Abstract
Objectives
Changes in the oral cavity can reflect other changes throughout the body. This study aimed to investigate the association of dental caries with muscle mass, muscle strength, and sarcopenia, and also to describe the microbial diversity, composition, and community structure of severe dental caries and sarcopenia.
Design
Cross-sectional study based on a Chinese population aged from 50 to 85 years.
Setting
Communities from Lanxi City, Zhejiang Province, China.
Participants
A total of 1,442 participants aged from 50 to 85 years from a general community (62.8% women; median age 61.0 [interquartile range: 55.0, 68.0]).
Measurements
Dental caries was assessed by the decayed, missing, and filled teeth (DMFT) index. Sarcopenia was defined as the presence of both low muscle mass (assessed by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry scanning) and low muscle strength (assessed by handgrip strength). Multivariate logistic regression models were used to analyze the association of dental caries with muscle mass, muscle strength, and sarcopenia. Fecal samples underwent 16S rRNA profiling to evaluate the diversity and composition of the gut microbiota in patients with severe dental caries and/or sarcopenia.
Results
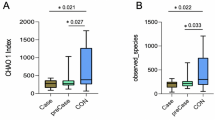
In the fully adjusted logistic models, dental caries was positively associated with low muscle strength (DMFT ≥ 7: OR, 1.61; 95% CI, 1.25–2.06), and sarcopenia (DMFT ≥ 7: OR, 1.51; 95% CI, 1.01–2.26), but not low muscle mass. Severe dental caries was positively associated with higher alpha-diversity indices (richness, chao1, and ACE, all p < 0.05) and associated with beta-diversity based on Bray-Curtis distance (p = 0.006). The severe dental caries group and the sarcopenia group overlapped with 11 depleted and 13 enriched genera.
Conclusion
Dental caries was positively associated with low muscle strength and sarcopenia but not muscle mass, and this association was more pronounced in male individuals. Significant differences were observed in gut microbiota composition both in severe dental caries and sarcopenia, and there was an overlap of the genera features. Future longitudinal studies are needed to clarify causal relationships.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Sayer AA. Sarcopenia. Lancet. 2019;393(10191):2636–2646. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31138-9.
Chen LK, Woo J, Assantachai P, Auyeung TW, Chou MY, Iijima K, Jang HC, Kang L, Kim M, Kim S, et al. Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 Consensus Update on Sarcopenia Diagnosis and Treatment. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2020;21(3):300–307. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2019.12.012.
Gao L, Xu T, Huang G, Jiang S, Gu Y, Chen F. Oral microbiomes: more and more importance in oral cavity and whole body. Protein Cell. 2018;9(5):488–500. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-018-0548-1.
Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Bahat G, Bauer J, Boirie Y, Bruyere O, Cederholm T, Cooper C, Landi F, Rolland Y, Sayer AA, et al. Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing. 2019;48(1):16–31. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afy169.
Raphael C. Oral Health and Aging. Am J Public Health. 2017;107(S1):S44–S45. doi: https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.2017.303835.
Peres MA, Macpherson L, Weyant RJ, Daly B, Venturelli R, Mathur MR, Listl S, Celeste RK, Guarnizo-Herreno CC, Kearns C, et al. Oral diseases: a global public health challenge. Lancet. 2019;394(10194):249–260. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31146-8.
Selwitz RH, Ismail AI, Pitts NB. Dental caries. Lancet. 2007;369(9555):51–59. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60031-2.
Frencken JE, Sharma P, Stenhouse L, Green D, Laverty D, Dietrich T. Global epidemiology of dental caries and severe periodontitis — a comprehensive review. J Clin Periodontol. 2017;44 Suppl 18:S94–S105. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.12677.
Eremenko M, Pink C, Biffar R, Schmidt CO, Ittermann T, Kocher T, Meisel P. Cross-sectional association between physical strength, obesity, periodontitis and number of teeth in a general population. J Clin Periodontol. 2016;43(5):401–407. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.12531.
Shin HS. Handgrip strength and the number of teeth among Korean population. J Periodontol. 2019;90(1):90–97. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/JPER.18-0242.
Yun J, Lee Y. Association between oral health status and handgrip strength in older Korean adults. Eur Geriatr Med. 2020;11(3):459–464. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41999-020-00318-x.
Murakami M, Hirano H, Watanabe Y, Sakai K, Kim H, Katakura A. Relationship between chewing ability and sarcopenia in Japanese community-dwelling older adults. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2015;15(8):1007–1012. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/ggi.12399.
Inui A, Takahashi I, Sawada K, Naoki A, Oyama T, Tamura Y, Osanai T, Satake A, Nakaji S, Kobayashi W. Teeth and physical fitness in a community-dwelling 40 to 79-year-old Japanese population. Clin Interv Aging. 2016;11:873–878. doi: https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S108498.
Zhou Z, Gu Y, Zhang Q, Liu L, Wu H, Meng G, Bao X, Zhang S, Sun S, Wang X, et al. Association between tooth loss and handgrip strength in a general adult population. Plos One. 2020;15(7):e236010. doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0236010.
Daboul A, Schwahn C, Bulow R, Kiliaridis S, Kocher T, Klinke T, Mundt T, Mourad S, Volzke H, Habes M, et al. Influence of Age and Tooth Loss on Masticatory Muscles Characteristics: A Population Based MR Imaging Study. J Nutr Health Aging. 2018;22(7):829–836. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-018-1029-1.
Yamaguchi K, Tohara H, Hara K, Nakane A, Yoshimi K, Nakagawa K, Minakuchi S. Factors associated with masseter muscle quality assessed from ultrasonography in community-dwelling elderly individuals: A cross-sectional study. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2019;82:128–132. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archger.2019.02.003.
Hamalainen P, Rantanen T, Keskinen M, Meurman JH. Oral health status and change in handgrip strength over a 5-year period in 80-year-old people. Gerodontology. 2004;21(3):155–160. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1741-2358.2004.00022.x.
Paksoy T, Ustaoglu G, Peker K. Association of socio-demographic, behavioral, and comorbidity-related factors with severity of periodontitis in Turkish patients. Aging Male. 2020;23(3):232–241. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/13685538.2020.1748002.
Leite MA, de Mattia TM, Kakihata C, Bortolini BM, de Carli RP, Bertolini G, Brancalhao R, Ribeiro L, Nassar CA, Nassar PO. Experimental Periodontitis in the Potentialization of the Effects of Immobilism in the Skeletal Striated Muscle. Inflammation. 2017;40(6):2000–2011. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-017-0640-3.
Delzenne NM, Cani PD. Interaction between obesity and the gut microbiota: relevance in nutrition. Annu Rev Nutr. 2011;31:15–31. doi: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurevnutr-072610-145146.
Krautkramer KA, Fan J, Backhed F. Gut microbial metabolites as multi-kingdom intermediates. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2021;19(2):77–94. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-020-0438-4.
Picca A, Fanelli F, Calvani R, Mule G, Pesce V, Sisto A, Pantanelli C, Bernabei R, Landi F, Marzetti E. Gut Dysbiosis and Muscle Aging: Searching for Novel Targets against Sarcopenia. Mediators Inflamm. 2018;2018:7026198. doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7026198.
Ticinesi A, Nouvenne A, Cerundolo N, Catania P, Prati B, Tana C, Meschi T. Gut Microbiota, Muscle Mass and Function in Aging: A Focus on Physical Frailty and Sarcopenia. Nutrients. 2019;11(7). doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11071633.
Ni Y, Yang X, Zheng L, Wang Z, Wu L, Jiang J, Yang T, Ma L, Fu Z. Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium Improves Physiological Function and Cognitive Ability in Aged Mice by the Regulation of Gut Microbiota. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2019;63(22):e1900603. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201900603.
Buigues C, Fernandez-Garrido J, Pruimboom L, Hoogland AJ, Navarro-Martinez R, Martinez-Martinez M, Verdejo Y, Mascaros MC, Peris C, Cauli O. Effect of a Prebiotic Formulation on Frailty Syndrome: A Randomized, Double-Blind Clinical Trial. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(6). doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060932.
Xu AA, Hoffman K, Gurwara S, White DL, Kanwal F, El-Serag HB, Petrosino JF, Jiao L. Oral Health and the Altered Colonic Mucosa-Associated Gut Microbiota. Dig Dis Sci. 2021;66(9):2981–2991. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-020-06612-9.
Li B, Ge Y, Cheng L, Zeng B, Yu J, Peng X, Zhao J, Li W, Ren B, Li M, et al. Oral bacteria colonize and compete with gut microbiota in gnotobiotic mice. Int J Oral Sci. 2019;11(1):10. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41368-018-0043-9.
Wei C, Ye S, Ru Y, Gan D, Zheng W, Huang C, Chen L, Gao P, Li J, Yang M, et al. Cohort profile: the Lanxi Cohort study on obesity and obesity-related non-communicable diseases in China. Bmj Open. 2019;9(5):e25257. doi: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2018-025257.
Chen LK, Liu LK, Woo J, Assantachai P, Auyeung TW, Bahyah KS, Chou MY, Chen LY, Hsu PS, Krairit O, et al. Sarcopenia in Asia: consensus report of the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2014;15(2):95–101. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2013.11.025.
Lexell J, Taylor CC, Sjostrom M. What is the cause of the ageing atrophy? Total number, size and proportion of different fiber types studied in whole vastus lateralis muscle from 15- to 83-year-old men. J Neurol Sci. 1988;84(2–3):275–294. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-510x(88)90132-3.
Miao Z, Lin JS, Mao Y, Chen GD, Zeng FF, Dong HL, Jiang Z, Wang J, Xiao C, Shuai M, et al. Erythrocyte n-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids, Gut Microbiota, and Incident Type 2 Diabetes: A Prospective Cohort Study. Diabetes Care. 2020;43(10):2435–2443. doi: https://doi.org/10.2337/dc20-0631.
Yeung CA: Book review: Oral health surveys: Basic methods, 5th edition. ‘Edited. London, Nature Publishing Group;2014. pp. 333.
Wright DR, Glanz K, Colburn T, Robson SM, Saelens BE. The accuracy of parent-reported height and weight for 6–12 year old U.S. children. Bmc Pediatr. 2018;18(1):52. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-018-1042-x.
Cleland C, Ferguson S, Ellis G, Hunter RF. Validity of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) for assessing moderate-to-vigorous physical activity and sedentary behaviour of older adults in the United Kingdom. Bmc Med Res Methodol. 2018;18(1):176. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-018-0642-3.
Hsing JC, Nguyen MH, Yang B, Min Y, Han SS, Pung E, Winter SJ, Zhao X, Gan D, Hsing AW, et al. Associations Between Body Fat, Muscle Mass, and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Population-Based Study. Hepatol Commun. 2019;3(8):1061–1072. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/hep4.1392.
Gan D, Wang L, Jia M, Ru Y, Ma Y, Zheng W, Zhao X, Yang F, Wang T, Mu Y, et al. Low muscle mass and low muscle strength associate with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Nutr. 2020;39(4):1124–1130. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2019.04.023.
Alberti G ZPSJ. 2020-07-29. Internet: https://www.idf.org/component/attachments/attachments.html?id=705&task=download (accessed 17 Nov 2021).
Myers GL, Christenson RH, Cushman M, Ballantyne CM, Cooper GR, Pfeiffer CM, Grundy SM, Labarthe DR, Levy D, Rifai N, et al. National Academy of Clinical Biochemistry Laboratory Medicine Practice guidelines: emerging biomarkers for primary prevention of cardiovascular disease. Clin Chem. 2009;55(2):378–384. doi: https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2008.115899.
Liu YX, Qin Y, Chen T, Lu M, Qian X, Guo X, Bai Y. A practical guide to amplicon and metagenomic analysis of microbiome data. Protein Cell. 2021;12(5):315–330. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-020-00724-8.
Sabharwal A, Stellrecht E, Scannapieco FA. Associations between dental caries and systemic diseases: a scoping review. Bmc Oral Health. 2021;21(1):472. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12903-021-01803-w.
McLean RR, Mangano KM, Hannan MT, Kiel DP, Sahni S. Dietary Protein Intake Is Protective Against Loss of Grip Strength Among Older Adults in the Framingham Offspring Cohort. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2016;71(3):356–361. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glv184.
Bano G, Trevisan C, Carraro S, Solmi M, Luchini C, Stubbs B, Manzato E, Sergi G, Veronese N. Inflammation and sarcopenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Maturitas. 2017;96:10–15. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.maturitas.2016.11.006.
Wong JM, de Souza R, Kendall CW, Emam A, Jenkins DJ. Colonic health: fermentation and short chain fatty acids. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2006;40(3):235–243. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/00004836-200603000-00015.
St LR, O’Brien LM, Ahmad ST. Sodium butyrate improves locomotor impairment and early mortality in a rotenone-induced Drosophila model of Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience. 2013;246:382–390. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.04.037.
Agnello M, Marques J, Cen L, Mittermuller B, Huang A, Chaichanasakul TN, Shi W, He X, Schroth RJ. Microbiome Associated with Severe Caries in Canadian First Nations Children. J Dent Res. 2017;96(12):1378–1385. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034517718819.
Xu L, Chen X, Wang Y, Jiang W, Wang S, Ling Z, Chen H. Dynamic Alterations in Salivary Microbiota Related to Dental Caries and Age in Preschool Children With Deciduous Dentition: A 2-Year Follow-Up Study. Front Physiol. 2018;9:342. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.00342.
Lira-Junior R, Akerman S, Klinge B, Bostrom EA, Gustafsson A. Salivary microbial profiles in relation to age, periodontal, and systemic diseases. Plos One. 2018;13(3):e189374. doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0189374.
Watanabe K, Katagiri S, Takahashi H, Sasaki N, Maekawa S, Komazaki R, Hatasa M, Kitajima Y, Maruyama Y, Shiba T, et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis impairs glucose uptake in skeletal muscle associated with altering gut microbiota. Faseb J. 2021;35(2):e21171. doi: https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.202001158R.
Margiotta E, Caldiroli L, Callegari ML, Miragoli F, Zanoni F, Armelloni S, Rizzo V, Messa P, Vettoretti S. Association of Sarcopenia and Gut Microbiota Composition in Older Patients with Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease, Investigation of the Interactions with Uremic Toxins, Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. Toxins (Basel). 2021;13(7). doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13070472.
Marzetti E, Calvani R, Tosato M, Cesari M, Di Bari M, Cherubini A, Collamati A, D’Angelo E, Pahor M, Bernabei R, et al. Sarcopenia: an overview. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2017;29(1):11–17. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-016-0704-5.
Clark BC, Manini TM. Sarcopenia =/= dynapenia. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2008;63(8):829–834. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/63.8.829.
Goodpaster BH, Park SW, Harris TB, Kritchevsky SB, Nevitt M, Schwartz AV, Simonsick EM, Tylavsky FA, Visser M, Newman AB. The loss of skeletal muscle strength, mass, and quality in older adults: the health, aging and body composition study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2006;61(10):1059–1064. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/61.10.1059.
Liu FT, Lin HS. Effect of the contraceptive steroids norethynodrel and mestranol on dental caries activity in young adult female rats. J Dent Res. 1973;52(4):753–757. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/00220345730520041901.
Lukacs JR, Largaespada LL. Explaining sex differences in dental caries prevalence: saliva, hormones, and “life-history” etiologies. Am J Hum Biol. 2006;18(4):540–555. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/ajhb.20530.
DELMAN LA. Effect of gonadectomy on dental caries: review of the literature. J Am Dent Assoc. 1955;51(2):155–158. doi: https://doi.org/10.14219/jada.archive.1955.0175.
Serra C, Tangherlini F, Rudy S, Lee D, Toraldo G, Sandor NL, Zhang A, Jasuja R, Bhasin S. Testosterone improves the regeneration of old and young mouse skeletal muscle. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2013;68(1):17–26. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/gls083.
Dubois V, Laurent M, Boonen S, Vanderschueren D, Claessens F. Androgens and skeletal muscle: cellular and molecular action mechanisms underlying the anabolic actions. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012;69(10):1651–1667. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-011-0883-3.
Kitajima Y, Ono Y. Estrogens maintain skeletal muscle and satellite cell functions. J Endocrinol. 2016;229(3):267–275. doi: https://doi.org/10.1530/JOE-15-0476.
Ikeda K, Horie-Inoue K, Inoue S. Functions of estrogen and estrogen receptor signaling on skeletal muscle. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2019;191:105375. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2019.105375.
Hansen M. Female hormones: do they influence muscle and tendon protein metabolism? Proc Nutr Soc. 2018;77(1):32–41. doi: https://doi.org/10.1017/S0029665117001951.
Funding
Funding statement: This work was supported by the Cyrus Tang Foundation (419600-11102), Zhejiang University Education Foundation (100000-11320), Hsun K. Chou Fund of Zhejiang University Education Foundation (419600-11107), and the Key R&D Program of Zhejiang (2022C03060).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Author contributions: SKZ and YY designed the study and wrote the manuscript. YY, SLD, CCW, YFW, YWS, JHL, and NLW collected and analyzed the data. YY, YF, CCW, YFW, JHL, and LKS were involved in data interpretation, drafting the manuscript, and revising it critically. HMW and SKZ supervised the study. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical standards: This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the School of Public Health Zhejiang University (NO: ZGL201905-1) and was conducted in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2013.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Deng, S., Wang, C. et al. Association of Dental Caries with Muscle Mass, Muscle Strength, and Sarcopenia: A Community-Based Study. J Nutr Health Aging 27, 10–20 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-022-1875-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-022-1875-8