Abstract
Objectives
Frailty is one of the major health problems facing aging societies worldwide. We investigated the association between serum SIRT6 and frailty in older adults.
Design
Cross-sectional analysis of associations of serum SIRT6 and frailty in older people.
Setting
Enrolled community-dwelling and hospital outpatient clinic adults older than 65 years old in Wuhan City, Hubei Province, China.
Participants
A total of 540 community-dwelling older adults (age ≥ 65 years) in Wuhan were included in the study.
Measures
We used Frailty Phenotype criteria for classifying participants based on their frailty status. Serum SIRT6 was measured using an ELISA kit.
Results
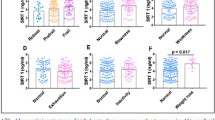
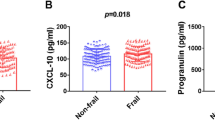
A total of 540 older adults were included in this cross-sectional study. Serum SIRT6 was lower in the slowness group (7.23±1.81 vs 5.89±1.74, p<0.001), weakness group (6.87±1.88 vs 5.68±1.64, p<0.001), and exhaustion group (6.73±1.90 vs 5.88±1.74, p<0.001) compare with the normal group. ROC curves were used to assess the efficiency of SIRT6 in predicting frailty in older adults. The AUC for SIRT6 was 0.792 (95% CI: 0.7514 to 0.8325), with the highest sensitivity of 68.0% and the specificity of 91.9%, and the optimal critical value of 4.65ng/ml according to Youden’s index. Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that serum SIRT6 level was independently associated with frailty in older people.
Conclusion
In conclusion, serum SIRT6 was decreased in frailty compared with robust older adults. A decreased serum SIRT6 was independently associated with an increased risk of frailty. SIRT6 may be a potential target for the treatment of patients with frailty.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials: Data for this study are available from the corresponding author.
References
Hoogendijk EO, Afilalo J, Ensrud KE, Kowal P, Onder G, Fried LP. Frailty: implications for clinical practice and public health. Lancet. 2019;394(10206):1365–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31786-6.
Dent E, Martin FC, Bergman H, Woo J, Romero-Ortuno R, Walston JD. Management of frailty: opportunities, challenges, and future directions. Lancet. 2019;394(10206):1376–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31785-4.
Veronese N, Custodero C, Cella A, Demurtas J, Zora S, Maggi S, et al. Prevalence of multidimensional frailty and pre-frailty in older people in different settings: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ageing Res Rev. 2021;72:101498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2021.101498.
Fried LP, Tangen CM, Walston J, Newman AB, Hirsch C, Gottdiener J, et al. Frailty in older adults: evidence for a phenotype. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2001;56(3):M146–M56. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/56.3.m146.
Kumar R, Mohan N, Upadhyay AD, Singh AP, Sahu V, Dwivedi S, et al. Identification of serum sirtuins as novel noninvasive protein markers for frailty. Aging Cell. 2014;13(6):975–80. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12260.
Ijaz N, Buta B, Xue Q-L, Mohess DT, Bushan A, Tran H, et al. Interventions for Frailty Among Older Adults With Cardiovascular Disease: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022;79(5):482–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2021.11.029.
Tasselli L, Zheng W, Chua KF. SIRT6: Novel Mechanisms and Links to Aging and Disease. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2017;28(3):168–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2016.10.002.
Yang X, Feng J, Liang W, Zhu Z, Chen Z, Hu J, et al. Roles of SIRT6 in kidney disease: a novel therapeutic target. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021;79(1):53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-021-04061-9.
Chang AR, Ferrer CM, Mostoslavsky R. SIRT6, a Mammalian Deacylase with Multitasking Abilities. Physiol Rev. 2020;100(1):145–69. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00030.2018.
Guo Z, Li P, Ge J, Li H. SIRT6 in Aging, Metabolism, Inflammation and Cardiovascular Diseases. Aging Dis. 2022;13(6):1787–822. https://doi.org/10.14336/AD.2022.0413.
Mostoslavsky R, Chua KF, Lombard DB, Pang WW, Fischer MR, Gellon L, et al. Genomic instability and aging-like phenotype in the absence of mammalian SIRT6. Cell. 2006;124(2):315–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2005.11.044.
Roichman A, Elhanati S, Aon MA, Abramovich I, Di Francesco A, Shahar Y, et al. Restoration of energy homeostasis by SIRT6 extends healthy lifespan. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):3208. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23545-7.
Vitiello M, Zullo A, Servillo L, Mancini FP, Borriello A, Giovane A, et al. Multiple pathways of SIRT6 at the crossroads in the control of longevity, cancer, and cardiovascular diseases. Ageing Res Rev. 2017;35:301–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2016.10.008.
Santos-Barriopedro I, Bosch-Presegué L, Marazuela-Duque A, de la Torre C, Colomer C, Vazquez BN, et al. SIRT6-dependent cysteine monoubiquitination in the PRE-SET domain of Suv39h1 regulates the NF-ϰB pathway. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):101. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-02586-x.
Xiao C, Wang R-H, Lahusen TJ, Park O, Bertola A, Maruyama T, et al. Progression of chronic liver inflammation and fibrosis driven by activation of c-JUN signaling in Sirt6 mutant mice. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(50):41903–13. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.415182.
Liu G, Chen H, Liu H, Zhang W, Zhou J. Emerging roles of SIRT6 in human diseases and its modulators. Med Res Rev. 2021;41(2):1089–137. https://doi.org/10.1002/med.21753.
Korotkov A, Seluanov A, Gorbunova V. Sirtuin 6: linking longevity with genome and epigenome stability. Trends Cell Biol. 2021;31(12). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2021.06.009.
Chen J, Xie J-J, Jin M-Y, Gu Y-T, Wu C-C, Guo W-J, et al. Sirt6 overexpression suppresses senescence and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells by inducing autophagy in a model of intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(2):56. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-017-0085-5.
Angulo J, El Assar M, Álvarez-Bustos A, Rodríguez-Mañas L. Physical activity and exercise: Strategies to manage frailty. Redox Biol. 2020;35:101513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2020.101513.
Zhao Y, Bai X, Jia X, Lu Y, Cheng W, Shu M, et al. Age-related changes of human serum Sirtuin6 in. adults. BMC Geriatr. 2021;21(1):452. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-021-02399-0.
Bian C, Gao J, Wang Y, Li J, Luan Z, Lu H, et al. Association of SIRT6 circulating levels with urinary and glycometabolic markers in pre-diabetes and diabetes. Acta Diabetol. 2021;58(11):1551–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-021-01759-x.
Pradhan R, Singh AK, Kumar P, Bajpai S, Pathak M, Chatterjee P, et al. Blood Circulatory Level of Seven Sirtuins in Alzheimer’s Disease: Potent Biomarker Based on Translational Research. Mol Neurobiol. 2022;59(3):1440–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-021-02671-9.
Yan Z, Wang X, Liu YS, Xing XW, Zhang XG, Lu QH. Decreased serum SIRT6 as a novel predictor of coronary artery disease. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021;25(21):6660–9. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202111_27110.
Liberale L, Ministrini S, Arnold M, Puspitasari YM, Pokorny T, Beer G, et al. Serum circulating sirtuin 6 as a novel predictor of mortality after acute ischemic stroke. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):20513. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-23211-y.
Hooshmand-Moghadam B, Eskandari M, Golestani F, Rezae S, Mahmoudi N, Gaeini AA. The effect of 12-week resistance exercise training on serum levels of cellular aging process parameters in elderly men. Exp Gerontol. 2020;141:111090. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2020.111090.
Bétry C, Meugnier E, Pflieger M, Grenet G, Hercberg S, Galan P, et al. High expression of CPT1b in skeletal muscle in metabolically healthy older subjects. Diabetes Metab. 2019;45(2):152–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabet.2018.01.018.
Song M-Y, Han CY, Moon YJ, Lee JH, Bae EJ, Park B-H. Sirt6 reprograms myofibers to oxidative type through CREB-dependent Sox6 suppression. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):1808. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-29472-5.
Clegg A, Young J, Iliffe S, Rikkert MO, Rockwood K. Frailty in elderly people. Lancet. 2013;381(9868):752–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(12)62167-9.
Taylor JA, Greenhaff PL, Bartlett DB, Jackson TA, Duggal NA, Lord JM. Multisystem physiological perspective of human frailty and its modulation by physical activity. Physiol Rev. 2023;103(2):1137–91. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00037.2021.
Mishra S, Cosentino C, Tamta AK, Khan D, Srinivasan S, Ravi V, et al. Sirtuin 6 inhibition protects against glucocorticoid-induced skeletal muscle atrophy by regulating IGF/PI3K/AKT signaling. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):5415. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-32905-w.
Cui X, Yao L, Yang X, Gao Y, Fang F, Zhang J, et al. SIRT6 regulates metabolic homeostasis in skeletal muscle through activation of AMPK. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2017;313(4):E493–E505. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00122.2017.
Wu X, Liu H, Brooks A, Xu S, Luo J, Steiner R, et al. SIRT6 Mitigates Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction in Diabetes. Circ Res. 2022;131(11):926–43. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.318988.
Saiyang X, Deng W, Qizhu T. Sirtuin 6: A potential therapeutic target for cardiovascular diseases. Pharmacol Res. 2021;163:105214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105214.
Zhang X-Y, Li W, Zhang J-R, Li C-Y, Zhang J, Lv X-J. Roles of sirtuin family members in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir Res. 2022;23(1):66. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-022-01986-y.
He T, Shang J, Gao C, Guan X, Chen Y, Zhu L, et al. A novel SIRT6 activator ameliorates neuroinflammation and ischemic brain injury via EZH2/FOXC1 axis. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021;11(3):708–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2020.11.002.
Song M-Y, Yi F, Xiao H, Yin J, Huang Q, Xia J, et al. Energy restriction induced SIRT6 inhibits microglia activation and promotes angiogenesis in cerebral ischemia via transcriptional inhibition of TXNIP. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(5):449. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-022-04866-x.
Li Y, Jin J, Wang Y. SIRT6 Widely Regulates Aging, Immunity, and Cancer. Front Oncol. 2022;12:861334. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.861334.
Koo J-H, Jang H-Y, Lee Y, Moon YJ, Bae EJ, Yun S-K, et al. Myeloid cell-specific sirtuin 6 deficiency delays wound healing in mice by modulating inflammation and macrophage phenotypes. Exp Mol Med. 2019;51(4). https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-019-0248-9.
Lappas M. Anti-inflammatory properties of sirtuin 6 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Mediators Inflamm. 2012;2012:597514. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/597514.
Qin Y, Cao L, Hu L. Sirtuin 6 mitigated LPS-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cells inflammatory responses through modulating nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(7):11305–17. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28407.
He Y, Yang G, Yao F, Xian Y, Wang G, Chen L, et al. Sitagliptin inhibits vascular inflammation via the SIRT6-dependent signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;75:105805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105805.
Kim HG, Huang M, Xin Y, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Wang G, et al. The epigenetic regulator SIRT6 protects the liver from alcohol-induced tissue injury by reducing oxidative stress in mice. J Hepatol. 2019;71(5):960–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2019.06.019.
Zhou Y, Fan X, Jiao T, Li W, Chen P, Jiang Y, et al. SIRT6 as a key event linking P53 and NRF2 counteracts APAP-induced hepatotoxicity through inhibiting oxidative stress and promoting hepatocyte proliferation. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021;11(1):89–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2020.06.016.
Acknowledgments: Study concept and design: ZX, MZ; Data curation and analysis: MZ, XY Writing - original draft: MZ; Writing - review, and editing: ZX, MZ, XY, YH, ZW. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
Funding: This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFC2002000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement: The research protocol was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Liyuan Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology (IRB ID: [2022] IEC (RYJ010)). All the participants gave written informed consent.
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, M., Yang, X., Huang, Y. et al. Serum SIRT6 Levels Are Associated with Frailty in Older Adults. J Nutr Health Aging 27, 719–725 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-023-1969-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-023-1969-y