Abstract
Objective
Lingual strengthening exercises are established to improve lingual function, thereby oral swallowing. This study measured submental muscle activation during maximum isometric pressure (MIP) lingual tasks in healthy adults, tasks that are or can be adopted in lingual strengthening exercises. In addition, the effects of age and gender on submental muscle activation are examined.
Method
Forty-nine participants between the ages of 18 to 35 years and greater than 60 years were included in the study. Participants completed trials of intraoral MIP lingual elevation, protrusion, and depression, during which submental muscle activation was measured using surface electromyography (sEMG). Peak amplitude measures were normalized and log transformed, following which a three-way ANOVA was performed.
Results
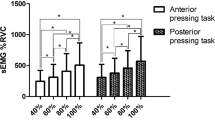
Peak amplitudes of submental muscle activation were highest during lingual MIP protrusion, followed by lingual depression, and were least during lingual elevation. No significant differences in peak amplitudes were observed between older and younger adults, but higher peak amplitudes were recorded in women.
Conclusion
The differential effects of lingual task, age, and gender on peak submental muscle activation are examined. The potential impact of incorporating tasks adopted in this study in lingual strengthening exercises to improve oral and pharyngeal swallowing is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ertekin C, Aydogdu I. Neurophysiology of swallowing. Clin Neurophysiol 2008;114(12): 2226–2244. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.10.012
Sella O, Jones RD, Huckabee ML. Age and gender effects on submental motor-evoked potentials. Age 2014;36(6):9735–9746. doi:10.1007/s11357-014-9735-z
Robbins JA, Levine R, Wood J, Roecker EB, Luschei E. Age effects on lingual pressure generation as a risk factor for dysphagia. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 1995;50(5): M257–M262. doi: 108.1093/gerona/50A.5.M257
Robbins J, Humpal NS, Banaszynski K, Hind J, Rogus-Pulia N. Age-related differences in pressures generated during isometric presses and swallows by healthy adults. Dysphagia 2016;31(1):90–96. doi: 10.1007/s00455-015-9662-x
Robbins JA. Oral strengthening and swallowing outcomes. Persp Swallowing A Swallowing Dis 2003;12(1):16–20. doi:10.1044/sasd12.1.16
Vaiman M, Eviatar E, Segal S. Surface electromyographic studies of swallowing in normal subjects: A review of 440 adults. Report 2. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2004;131(5):773–780. doi:10.1016/j.otohns.2004.03.014
Robin DA, Goel A, Somodi LB, Luschei, ES. Tongue strength and endurance relation to highly skilled movements. J Speech Lang Hear Res 1992;35(6):1239–1245. doi:10.1044/jshr.3506.1239
Nicosia MA, Hind JA, Roecker EB, Carnes M, Doyle J, Dengel GA, Robbins JA. Age effects on the temporal evolution of isometric and swallowing pressure. J Gerontol 2000;55A(11):M634–M640. doi:10.1093/gerona/55.11.M634
Logemann, JA, Pauloski BR, Rademaker AW, Colangelo LA, Kahrilas PJ, Smith CH. Temporal and biomechanical characteristics of oropharyngeal swallow in younger and older men. J Speech Lang Hear Res 2000;43:1264–1274. doi:1092-4388/00/4305-1264
Youmans SR, Stierwalt JAG. Measures of tongue function related to normal swallowing. Dysphagia 2006;21(2): 102–111. doi:10.1007/s00455-006-9013-z
Youmans SR, Youmans GL, Stierwalt JAG. Differences in tongue strength across age and gender: is there a diminished strength reserve? Dysphagia 2009;24:57–65. doi:10.1007/s00455-008-9171-2
Fei T, Polacco RC, Hori SE, Molfenter SM, Peladeau-Pigeon M, Tsang C, Steele CM. Age-related differences in tongue-palate pressures for strength and swallowing tasks. Dysphagia 2013;28(4):575–581. doi: 10.1007/s00455-013-9469-6
Vanderwegen J, Guns C, Van Nuffelen G, Elen R, De Bodt M. The influence of age, sex, bulb position, visual feedback, and the order of testing on maximum anterior and posterior tongue strength and endurance in healthy Belgian adults. Dysphagia 2013;28(2):159–166. doi:10.1044/1092-4388(2008/060)
Palmer PM, Jaffe DM, McCulloch TM, Finnegan EM, Van Daele DJ, Luschei ES. Quantitative contributions of the muscles of the tongue, floor-of-mouth, jaw, and velum to tongue-to-palate pressure generation. J Speech Lang Hear Res 2008;51(4):828–835. doi:10.1044/1092-4388(2008/060)
Wheeler-Hegland KM, Rosenbek JC, Sapienza CM. Submental sEMG and hyoid movement during Mendelsohn Maneuver, effortful swallow, and expiratory muscle strength training. J Speech Lang Hear Res 2008;51:1072–1087. doi:10.1044/1092-4388(2008/07-0016
Rogus-Pulia N, Rusche N, Hind JA, Zielinski J, Gangnon R, Safdar N, Robbins J. Effects of device-facilitated isometric progressive resistance oropharyngeal therapy on swallowing and health-related outcomes in older adults with dysphagia. J Am Geriatr Soc 2016;64(2):417–424. doi: 10.1111/jgs.13933
Steele CM. Bayley MT, Peladeau-Pigeon M, Nagy A, Namasivayam AM, Stokely SL, Wolkin T. A randomized trial comparing two tongue-pressure resistance training protocols for post-stroke dysphagia. Dysphagia 2016;31(3):452–461. doi:10.1007/s00455-016-9699-5
Clark HM, O’Brien K, Calleja A, Corrie SN. Effects of directional exercise on lingual strength. J Speech Lang Hear Res 2009;52(4):1034–1047. doi:10.1044/1092-4388(2009/08-0062)
Stepp C. Surface electromyography for speech swallowing systems: measurement, analysis, and interpretation. J Speech Lang Hear Res 2012;55(4):1232–1246. doi:10.1044/1092-4388(2011/11-0214)
Kay Elemetrics Corp. Swallowing signals lab model 7120B service manual. Lincoln Park, NJ: Kay Elemetrics, 2005
Lenius K, Carnaby-Mann G, Crary M. The relationship between lingual-palatal pressures and submental surface electromyographic signals. J Oral Rehabil 2009;36:118–123. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2842.2008.01921.x
Clark HM, Solomon NP. Age and sex differences in orofacial strength. Dysphagia 2012;27: 2–9. doi:10.1007/s00455-011-9328-2
Hughes T, Watts CR. Effects of 2 resistive exercises on electrophysiological measures of submandibular muscle activity. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2016;97(9):1552–1557. doi. org/10.1016/j.apmr.2015.11.004
Robbins JA, Kays SA, Gangnon RE, Hind JA, Hewitt AL, Gentry LR, Taylor AJ. The effects of lingual exercise in stroke patients with dysphagia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2007;88(2):150–158. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2006.11.002
Robbins JA, Gangnon RE, Theis SM, Kays SA, Hewitt AL, Hind JA. The effects of lingual exercise on swallowing in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc 2005;53(9):1483–1489. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2005.53467.x
Logemann JA, Pauloski BR, Rademaker AW, Kahrilas PJ. Oropharyngeal swallow in younger and older women: Videofluoroscopic analysis. J Speech Lang Hear Res 2002;45:434–445. doi:1092-4388/02/4503-0434
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oommen, E.R., Kim, Y. Submental Muscle Activation During Lingual Tasks in Healthy Adults. J Nutr Health Aging 22, 1133–1137 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-018-1084-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-018-1084-7