Abstract
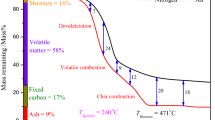
Combustion kinetics of the hydrochar was investigated using a multi-Gaussian-distributed activation energy model (DAEM) to expand the knowledge on the combustion mechanisms. The results demonstrated that the kinetic parameters calculated by the multi-Gaussian-DAEM accurately represented the experimental conversion rate curves. Overall, the feedstock combustion could be divided into four stages: the decomposition of hemicellulose, cellulose, lignin, and char combustion. The hydrochar combustion could in turn be divided into three stages: the combustion of cellulose, lignin, and char. The mean activation energy ranges obtained for the cellulose, lignin, and char were 273.7–292.8, 315.1–334.5, and 354.4–370 kJ/mol, respectively, with the standard deviations of 2.1–23.1, 9.5–27.4, and 12.1–22.9 kJ/mol, respectively. The cellulose and lignin contents first increased and then decreased with increasing hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) temperature, while the mass fraction of char gradually increased.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Barzegar, A. Yozgatligil, H. Olgun, and A.T. Atimtay, TGA and kinetic study of different torrefaction conditions of wood biomass under air and oxy-fuel combustion atmospheres, J. Energy Inst., 93(2020), No. 3, p. 889.
X.E. Wang, K.X. Li, J.N. Song, H.Y. Duan, and S. Wang, Integrated assessment of straw utilization for energy production from views of regional energy, environmental and socioeconomic benefits, J. Clean. Prod., 190(2018), p. 787.
W. Xiong, G.Q. Wang, and S.X. Zhou, Comparison of energy consumption and environmental impact of replacement of coal with straw injection into blast furnace, Environ. Sci. Technol., 36(2013), No. 4, p. 137.
J.B. Chen, Y.H. Wang, X.M. Lang, X.E. Ren, and S.S. Fan, Evaluation of agricultural residues pyrolysis under non-isothermal conditions: Thermal behaviors, kinetics, and thermodynamics, Bioresour. Technol., 241(2017), p. 340.
M. Heidari, A. Dutta, B. Acharya, and S. Mahmud, A review of the current knowledge and challenges of hydrothermal carbonization for biomass conversion, J. Energy Inst., 92(2019), No. 6, p. 1779.
N. Zhang, G.W. Wang, J.L. Zhang, X.J. Ning, Y.J. Li, W. Liang, and C. Wang, Study on co-combustion characteristics of hydrochar and anthracite coal, J. Energy Inst., 93(2020), No. 3, p. 1125.
Z.H. Chen, M. Hu, X.L. Zhu, D.B. Guo, S.M. Liu, Z.Q. Hu, B. Xiao, J.B. Wang, and M. Laghari, Characteristics and kinetic study on pyrolysis of five lignocellulosic biomass via thermo-gravimetric analysis, Bioresour. Technol., 192(2015), p. 441.
K.Y. Park, K. Lee, and D. Kim, Characterized hydrochar of algal biomass for producing solid fuel through hydrothermal carbonization, Bioresour. Technol., 258(2018), p. 119.
J. Zhao, H.B. Zuo, J.S. Wang, and Q.G. Xue, The mechanism and products for co-thermal extraction of biomass and low-rank coal with NMP, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 26(2019), No. 12, p. 1512.
G.K. Parshetti, A. Quek, R. Betha, and R. Balasubramanian, TGA-FTIR investigation of co-combustion characteristics of blends of hydrothermally carbonized oil palm biomass (EFB) and coal, Fuel Process. Technol., 118(2014), p. 228.
H. Li, S.Y. Wang, X.Z. Yuan, Y.N. Xi, Z.L. Huang, M.J. Tan, and C.Z. Li, The effects of temperature and color value on hydrochars’ properties in hydrothermal carbonization, Bioresour. Technol., 249(2018), p. 574.
Z.L. Yao, X.Q. Ma, and Y.S. Lin, Effects of hydrothermal treatment temperature and residence time on characteristics and combustion behaviors of green waste, Appl. Therm. Eng., 104(2016), p. 678.
H.B. Sharma, S. Panigrahi, and B.K. Dubey, Hydrothermal carbonization of yard waste for solid bio-fuel production: Study on combustion kinetic, energy properties, grindability and flowability of hydrochar, Waste Manage., 91(2019), p. 108.
D. Chiaramonti, M. Prussi, M. Buffi, A.M. Rizzo, and L. Pari, Review and experimental study on pyrolysis and hydrothermal liquefaction of microalgae for biofuel production, Appl. Energy, 185(2017), p. 963.
F.Y. Liu, R.D. Yu, X.D. Ji, and M.H. Guo, Hydrothermal carbonization of holocellulose into hydrochar: Structural, chemical characteristics, and combustion behavior, Bioresour. Technol., 263(2018), p. 508.
G.K. Zhu, L. Yang, Y. Gao, J.Y. Xu, H.J. Chen, Y.Z. Zhu, Y.F. Wang, C.H. Liao, C. Lu, and C. Zhu, Characterization and pelletization of cotton stalk hydrochar from HTC and combustion kinetics of hydrochar pellets by TGA, Fuel, 244(2019), p. 479.
N. Zhang, G.W. Wang, C.M. Yu, J.L. Zhang, H. Dang, C.L. Zhang, X.J. Ning, and C. Wang, Physicochemical structure characteristics and combustion kinetics of low-rank coal by hydrothermal carbonization, Energy, 238(2022), art. No. 121682.
M.A. Islam, G. Kabir, M. Asif, and B.H. Hameed, Combustion kinetics of hydrochar produced from hydrothermal carbonisation of Karanj (Pongamia pinnata) fruit hulls via thermogravimetric analysis, Bioresour. Technol., 194(2015), p. 14.
C. He, A. Giannis, and J.Y. Wang, Conversion of sewage sludge to clean solid fuel using hydrothermal carbonization: Hydrochar fuel characteristics and combustion behavior, Appl. Energy, 111(2013), p. 257.
Q.V. Bach, K.Q. Tran, and Ø. Skreiberg, Combustion kinetics of wet-torrefied forest residues using the distributed activation energy model (DAEM), Appl. Energy, 185(2017), p. 1059.
J.Z. Zhang, T.J. Chen, J.L. Wu, and J.H. Wu, Multi-Gaussian-DAEM-reaction model for thermal decompositions of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin: Comparison of N2 and CO2 atmosphere, Bioresour. Technol., 166(2014), p. 87.
G.W. Wang, J.L. Zhang, J.Y. Lee, X.M. Mao, L. Ye, W.R. Xu, X.J. Ning, N. Zhang, H.P. Teng, and C. Wang, Hydrothermal carbonization of maize straw for hydrochar production and its injection for blast furnace, Appl. Energy, 266(2020), art. No. 114818.
Z.Z. Ma, J.H. Xie, N.B. Gao, and C. Quan, Pyrolysis behaviors of oilfield sludge based on Py-GC/MS and DAEM kinetics analysis, J. Energy Inst., 92(2019), No. 4, p. 1053.
J.M. Cai, W.X. Wu, and R.H. Liu, Sensitivity analysis of three-parallel-DAEM-reaction model for describing rice straw pyrolysis, Bioresour. Technol., 132(2013), p. 423.
D. Kim, K. Lee, and K.Y. Park, Upgrading the characteristics of biochar from cellulose, lignin, and xylan for solid biofuel production from biomass by hydrothermal carbonization, J. Ind. Eng. Chem., 42(2016), p. 95.
Y.W. Huang, M.Q. Chen, and H.F. Luo, Nonisothermal torrefaction kinetics of sewage sludge using the simplified distributed activation energy model, Chem. Eng. J., 298(2016), p. 154.
J.J. Xu, H.B. Zuo, G.W. Wang, J.L. Zhang, K. Guo, and W. Liang, Gasification mechanism and kinetics analysis of coke using distributed activation energy model (DAEM), Appl. Therm. Eng., 152(2019), p. 605.
J.M. Cai, W.X. Wu, and R.H. Liu, An overview of distributed activation energy model and its application in the pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass, Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev., 36(2014), p. 236.
J.X. Cai, B. Li, C.Y. Chen, J. Wang, M. Zhao, and K. Zhang, Hydrothermal carbonization of tobacco stalk for fuel application, Bioresour. Technol., 220(2016), p. 305.
Q. Wu, S.T. Yu, N.J. Hao, T. Wells, X.Z. Meng, M. Li, Y.Q. Pu, S.X. Liu, and A.J. Ragauskas, Characterization of products from hydrothermal carbonization of pine, Bioresour. Technol., 244(2017), p. 78.
H.P. Yang, R. Yan, H.P. Chen, D.H. Lee, and C.G. Zheng, Characteristics of hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin pyrolysis, Fuel, 86(2007), No. 12–13, p. 1781.
D.Y. Chen, Y. Zheng, and X.F. Zhu, In-depth investigation on the pyrolysis kinetics of raw biomass. Part I: Kinetic analysis for the drying and devolatilization stages, Bioresour. Technol., 131(2013), p. 40.
M. Hu, Z.H. Chen, S.K. Wang, D.B. Guo, C.F. Ma, Y. Zhou, J. Chen, M. Laghari, S. Fazal, B. Xiao, B.P. Zhang, and S. Ma, Thermogravimetric kinetics of lignocellulosic biomass slow pyrolysis using distributed activation energy model, Fraser-Suzuki deconvolution, and iso-conversional method, Energy Convers. Manage., 118(2016), p. 1.
Y.J. Wang, L. Qiu, M.Q. Zhu, G.T. Sun, T.L. Zhang, and K. Kang, Comparative evaluation of hydrothermal carbonization and low temperature pyrolysis of Eucommia ulmoides Oliver for the production of solid biofuel, Sci. Rep., 9(2019), No. 1, art. No. 5535.
G. Várhegyi, P. Szabó, E. Jakab, F. Till, and J.R. Richard, Mathematical modeling of char reactivity in Ar-O2 and CO2-O2 mixtures, Energy Fuels, 10(1996), No. 6, p. 1208.
Q.V. Bach, K.Q. Tran, and Ø. Skreiberg, Comparative study on the thermal degradation of dry- and wet-torrefied woods, Appl. Energy, 185(2017), p. 1051.
X.S. Yuan, T. He, H.L. Cao, and Q.X. Yuan, Cattle manure pyrolysis process: Kinetic and thermodynamic analysis with isoconversional methods, Renew. Energy, 107(2017), p. 489.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 52074029, 51804026) and the USTB—NTUT Joint Research Program (No. 06310063). Chuan Wang would like to acknowledge the funding support from Vinnova (dnr: 2017-01327).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, C., Ren, S., Wang, G. et al. Kinetic analysis and modeling of maize straw hydrochar combustion using a multi-Gaussian-distributed activation energy model. Int J Miner Metall Mater 29, 464–472 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-021-2305-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-021-2305-3