Abstract
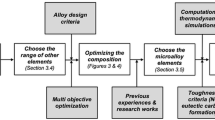
To develop a high strength low alloy (HSLA) steel with high strength and high toughness, a series of martensitic steels were studied through alloying with various elements and thermodynamic simulation. The microstructure and mechanical properties of the designed steel were investigated by optical microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, tensile testing and Charpy impact test. The results show that cementite exists between 500°C and 700°C, M7C3 exits below 720°C, and they are much lower than the austenitizing temperature of the designed steel. Furthermore, the Ti(C,N) precipitate exists until 1280°C, which refines the microstructure and increases the strength and toughness. The optimal alloying components are 0.19% C, 1.19% Si, 2.83% Mn, 1.24% Ni, and 0.049% Ti; the tensile strength and the V notch impact toughness of the designed steel are more than 1500 MPa and 100 J, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Krauss, Deformation and fracture in martensitic carbon steels tempered at low temperatures, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 32(2001), p. 205.
M. Saeglitz and G. Krauss, Deformation, fracture, and mechanical properties of low-temperature-tempered martensite in SAE 43xx steels, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 28(1997), p. 377.
L.Y. Li, Y. Wang, T. Han, and C.W. Li, Microstructure and embrittlement of the fine-grained heat-affected zone of ASTM4130 steel, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 18(2011), No. 4, p. 419.
Y.W. Gao, T.F. Jing, G.Y. Qiao, J.K. Yu, T.S. Wang, Q. Li, X.Y. Song, S.Q. Wang, and H. Gao, Microstructural evolution and tensile properties of low-carbon steel with martensitic microstructure during warm deforming and annealing, J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing, 15(2008), No. 3, p. 245.
C.F. Wang, M.Q. Wang, J. Shi, W.J. Hui, and H. Dong, Effect of microstructure refinement on the strength and toughness of low alloy martensitic steel, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 23(2007), p. 659.
S. Morito, H. Yoshida, T. Maki, and X. Huang, Effect of block size on the strength of lath martensite in low carbon steels, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 438–440(2006), p. 237.
L.J. Wang, Q.W. Cai, H.B. Wu, and W. Yu, Effects of Si on the stability of retained austenite and temper embrittlement of ultrahigh strength steels, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 18(2011), No. 5, p. 543.
J. Chakraborty, P.P. Chattopadhyay, D. Bhattacharjee, and I. Manna, Microstructural refinement of bainite and martensite for enhanced strength and toughness in high-carbon low-alloy steel, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 41(2010), p. 2871.
M.Y. Liu, B. Shi, C. Wang, S.K. Ji, X. Cai, and H.W. Song, Normal Hall-Petch behavior of mild steel with submicron grains, Mater. Lett., 57(2003), p. 2798.
H.J. Rack, Age hardening-grain size relationships in 18Ni maraging steels, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 34(1978), p. 263.
R. Ishibashi, H. Arakawa, T. Abe, and Y. Aono, Tensile strength of austenitic stainless steels with grain refinement by mechanical milling, ISIJ Int., 40(2000), Suppl., p. S169.
B. Hwang, T.H. Lee, and S.J. Kim, Effects of deformation-induced martensite and grain size on ductile-to-brittle transition behavior of austenitic 18Cr-10Mn-N stainless steels, Met. Mater. Int., 16(2010), No. 6, p. 905.
A. Di Schino and J.M. Kenny, Grain size dependence of the fatigue behaviour of a ultrafine-grained AISI 304 stainless steel, Mater. Lett., 57(2003), p. 3182.
C.Y. Zhang, Q.F. Wang, J.X. Ren, R.X. Li, M.Z. Wang, F.C. Zhang, and Z.S. Yan, Effect of microstructure on the strength of 25CrMo48V martensitic steel tempered at different temperature and time, Mater. Des., 36(2012), p. 220.
Z.M. Shi, K. Liu, M.Q. Wang, J. Shi, H. Dong, J. Pu, B. Chi, Y.S. Zhang, and J. Li, Effect of tensile deformation of austenite on the morphology and strength of lath martensite, Met. Mater. Int., 18(2012), No. 2, p. 317.
P. Berthod, P. Lemoine, and L. Aranda, Experimental and thermodynamic study of nickel-based alloys containing chromium carbides: Part I. Study of the Ni-30wt% Cr-xC system over the [0–2.0wt% C] range, Calphad, 32(2008), p. 485.
V. Kneževi J. Balun, G. Sauthoff, G. Inden, and A. Schneider, Design of martensitic/ferritic heat-resistant steels for application at 650° with supporting thermodynamic modelling, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 477(2008), p. 334.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Yj., Ren, Xp., Yang, Wc. et al. Design of a low-alloy high-strength and high-toughness martensitic steel. Int J Miner Metall Mater 20, 733–740 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-013-0791-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-013-0791-7