Abstract
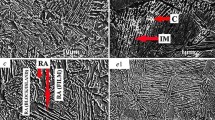
We present a study concerning Fe–0.176C–1.31Si–1.58Mn–0.26Al–0.3Cr (wt%) steel subjected to a quenching and partitioning (Q&P) process. The results of scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and tensile tests demonstrate that the microstructures primarily consist of lath martensite, retained austenite, lower bainite (LB), and a small amount of tempered martensite; moreover, few twin austenite grains were observed. In the microstructure, three types of retained austenite with different sizes and morphologies were observed: blocky retained austenite (~300 nm in width), film-like retained austenite (80–120 nm in width), and ultra- fine film-like retained austenite (30–40 nm in width). Because of the effect of the retained austenite/martensite/LB triplex microstructure, the specimens prepared using different quenching temperatures exhibit high ultimate tensile strength and yield strength. Furthermore, the strength effect of LB can partially counteract the decreasing strength effect of martensite. The formation of LB substantially reduces the amount of retained austenite. Analyses of the retained austenite and the amount of blocky retained austenite indicated that the carbon content is critical to the total elongation of Q&P steel.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Malakondaiah, M. Srinivas, and P. Rama Rao, Ultra-high-strength low-alloy steels with enhanced fracture toughness, Prog. Mater. Sci., 42(1997), No. 1-4, p. 209.
J. Speer, D.K. Matlock, B.C. De Cooman, and J.G. Schroth, Carbon partitioning into austenite after martensite transformation, Acta Mater., 51(2003), No. 9, p. 2611.
J.G. Speer, F.C. Rizzo Assunção, D.K. Matlock, and D.V. Edmonds, The “quenching and partitioning” process: background and recent progress, Mater. Res., 8(2005), No. 4, p. 417.
L.Y. Zhou, D. Zhang, and Y.Z. Liu, Influence of silicon on the microstructures, mechanical properties and stretchflangeability of dual phase steels, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 21(2014), No. 8, p. 755.
S. Zaefferer, J. Ohlert, and W. Bleck, A study of microstructure, transformation mechanisms and correlation between microstructure and mechanical properties of a low alloyed TRIP steel, Acta Metall., 52(2004), No. 9, p. 2765.
H.X. Yin, A.M. Zhao, Z.Z. Zhao, X. Li, S.J. Li, H.J. Hu, and W.G. Xia, Influence of original microstructure on the transformation behavior and mechanical properties of ultra-highstrength TRIP-aided steel, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 22(2015), No. 3, p. 262.
Y.J. Zhao, X.P. Ren, W.C. Yang, and Y. Zang, Design of a low-alloy high-strength and high-toughness martensitic steel, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 20(2013), No. 8, p. 733.
M.J. Santofimia, L. Zhao, R. Petrov, and J. Sietsma, Characterization of the microstructure obtained by the quenching and partitioning process in a low-carbon steel, Mater. Charact., 59(2008), No. 12, p. 1758.
Y. Wang, Z.H. Guo, N.L. Chen, and Y.H. Rong, Deformation temperature dependence of mechanical properties and microstructures for a novel quenching-partitioning-tempering steel, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 29(2013), No. 5, p. 451.
H.Y. Li, X.W. Lu, X.C. Wu, Y.A. Min, and X.J. Jin, Bainitic transformation during the two-step quenching and partitioning process in a medium carbon steel containing silicon, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 527(2010), No. 23, p. 6255.
H. F. Xu, J. Zhao, W. Q. Cao, J. Shi, C. Y. Wang, J. Li, and H. Dong, Tempering effects on the stability of retained austenite and mechanical properties in a medium manganese steel, ISIJ Int., 52(2012), No. 5, p. 868.
R.H. Davies, A.T. Dinsdale, J.A. Gisby, J. Robinson, and S.M. Martin, MTDATA-thermodynamic and phase equilibrium software from the national physical laboratory, Calphad, 26(2002), No. 2, p. 229.
C.F. Jatczak, Retained Austenite and its Measurement by X-ray Diffraction, Society of Automotive Engineers Inc., Warrendale, PA, 1980, p. 9.
D.J. Dyson and B. Holmes, Effect of alloying additions on lattice parameter of austenite, J. Iron Steel Inst., 208(1970), p. 469.
N.H. van Dijk, A.M. Butt, L. Zhao, J. Sietsma, S.E. Offerman, J.P. Wright, and S. van der Zwaag, Thermal stability of retained austenite in TRIP steels studied by synchrotron X-ray diffraction during cooling, Acta Mater., 53(2005), No. 20, p. 5439.
Z.G. Yang and H.S. Fang, An overview on bainite formation in steels, Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci., 9(2005), No. 6, p. 277.
S.M.C. van Bohemen, M.J. Santofimia, and J. Sietsma, Experimental evidence for bainite formation below Ms in Fe-0.66C, Scripta Mater., 58(2008), No. 6, p. 488.
G.H. Gao, H. Zhang, Z.L. Tan, W.B. Liu, and B.Z. Bai, A carbide-free bainite/martensite/austenite triplex steel with enhanced mechanical properties treated by a novel quenching -partitioning-tempering process, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 559(2013), p. 165.
J. Sun and H. Yu, Microstructure development and mechanical properties of quenching and partitioning (Q&P) steel and an incorporation of hot-dipping galvanization during Q&P process, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 586(2013), p. 100.
M.J. Santofimia, L. Zhao, and J. Sietsma, Microstructural evolution of a low-carbon steel during application of quenching and partitioning heat treatments after partial austenitization, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 40(2009), No.1, p. 46.
M.J. Santofimia, T. Nguyen-Minh, L. Zhao, R. Petrov, I. Sabirov, and J. Sietsma, New low carbon Q&P steels containing film-like intercritical ferrite, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 527(2010), p. 6429.
J.G. Speer, D.K. Matlock, B.C. De Cooman, and J.G. Schroth, Comments on “On the definitions of paraequilibrium and orthoequilibrium” by M. Hillert and J. Ågren, Scripta Materialia, 50, 697-9 (2004), Scripta Mater. 52(2005), No. 1, p. 83.
H. Kitahara, R. Ueji, N. Tsuji, and Y. Minamino, Crystallographic features of lath martensite in low-carbon steel, Acta Mater., 54(2006), No. 5, p. 1279.
H.Y. Li, X.W. Lu, W.J. Li, and X.J. Jin, Microstructure and mechanical properties of an ultrahigh-strength 40SiMnNiCr steel during the one-step quenching and partitioning process, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 41(2010), No. 5, p. 1284.
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, and D.V. Edmonds, The bainite transformation in a silicon steel, Metall. Trans. A, 10(1979), No. 7, p. 895.
H.L. Yi, P. Chen, and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, Optimizing the morphology and stability of retained austenite in a d-TRIP steel, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 45(2014), No. 8, p. 3512.
R. Ding, D. Tang, and A.M. Zhao, A novel design to enhance the amount of retained austenite and mechanical properties in low-alloyed steel, Scripta Mater., 88(2014), p. 21.
G.K. Tirumalasetty, M.A. van Huis, C. Kwakernaak, J. Sietsma, W.G. Sloof, and H.W. Zandbergen, Deformation-induced austenite grain rotation and transformation in TRIP-assisted steel, Acta Mater., 60(2012), No. 3, p. 1311.
D.P. Koistinen and R.E. Marburger, A general equation prescribing the extent of the austenite-martensite transformation in pure iron-carbon alloys and plain carbon steels, Acta Metall., 7(1959), No. 1, p. 59.
H.P. Liu, X.W. Lua, X.J. Jin, H. Dong, and J. Shi, Enhanced mechanical properties of a hot stamped advanced high-strength steel treated by quenching and partitioning process, Scripta Mater., 64(2011), No. 8, p. 749.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Ws., Gao, Hy., Li, Zy. et al. Effect of lower bainite/martensite/retained austenite triplex microstructure on the mechanical properties of a low-carbon steel with quenching and partitioning process. Int J Miner Metall Mater 23, 303–313 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-016-1239-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-016-1239-7