Abstract
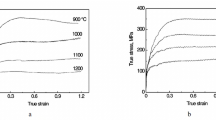
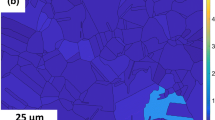
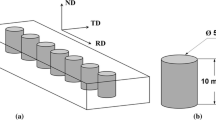
Single- and two-step hot compression experiments were carried out on 16Cr25Ni6Mo superaustenitic stainless steel in the temperature range from 950 to 1150°C and at a strain rate of 0.1 s-1. In the two-step tests, the first pass was interrupted at a strain of 0.2; after an interpass time of 5, 20, 40, 60, or 80 s, the test was resumed. The progress of dynamic recrystallization at the interruption strain was less than 10%. The static softening in the interpass period increased with increasing deformation temperature and increasing interpass time. The static recrystallization was found to be responsible for fast static softening in the temperature range from 950 to 1050°C. However, the gentle static softening at 1100 and 1150°C was attributed to the combination of static and metadynamic recrystallizations. The correlation between calculated fractional softening and microstructural observations showed that approximately 30% of interpass softening could be attributed to the static recovery. The microstructural observations illustrated the formation of fine recrystallized grains at the grain boundaries at longer interpass time. The Avrami kinetics equation was used to establish a relationship between the fractional softening and the interpass period. The activation energy for static softening was determined as 276 kJ/mol.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.S. Chen, K.K. Li, Y.C. Lin, and W.Q. Yuan, An improved kinetics model to describe dynamic recrystallization behavior under inconstant deformation conditions, J. Mater. Res., 31(2016), No. 19, p. 2994.
M.Y. Li, Y.Z. Liu, T. Zhu, and Y. Wang, Microstructure homogenization control of Nb-bearing X65 pipeline steel by the CSP process, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 18(2011), No. 1, p. 35.
A. Momeni, G.R. Ebrahimi, M. Jahazi, and P. Bocher, Microstructure evolution at the onset of discontinuous dynamic recrystallization: A physics-based model of subgrain critical size, J. Alloys Compd., 587(2014), p. 199.
F.J. Humphrey and M. Hatherly, Recrystallization and Related Annealing Phenomena, 2nd ed., Oxford, 2004, p. 255.
D. Ponge and G. Gottstein, Necklace formation during dynamic recrystallization: mechanisms and impact on flow behavior, Acta Mater., 46(1998), No. 1, p. 69.
G. Gottstein, E. Brunger, and D. Ponge, Advances in Hot Deformation Textures and Microstructures, TMS, Pennsylvania, 1995, p. 477.
A. Momeni, S.M. Abbasi, M. Morakabati, H. Badri, and X. Wang, Dynamic recrystallization behavior and constitutive analysis of Incoloy 901 under hot working condition, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 615(2014), p. 51
M. Ueki, S. Horie, and T. Nakamura, Factors affecting dynamic recrystallization of metals and alloys, Mater. Sci. Technol., 3(1987), No. 5, p. 329.
T. Sakai and J.J. Jonas, Dynamic recrystallization: Mechanical and microstructural considerations, Acta Metall., 32(1984), No. 2, p. 189.
A. Belyakov, H. Miura, and T. Sakai, Dynamic recrystallization in ultra fine-grained 304 stainless steel, Scripta Metall., 43(2000), No. 1, p. 21.
D.G. He, Y.C. Lin, M.S. Chen, and L. Li, Kinetics equations and microstructural evolution during metadynamic recrystallization in a nickel-based superalloy with δ phase, J. Alloys Compd., 690(2017), p. 971.
H.J. Mao, R. Zhang, L. Hua, and F. Yin, Study of static recrystallization behaviors of GCr15 steel under two-pass hot compression deformation, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 24(2015), No. 2, p. 930.
B. Ma, Y. Peng, Y.F. Liu, and B. Jia, Modeling of metadynamic recrystallization kinetics after hot deformation of low-alloy steel Q345B, J. Cent. South Univ. Technol., 17(2010), No. 5, p. 911.
A. Dehghan-Manshadi, M.R. Barnett, and P.D. Hodgson, Hot deformation and recrystallization of austenitic stainless steel: Part I. Dynamic recrystallization, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 39(2008), No. 6, p. 1359.
A.R. Morgridge, Metadynamic recrystallization in C steels, Bull. Mater. Sci., 25(2002), No. 4, p. 291.
P.D. Hodgson, Mathematical Modelling of Recrystallization Processes During the Hot Rolling of Steel [Dissertation], University of Queensland, Brisbane, 1993.
C. Roucoules, P.D. Hodgson, S. Yue, and J.J. Jonas, Softening and microstructural change following the dynamic recrystallization of austenite, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 25(1994), No. 2, p. 389.
W.P. Sun and E.B. Hawbolt, Comparison between static and metadynamic recrystallization—an application to the hot rolling of steels, ISIJ Int., 37(1997), No. 10, p. 1000.
A.M. Elwazri, P. Wanjara, and S. Yue, Metadynamic and static recrystallization of hypereutectoid steel, ISIJ Int., 43(2003), No. 7, p. 1080.
L.P. Karjalainen, T.M. Maccagno, and J.J. Jonas, Softening and flow stress behaviour of Nb microalloyed steels during hot rolling simulation, ISIJ Int., 35(1995), No. 12, p. 1523.
J.J. Jonas, The hot strip mill as an experimental tool, ISIJ Int., 40(2000), No. 8, p. 731.
B. Derby and M.F. Ashby, On dynamic recrystallization, Scripta Metall., 21(1987), p. 879.
A. Dehghan-Manshadi, H. Beladi, and M.R. Barnett, Recrystallization in 304 austenitic stainless steel, Mater. Sci. Forum, 467-470(2004), p. 1163.
A. Dehghan Manshadi, The Evolution of Recrystallization During and Following Hot Deformation [Dissertation], Deakin University Geelong, Victoria, 2007.
S. Venugopal, S.L. Mannan, and Y.V.R.K. Prasad, Processing maps for hot working of commercial grade wrought stainless steel type AISI 304, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 177(1994), No. 1-2, p. 143.
I. Salvatori, T. Inoue, and K. Nagai, Ultrafine grain structure through dynamic recrystallization for Type 304 stainless steel, ISIJ Int., 42(2002), No. 7, p. 744.
E.I. Poliak and J.J. Jonas, A one-parameter approach to determining the critical conditions for the initiation of dynamic recrystallization, Acta Mater., 44(1996), No. 1, p. 127.
G.R. Ebrahimi, H. Keshmiri, A.R. Maldad, and A. Momeni, Dynamic recrystallization behavior of 13%Cr martensitic stainless steel under hot working condition, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 28(2012), No. 5, p. 467.
A. Momeni, S.M. Abbasi, and A. Shokuhfar, Dynamic and metadynamic recrystallization of a martensitic precipitation hardenable stainless steel, Can. Metall. Q., 46(2007), No. 2, p. 189.
A. Najafizadeh, J.J. Jonas, G.R. Stewart, and E.I. Poliak, The strain dependence of postdynamic recrystallization in 304 H stainless steel, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 37(2006), No. 6, p. 1899.
J. Liu, Y.G. Liu, H. Lin, and M.Q. Li, The metadynamic recrystallization in the two-stage isothermal compression of 300M steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 565(2013), p. 126.
X.W. Duan, M.M. Chen, H.Q. Chen, and J.S. Liu, Study on static recrystallization softening behavior of 316LN steel, [in] Third International Conference on Measuring Technology and Mechatronics Automation (ICMTMA), 2011, Washington, p. 522.
J. Liu, G.W. Fan, P.D. Han, J.F. Yang, J.S. Liu, D.S. Ge, and G.J. Qiao, Study on the static recrystallization behavior of thermal deformation of austenitic stainless steel for nuclear power, Mater. Sci. Forum, 658(2010), p. 165.
H.Y. Wu, L.X. Du, Z.R. Ai, and X.H. Liu, Static recrystallization and precipitation behavior of a weathering steel microalloyed with vanadium, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 29(2013), No. 12, p. 1197.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bayat, N., Ebrahimi, G.R., Momeni, A. et al. Microstructural evolution of a superaustenitic stainless steel during a two-step deformation process. Int J Miner Metall Mater 25, 181–189 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-018-1561-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-018-1561-3