000012858 and 0000016012.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Briceño, A., Muñoz, P., Brito, P. et al. Aminochrome Toxicity is Mediated by Inhibition of Microtubules Polymerization Through the Formation of Adducts with Tubulin. Neurotox Res 29, 381–393 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-015-9560-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-015-9560-x