Abstract
Objectives
To examine associations of dietary variety with changes in lean mass and physical performance during a 4-year period in an elderly Japanese population. Design: Four-year prospective study.
Setting
The Hatoyama Cohort Study and Kusatsu Longitudinal Study, Japan.
Participants
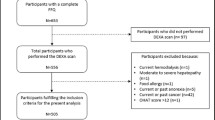
935 community-dwelling Japanese aged 65 years or older.
Measurements
Dietary variety was assessed using a 10-item food frequency questionnaire. Body composition was determined by multifrequency bioelectrical impedance analysis, and physical performance (grip strength and usual gait speed) was measured in surveys at baseline and 4 years later. Longitudinal analysis included only participants who were originally in the upper three quartiles of lean body mass, appendicular lean mass, grip strength, and usual gait speed. The outcome measures were decline in lean body mass, appendicular lean mass, grip strength, and usual gait speed, defined as a decrease to the lowest baseline quartile level at the 4-year follow-up survey. Associations of dietary variety with the outcome measures were examined by logistic regression analysis adjusted for potential confounders.
Results
In the fully adjusted model, the odds ratios for decline in grip strength and usual gait speed were 0.43 (95% confidence interval, 0.19–0.99) and 0.43 (confidence interval, 0.19–0.99), respectively, for participants in the highest category of dietary variety score as compared with those in the lowest category. Dietary variety was not significantly associated with changes in lean body mass or appendicular lean mass.
Conclusion
Among older adults, greater dietary variety may help maintain physical performance, such as grip strength and usual gait speed, but not lean mass.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Baeyens JP, Bauer JM, Boirie Y, Cederholm T, Landi F, Martin FC, Michel J-P, Rolland Y, et al. Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis: Report of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People. Age Ageing. 2010;39:412–23.
Tanimoto Y, Watanabe M, Sun W, Sugiura Y, Tsuda Y, Kimura M, Hayashida I, Kusabiraki T, Kono K. Association between sarcopenia and higher-level functional capacity in daily living in community-dwelling elderly subjects in Japan. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2012;55:e9–13.
Tanimoto Y, Watanabe M, Sun W, Tanimoto K, Shishikura K, Sugiura Y, Kusabiraki T, Kono K. Association of sarcopenia with functional decline in community-dwelling elderly subjects in Japan. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2013;13:958–63.
Tanimoto Y, Watanabe M, Sun W, Sugiura Y, Hayashida I, Kusabiraki T, Tamaki J. Sarcopenia and falls in community-dwelling elderly subjects in Japan: Defining sarcopenia according to criteria of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2014;59:295–9.
Denison HJ, Cooper C, Sayer AA, Robinson SM. Prevention and optimal management of sarcopenia: a review of combined exercise and nutrition interventions to improve muscle outcomes in older people. Clin Interv Aging. 2015;10:859–69.
Xu B, Houston DK, Locher JL, Ellison KJ, Gropper S, Buys DR, Zizza CA. Higher Healthy Eating Index-2005 scores are associated with better physical performance. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2012;67:93–9.
Xu B, Houston D, Locher JL, Zizza C. The association between Healthy Eating Index-2005 scores and disability among older Americans. Age Ageing. 2012;41:365–71.
Houston DK, Nicklas BJ, Ding J, Harris TB, Tylavsky FA, Newman AB, Lee JS, Sahyoun NR, Visser M, Kritchevsky SB. Dietary protein intake is associated with lean mass change in older, community-dwelling adults: the Health, Aging, and Body Composition (Health ABC) Study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008;87:150–5.
Robinson SM, Jameson KA, Batelaan SF, Martin HJ, Syddall HE, Dennison EM, Cooper C, Sayer AA. Diet and its relationship with grip strength in communitydwelling older men and women: the Hertfordshire cohort study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2008;56:84–90.
Cesari M, Pahor M, Bartali B, Cherubini A, Penninx BWJH, Williams GR, Atkinson H, Martin A, Guralnik JM, Ferrucci L. Antioxidants and physical performance in elderly persons: the Invecchiare in Chianti (InCHIANTI) study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004;79:289–94.
Shahar DR, Houston DK, Hue TF, Lee J-S, Sahyoun NR, Tylavsky FA, Geva D, Vardi H, Harris TB. Adherence to mediterranean diet and decline in walking speed over 8 years in community-dwelling older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2012;60:1881–8.
Beasley JM, Wertheim BC, LaCroix AZ, Prentice RL, Neuhouser ML, Tinker LF, Kritchevsky S, Shikany JM, Eaton C, et al. Biomarker-calibrated protein intake and physical function in the Women’s Health Initiative. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2013;61:1863–71.
Chan R, Leung J, Woo J, Kwok T. Associations of dietary protein intake on subsequent decline in muscle mass and physical functions over four years in ambulant older Chinese people. J Nutr Health Aging. 2014;18:171–7.
Scott D, Blizzard L, Fell J, Giles G, Jones G. Associations between dietary nutrient intake and muscle mass and strength in community-dwelling older adults: The Tasmanian older adult cohort study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2010;58:2129–34.
Milaneschi Y, Bandinelli S, Corsi AM, Lauretani F, Paolisso G, Dominguez LJ, Semba RD, Tanaka T, Abbatecola AM, et al. Mediterranean diet and mobility decline in older persons. Exp Gerontol. 2011;46:303–8.
Kim J, Lee Y, Kye S, Chung Y-S, Kim K-M. Association of vegetables and fruits consumption with sarcopenia in older adults: the Fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Age Ageing. 2015;44:96–102.
Radavelli-Bagatini S, Zhu K, Lewis JR, Dhaliwal SS, Prince RL. Association of dairy intake with body composition and physical function in older community-dwelling women. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2013;113:1669–74.
Yokoyama Y, Nishi M, Murayama H, Amano H, Taniguchi Y, Nofuji Y, Narita M, Matsuo E, Seino S, et al. Association of dietary variety with body composition and physical function in community-dwelling elderly Japanese. J Nutr Health Aging (in press).
Shinkai S, Yoshida H, Fujiwara Y, Amano H, Fukaya T, Ri S, Watanabe N, Watanabe S, Kumagai O, et al. A 10-year community intervention for disability prevention and its effect on healthy aging in Kusatsu town]. Nihon Koshu Eisei Zasshi. 2013;60:596–605 (in Japanese).
Murayama H, Nishi M, Shimizu Y, Kim M-J, Yoshida H, Amano H, Fujiwara Y, Shinkai S. The Hatoyama Cohort Study: Design and Profile of Participants at Baseline. J Epidemiol. 2012;22:551–8.
Kumagai S, Watanabe S, Shibata H, Amano H, Fujiwara Y, Shinkai S, Yoshida H, Suzuki T, Yukawa H, et al. Effects of dietary variety on declines in high-level functional capacity in elderly people living in a community. Nihon Koshu Eisei Zasshi. 2003;50:1117–24 (in Japanese).
Kwon J, Suzuki T, Kumagai S, Shinkai S, Yukawa H. Risk factors for dietary variety decline among Japanese elderly in a rural community: a 8-year follow-up study from TMIG-LISA. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2006;60:305–11.
Kimura M, Moriyasu A, Kumagai S, Furuna T, Akita S, Kimura S, Suzuki T. Community-based intervention to improve dietary habits and promote physical activity among older adults: a cluster randomized trial. BMC Geriatr. 2013;13:8.
Kim M, Kim H. Accuracy of segmental multi-frequency bioelectrical impedance analysis for assessing whole-body and appendicular fat mass and lean soft tissue mass in frail women aged 75 years and older. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2013;67:395–400.
Kim M, Shinkai S, Murayama H, Mori S. Comparison of segmental multifrequency bioelectrical impedance analysis with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry for the assessment of body composition in a community-dwelling older population. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2015;15:1013–22.
Bohannon RW. Hand-grip dynamometry predicts future outcomes in aging adults. J Geriatr Phys Ther. 2008;31:3–10.
Mijnarends DM, Meijers JMM, Halfens RJG, Ter Borg S, Luiking YC, Verlaan S, Schoberer D, Cruz Jentoft AJ, Van Loon LJC, Schols JMGA. Validity and Reliability of Tools to Measure Muscle Mass, Strength, and Physical Performance in Community-Dwelling Older People: A Systematic Review. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2013;14:170–8.
Guralnik JM, Ferrucci L, Pieper CF, Leveille SG, Markides KS, Ostir G V, Studenski S, Berkman LF, Wallace RB. Lower extremity function and subsequent disability: consistency across studies, predictive models, and value of gait speed alone compared with the short physical performance battery. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2000;55:M221–31.
Shinkai S, Watanabe S, Kumagai S, Fujiwara Y, Amano H, Yoshida H, Ishizaki T, Yukawa H, Suzuki T, Shibata H. Walking speed as a good predictor for the onset of functional dependence in a Japanese rural community population. Age Ageing. 2000;29:441–6.
Studenski S, Perera S, Patel K, Rosano C, Faulkner K, Inzitari M, Brach J, Chandler J, Cawthon P, et al. Gait speed and survival in older adults. JAMA. 2011;305:50–8.
Volpi E, Kobayashi H, Sheffield-Moore M, Mittendorfer B, Wolfe RR. Essential amino acids are primarily responsible for the amino acid stimulation of muscle protein anabolism in healthy elderly adults. Am J Clin Nutr. 2003;78:250–8.
Tieland M, van de Rest O, Dirks ML, van der Zwaluw N, Mensink M, van Loon LJC, de Groot LCPGM. Protein Supplementation Improves Physical Performance in Frail Elderly People: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2012;13:720–6.
Karelis AD, Messier V, Suppère C, Briand P, Rabasa-Lhoret R. Effect of cysteinerich whey protein (immunocal®) supplementation in combination with resistance training on muscle strength and lean body mass in non-frail elderly subjects: a randomized, double-blind controlled study. J Nutr Health Aging. 2015;19:531–6.
Clark BC, Manini TM. Sarcopenia =/= dynapenia. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2008;63:829–34.
Abbatecola AM, Cherubini A, Guralnik JM, Andres Lacueva C, Ruggiero C, Maggio M, Bandinelli S, Paolisso G, Ferrucci L. Plasma polyunsaturated fatty acids and agerelated physical performance decline. Rejuvenation Res. 2009;12:25–32.
Rodacki CL, Rodacki AL, Pereira G, Naliwaiko K, Coelho I, Pequito D, Fernandes LC. Fish-oil supplementation enhances the effects of strength training in elderly women. Am J Clin Nutr. 2012;95:428–36.
Cesari M, Pahor M, Lauretani F, Zamboni V, Bandinelli S, Bernabei R, Guralnik JM, Ferrucci L. Skeletal muscle and mortality results from the InCHIANTI study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2009;64:377–84.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yokoyama, Y., Nishi, M., Murayama, H. et al. Dietary variety and decline in lean mass and physical performance in community-dwelling older Japanese: A 4-year follow-up study. J Nutr Health Aging 21, 11–16 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-016-0726-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-016-0726-x