Abstract
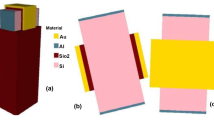
FinFETs are popular and forefront runner in integrated circuits (ICs) technology due to exceptional scalability and suppressed short channel effects (SCEs). The bottom spacer (BP) concept is adopted in FinFET to achieve ameliorated short-channel, reduced self heating issues and to solve width quantization effect. The dual-material-gate (DMG) concept provides novel features like threshold voltage roll-up, transconductance enhancement and suppression of SCEs by work function engineering. Further, the ground-plane (GP) concept is also introduced to minimize the interaction between source and drain region which results in suppressed drain induced barrier lowering (DIBL). This paper investigates the systematic analysis of novel DMBSGP FinFET. The electrical performance parameters are extracted for different bottom spacer height (BSH) and workfunction differences (∆W). The analog/RF figure of merits (FOMs) such as transconductance (gm), output conductance (gd), transconductance generation factor (gm/ID), early voltage (VEA), intrinsic gain (AV), cut-off frequency (fT), transconductance frequency product (TFP), gain frequency product (GFP) and gain transconductance frequency product (GTFP) are examined for different BSH of DMBSGP FinFET using 3-D ATLAS device simulator.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moore GE (1998) Cramming more components onto integrated circuits. Proc IEEE 86(1):82–85
Dennard RH, Gaensslen FH, Yu H-N, Rideout VL, Bassous E, LeBlanc AR (1974) Design of ion-Implanted MOSFET’s with very small physical dimensions. IEEE J Solid State Circuits 9(4):256–268
Roy K, Mukhopadhyay S, Mahmoodi-Meimand H (2003) Leakage current mechanisms and leakage reduction techniques in deep-submicrometer CMOS circuits. Proc IEEE 91(2):302–325
Yan R-H, Ourmazd A, Lee KF (1992) Scaling the Si MOSFET: from bulk to SOI to bulk. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 39(7):1704–1710
Veeraghavan S, Fossum JG (1989) Short-Channel effects in SOI MOSFET’s. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 36(3):522–528
Vandana B (2013) Study of floating body effect in SOI technology. Int J Modern Eng Res 3(3):1817–1824
Collinge J-P (1991) Problems and issues in SOI CMOS technology. Proc IEEE Int SOI Conf:126–127
Balestra F, Cristoloveanu S, Benachir M, Birni J, Elewa T (1987) Double-gate silicon-on-insulator transistor with volume inversion: a new device with greatly enhanced performance. IEEE Electron Device Letters 8(9):410–412
Kranti A, Chung TM, Flandre D, Raskin JP (2004) Laterally asymmetric channel engineering in fully depleted double gate SOI MOSFETs for high performance analog applications. Solid State Electron 48:947–959
Frank DJ, Laux SE, Fischetti MV (1992) Monte Carlo simulation of a 30 nm dual-gate MOSFET: how short can Si go? IEDM Tech Dig:553–556
Wong H-S, Frank DJ, Taur Y, Stork JMC (1994) Design and performance considerations for sub-0.1μm double-gate SOI MOSFETs. IEDM Tech. Dig.:747–750
Wong H-SP, Chan KK, Taur Y (1997) Self-aligned (top and bottom) double-gate MOSFET with a 25 nm thick silicon channel. IEDM Tech Dig:427–430
Lee J-H, Taraschi G, Wei A, Langdo TA, Fitzgerald EA, Antoniadis DA (1999) Super self-aligned double-gate (SSDG) MOSFETs utilizing oxidation rate difference and selective epitaxy. IEDM Tech Dig:71–74
Hisamoto D, Lee W-C, Kedzierski J, Takeuchi H, Asano K, Kuo C, Anderson R, King T-J, Bokor J, Hu C (2000) FinFET-a self-aligned double-gate MOSFET scalable to 20 nm. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 47:2320–2325
Mohapatra SK, Pradhan KP, Singh D, Sahu PK (2015) The role of geometry parameters and fin aspect ratio of sub-20nm SOI-FinFET: an analysis towards analog and RF circuit design. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol 14(3)
Narendar V (2018) Performance enhancement of FinFET devices with gate-stack (GS) high-K dielectrics for Nanoscale applications. Silicon 10(6):2419–2429
Shrivastava M, Baghini MS, Sachid AB, Sharma DK, Rao VR (2008) A novel and robust approach for common mode feedback using IDDG FinFET. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 55(11):3274–3282
Park T-S, Cho HJ, Choe JD, Han SY, Park D, Kim K, Yoon E, Lee J-H (2006) Characteristics of the full CMOS SRAM cell using body-tied TG MOSFETs (bulk FinFETs). IEEE Trans Electron Devices 53(3):481–487
Lee H, Lee C-H, Park D, Choi Y-K (2005) A study of negative-bias temperature instability of SOI and body-tied FinFETs. IEEE Electron Device Letters 26(5):326–328
Bansal A, Mukhopadhyay S, Roy K (2007) Device-optimization technique for robust and low-power FinFET SRAM Design in Nanoscale era. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 54(6):1409–1419
Narendar V, Mishra RA (2015) Analytical modeling and simulation of multigate FinFET devices and the impact of high-k dielectrics on short channel effects (SCEs). Superlattice Microst 85:357–369
Tripathi S, Narendar V (2015) A three-dimensional (3D) analytical model for subthreshold characteristics of uniformly doped FinFET. Superlattice Microst 83:476–487
Pei G, Kedzierski J, Oldiges P, Ieong M, Kan EC-C (2002) FinFET design considerations based on 3-D simulation and analytical modeling. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 49(8):1411–1419
Gu J, Keane J, Sapatnekar S, Kim C (2006) Width quantization aware FinFET circuit design. Proc IEEE CICC:721–724
Shrivastava M, Baghini MS, Sharma DK, Rao VR (2010) A novel bottom spacer FinFET structure for improved Short-Channel. Power-Delay Therm Perform, IEEE Trans Electron Devices 57(6):1287–1294
Long W, Ou H, Kuo J-M, Chin KK (1999) Dual-material gate (DMG) field effect transistor. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 46(5):865–870
Chaudhury A, Kumar MJ (2004) Investigation of the novel attributes of a fully depleted dual-material gate SOI MOSFET. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 51(9):1463–1467
Narendar V, Girdhardas KA (2018) Surface Potential Modeling of Graded-Channel Gate-Stack (GCGS) High-K Dielectric Dual-Material Double-Gate (DMDG) MOSFET and Analog/RF Performance Study. Silicon 10(6):2865–2875
Narendar V, Tripathi S, Naik RBS (2018) A Two-Dimensional (2D) Analytical Modeling and Improved Short Channel Performance of Graded-Channel Gate-Stack (GCGS) Dual-Material Double-Gate (DMDG) MOSFET. Silicon 10(6):2399–2407
Narendar V, Rai S, Tiwari S (2016) A two-dimensional (2D) analytical surface potential and subthreshold current model for underlap dual-material double-gate (DMDG) FinFET. J Comput Electron 15(4):1316–1325
Narendar V, Rai S, Tiwari S, Mishra RA (2016) A two-dimensional (2D) analytical subthreshold swing and transconductance model of underlap dual-material double-gate (DMDG) MOSFET for analog/RF applications. Superlattice Microst 100:274–289
Xiong W, Colinge JP (1999) Self-aligned implanted ground-plane fully depleted SOI MOSFET. Electron Lett 35(23):2059–2060
Yanagi S, Nakakubo A, Omura Y (2001) Proposal of partial-ground-plane (PGP) silicon-on-insulator (SOI) MOSFET for deep sub-0.1-μm channel regime. IEEE Electron Device Lett 22(6):278–280
Lolivier J, Widiez J, Vinet A, Poiroux T, Dauge F, Previtali B, Mouis A, Jommah J, Balestra F, Deleonibus S (2004) Experimental comparison between double gate, ground plane, and single gate SOI CMOSFETs. Proc ESSDERC:77–80
Kumar MJ, Siva M (2008) The ground plane in buried oxide for controlling Short-Channel effects in Nanoscale SOI MOSFETs. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 55(6)
Saremi M, Kusha AA, Mohammadi S (2012) Ground plane fin-shaped field effect transistor (GP-FinFET): a FinFET for low leakage power circuits. Microelectron Eng 95:74–82
Lombardi C, Manzini S, Saporito A, Vanzi M (1988) A physically based mobility model for numerical simulation of nonplanar devices. IEEE Trans Comp-Aided Des Integ Circ Syst 7(11):1164–1171
Shockley W, Read WT (1952) Statistics of the recombination of holes and electrons. Phys Rev 87:835–842
Hall RN (1952) Electron-hole recombination in germanium. Phys Rev 87:387
Yang IY, Lochtefeld A, Antoniadis DA (1996) Silicon on insulator with active substrate technology. Proc IEEE Int SOI Conf:106–107
Yang IY, Vieri C, Chandrakasan A, Antoniadis DA (1997) Back-gated CMOS on SOIAS for dynamic threshold voltage control. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 44(5):822–831
Bangsaruntip S, Cohen GM, Majumdar A, Zhang Y, Engelmann SU, Fuller NCM, Gignac LM, Mittal S, Newbury JS, Guillorn M, Barwicz T, Sekaric L, Frank MM, Sleight JW (2009) High performance and highly uniform gate-all-around silicon nanowire MOSFETs with wire size dependent scaling. IEDM Tech Dig:297–300
Lu Q, Yeo YC, Ranade P, Takeuchi H, King TJ, Hu C, Song SC, Luan HF, Kwong DL (2000) Dual-metal gate technology for deep-submicron CMOS transistors. Symp VLSI Tech:72–73
Yeo YC (2004) Metal gate technology for nanoscale transistors–material selection and process integration issues. Thin Solid Films 462–463:34–41
Yuan J, Woo JCS (2005) A novel split-gate MOSFET design realized by a fully silicided gate process for the improvement of transconductance and output resistance. IEEE Electron Device Lett 26(11):829–831
Zhang Z, Song SC, Huffman C, Hussain M, Barnett J, Moumen N, Alshareef H, Majhi P, Sim JH, Bae S, Lee BH (2005) Integration of Dual Metal Gate CMOS on High-k Dielectrics Utilizing a Metal Wet Etch Process. Electrochem Solid-State Lett 8:271–274
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Narendar, V., Narware, P., Bheemudu, V. et al. Investigation of Short Channel Effects (SCEs) and Analog/RF Figure of Merits (FOMs) of Dual-Material Bottom-Spacer Ground-Plane (DMBSGP) FinFET. Silicon 12, 2283–2291 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-019-00322-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-019-00322-2