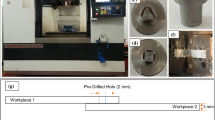
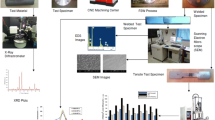
Abstract
Swept friction stir spot welding (SFSSW) is one of the preferred welding methods used in joining metals. The application of this joining process is limited by path deviation, insufficient tool plunging and vibrations caused by high torque and force during the welding. In order to improve the weld strength and weld repeatability, the optimum process parameters of SFSSW of aluminium 6061-T6 alloy were investigated through Grey rational analysis. Initially, Taguchi L16 array consisting of diameter of guide hole, tool rotational and traverse speeds was developed and experiments were conducted by filling guide hole with Silicon Carbide nanoparticles. Grey relational analysis of the experiments reports that guide hole diameter = 3 mm, rotational speed = 1600 rpm and traverse speed = 20 mm/min are found to be optimal parameters for attaining the maximum lap shear strength and hardness. The cause-and-effect analysis of data reports that the amount of SiC added to the guide hole is the most significant factor influencing the weld strength. Furthermore, mechanical and metallurgical characterisation of weld samples prepared at optimum condition were compared with neat samples. The microstructural analysis of stir zone and the fractured area were also presented. The addition of nanoparticles and use of predicted optimum weld condition results homogeneous distribution, refined grains in the stir zone that causes a noteworthy increase in the weld strength.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jurgen H (2011) Aluminium in innovative light-weight Car design. Mater Trans 52:818–824. https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.L-MZ201132
Olea CAW, Roldo L, Strohaecker TR, dos Santos JF (2006) Friction stir welding of precipitate Hardenable Aluminium alloys: a review. Weld World 50:78–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf03263464
Padhy GK, Wu CS, Gao S (2018) Friction stir based welding and processing technologies - processes, parameters, microstructures and applications: a review. J Mater Sci Technol 34:1–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2017.11.029
Suresh S, Venkatesan K, Rajesh S (2019) Optimization of process parameters for friction stir spot welding of AA6061/Al2O3 by Taguchi method. AIP Conf Proc 2128. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5117961
Addison AC, Robelou AJ (2004) Friction stir spot welding: principal parameters and their effects. Proceedings of the 5th international friction stir welding symposium, Metz, France, 14-16
Kalagara S, Muci-Kuchler KH, Arbegast W (2010) Visualization of material flow in a refill friction stir spot welding process using marker materials. SAE Int J Mater Manufact 3:628–651. https://doi.org/10.4271/2010-01-0971
Yang XW, Fu T, Li WY (2014) Friction stir spot welding: a review on joint macro and microstructure, property, and process Modelling. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2014:1–11
Badrinarayan H, Yang Q, Okamoto K (2011) Effect of weld orientation on static strength and failure mode of friction stir stitch welds in lap-shear specimens of aluminum 6022-T4 sheets. Fatigue Fract Eng Mater Struct 34:908–920. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-2695.2011.01584.x
Burford DA, Tweedy BM, Widener CA (2008) Fatigue Crack Growth in Integrally Stiffened Panels Joined Using Friction Stir Welding and Swept Friction Stir Spot Welding. J ASTM Int 5(4). Paper ID JAI101568, 2008
Shen Z, Yang X, Yang S, Zhang Z, Yin Y (2014) Microstructure and mechanical properties of friction spot welded 6061-T4 aluminum alloy. Mater Des 54:766–778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.08.021
Chowdhury SH, Chen DL, Bhole SD, Cao X, Wanjara P (2012) Lap shear strength and fatigue life of friction stir spot welded AZ31 magnesium and 5754 aluminum alloys. Mater Sci Eng A 556:500–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2012.07.019
Rao HM, Jordon JB, Barkey ME, Guo YB, Su X, Badarinarayan H (2013) Influence of structural integrity on fatigue behavior of friction stir spot welded AZ31 mg alloy. Mater Sci Eng A 564:369–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2012.11.076
Uematsu Y, Kakiuchi T, Tozaki Y, Kojin H (2013) Comparative study of fatigue behaviour in dissimilar Al alloy/steel and mg alloy/steel friction stir spot welds fabricated by scroll grooved tool without probe. Sci Technol Weld Join 17(5):348–356. https://doi.org/10.1179/1362171812Y.0000000014
Hossain MAM, Hasan MT, Hong ST, Miles M, Cho HH, Han HN (2013) Friction stir spot welded joints of 409L stainless steels fabricated by a convex shoulder tool. Met Mater Int 19:1243–1250
Hovanski Y, Santella ML, Grant GJ (2007) Friction stir spot welding of hot-stamped boron steel. Scr Mater 57(9):873–876. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2007.06.060
Su ZM, He RY, Lin PC, Dong K (2016) Fatigue of alclad AA2024-T3 swept friction stir spot welds in cross-tension specimens. J Mater Process Technol 236:162–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2016.05.014
Su ZM, He RY, Lin PC, Dong K (2014) Fatigue analyses for swept friction stir spot welds in lap-shear specimens of alclad 2024-T3 aluminum sheets. Int J Fatigue 61:129–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2013.11.021
Rathee S, Maheshwari S, Siddiquee AN, Srivastava M (2018) Investigating the effects of SiC particle sizes on microstructural and mechanical properties of AA5059/SiC surface composites during multi-pass FSP. Silicon 11:797–805. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-018-9958-1
Shojaeefard MH, Akbari M, Khalkhali A, Asadi P (2018) Effect of tool pin profile on distribution of reinforcement particles during friction stir processing of B4C/aluminum composites. Proc Inst Mech Engs Part L: J Mater: Design Appl 232(8):637–651. https://doi.org/10.1177/1464420716642471
Dolatkhah A, Golbabaei P, BesharatiGivi MK, Molaiekiya F (2012) Investigating effects of process parameters on microstructural and mechanical properties of Al5052/SiC metal matrix composite fabricated via friction stir processing. Mater Des 37:458–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2011.09.035
Mahmoud ERI, Ikeuchi K, Takahashi M (2008) Fabrication of SiC particle reinforced composite on aluminium surface by friction stir processing. Sci Technol Weld Join 13:607–618. https://doi.org/10.1179/136217108X333327
Suresh S, Venkatesan K, Elango N, Nanomater J (2018) Influence of SiC nanoparticle reinforcement on FSS welded 6061-T6 aluminum alloy. J Nanomater 2018:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7031867
Wu D, Shen J, Lv L, Wen L, Xie X (2017) Effects of nano-SiC on the FSSW welded AZ31 magnesium alloy joints. Mater Sci Technol 33:998–1003. https://doi.org/10.1080/02670836.2016.1254891
Tebyani SF, Dehghani K (2015) Friction stir spot welding of interstitial free steel with incorporating silicon carbide nanopowders. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 79:343–350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-6788-9
Lee SH, Lee DM, Lee KS (2017) Process optimisation and microstructural evolution of friction stir spot-welded Al6061 joints. Mater Sci Technol 33:719–730. https://doi.org/10.1080/02670836.2016.1230661
Karthikeyan R, Balasubramanian V (2010) Predictions of the optimized friction stir spot welding process parameters for joining AA2024 aluminum alloy using RSM. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 51:173–183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-010-2618-2
Abbass MK, Hussein SK, Khudhair AA (2016) Optimization of mechanical properties of friction stir spot welded joints for dissimilar aluminum alloys (AA2024-T3 and AA 5754-H114). Arab J Sci Eng 41:4563–4572. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-016-2172-9
Ojo OO, Taban E (2018) Hybrid multi-response optimization of friction stir spot welds: failure load, effective bonded size and flash volume as responses. Sadhana 43:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-018-0882-2
Sindhu D, Thakur L, Chandna P (2018) Multi-objective optimization of rotary ultrasonic machining parameters for quartz glass using Taguchi-Grey relational analysis (GRA). Silicon 11:2033–2044. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-018-0019-6
Thakur A, Manna A, Samir S (2019) Multi-response optimization of turning parameters during machining of EN-24 steel with SiC Nanofluids based minimum quantity lubrication. Silicon 12:71–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-019-00102-y
Lilly Mercy J, Prakash S, Krishnamoorthy A, Ramesh S, Alex Anand D (2017) Multi response optimisation of mechanical properties in self-healing glass fiber reinforced plastic using grey relational analysis. Measurement 110:344–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2017.07.013
Suresh S, Venkatesan K, Natarajan E, Rajesh S, Hong LW (2019) Evaluating weld properties of conventional and swept friction stir spot welded 6061-T6 aluminium alloy. Mater Express 9:851–860. https://doi.org/10.1166/mex.2019.1584
Suresh S, Venkatesan K, Natarajan E, Rajesh S (2020) Influence of tool rotational speed on the properties of friction stir spot welded AA7075-T6/Al2O3 composite joint. Mater Today: Proc 27:62–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.08.220
Suresh S, Elango N, Venkatesan K, Lim WH, Palanikumar K, Rajesh S (2020) Sustainable friction stir spot welding of 6061-T6 aluminium alloy using improved non-dominated sorting teaching learning algorithm. J Mater Res Technol 9(5):11650–11674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.08.043
Yuvanarasimman P, Malayalamurthi R (2017) Studies on fractures of friction stir welded Al matrix SiC-B4C reinforced metal composites. Silicon 10(4):1375–1383. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-017-9614-1
Singh T, Tiwari SK, Shukla DK (2019) Friction-stir welding of AA6061-T6: the effects of Al2O3 nano-particles addition. Results Mater 1:100005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinma.2019.100005
Dinaharan I, Sathishkumar R, Murugan N (2016) Effect of ceramic particulate type on microstructure and properties of copper matrix composites synthesized by friction stir processing. J Mater Res Technol 5:302–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2016.01.003
Singh T, Tiwari SK, Shukla DK (2019) Production of AA6061-T6/Al2O3 reinforced nanocomposite using friction stir welding. Eng Res Express 1(2). https://doi.org/10.1088/2631-8695/ab5e27
Srivastava M, Rathee S, Siddiquee AN, Maheshwari S (2018) Investigation on the effects of silicon carbide and cooling medium during multi-pass FSP of Al-mg/SiC surface composites. Silicon 11:2149–2157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-018-0037-4
Subramani V, Jayavel B, Sengottuvelu R, Lazar P (2019) Assessment of microstructure and mechanical properties of stir zone seam of friction stir welded magnesium AZ31B through Nano-SiC. Materials 12(7):1044. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12071044
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suresh, S., Venkatesan, K., Natarajan, E. et al. Performance Analysis of Nano Silicon Carbide Reinforced Swept Friction Stir Spot Weld Joint in AA6061-T6 Alloy. Silicon 13, 3399–3412 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-020-00751-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-020-00751-4