Abstract
Objectives
To determine the association between Mediterranean-Style Dietary Pattern Score and physical performance.
Design
Data analysis of a longitudinal study of a representative, age stratified, population sample.
Setting
The TREVISO LONGEVA (TRELONG) Study, in Treviso, Italy.
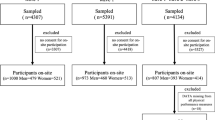
Participants
In 2010, 123 men and 181 women, age 77 years and over (mean age 86.3 ± 6.8 years).
Measurements
Performing a logistic regression in a multivariate analysis, hand grip strength and Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB) were tested in relation to Mediterranean-Style Dietary Pattern Score (MSDPS).
Results
The hand grip mean value was 10.9 kg (± 9.5) and the SPPB score was 6.3 (± 3.8). The MSDPS mean value in this study sample was 38.1/100 (± 8.1). A significant association (p=0.036) between a high adherence to the Mediterranean diet (fourth quartile) and higher performance lower limbs (SPPB>7) was found. No correlation was reported for the hand grip strength.
Conclusion
We found an association statistically significant between a high adherence to the Mediterranean diet and higher physical performance.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chan R, Chan D, Woo J. A cross sectional study to examine the association between dietary patterns and cognitive impairment in older Chinese people in Hong Kong. J Nutr Health Aging. 2013 Sep;17(9):757–65.
Sofi F, Cesari F, Abbate R, Gensini GF, Casini A. Adherence to Mediterranean diet and health status: meta-analysis. BMJ. 2008;337:a1344.
Roman B, Carta L, Martínez-González MA, Serra-Majem L. Effectiveness of the Mediterranean diet in the elderly. Clin Interv Aging. 2008;3(1):97–109.
Panagiotakos DB, Pitsavos C, Polychronopoulos E, Chrysohoou C, Zampelas A, Trichopoulou A. Can a Mediterranean diet moderate the development and clinical progression of coronary heart disease? A systematic review. Med Sci Monit Int Med J Exp Clin Res. 2004 Aug;10(8):RA193–8.
De Lorgeril M, Salen P, Martin JL, Monjaud I, Boucher P, Mamelle N. Mediterranean dietary pattern in a randomized trial: prolonged survival and possible reduced cancer rate. Arch Intern Med. 1998 Jun 8;158(11):1181–7.
Biesalski HK. Diabetes preventive components in the Mediterranean diet. Eur J Nutr. 2004 Mar;43 Suppl 1:I/26–30.
Psaltopoulou T, Naska A, Orfanos P, Trichopoulos D, Mountokalakis T, Trichopoulou A. Olive oil, the Mediterranean diet, and arterial blood pressure: the Greek European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004 Oct;80(4):1012–8.
Bondia-Pons I, Schröder H, Covas M-I, Castellote AI, Kaikkonen J, Poulsen HE, et al. Moderate consumption of olive oil by healthy European men reduces systolic blood pressure in non-Mediterranean participants. J Nutr. 2007 Jan;137(1):84–7.
Richard C, Couture P, Desroches S, Lamarche B. Effect of the Mediterranean diet with and without weight loss on markers of inflammation in men with metabolic syndrome. Obes Silver Spring Md. 2013 Jan;21(1):51–7.
Singh B, Parsaik AK, Mielke MM, Erwin PJ, Knopman DS, Petersen RC, et al. Association of mediterranean diet with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Alzheimers Dis JAD. 2014;39(2):271–82.
Sánchez-Villegas A, Delgado-Rodríguez M, Alonso A, Schlatter J, Lahortiga F, Serra Majem L, et al. Association of the Mediterranean dietary pattern with the incidence of depression: the Seguimiento Universidad de Navarra/University of Navarra follow-up (SUN) cohort. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2009 Oct;66(10):1090–8.
Mitrou PN, Kipnis V, Thiébaut ACM, Reedy J, Subar AF, Wirfält E, et al. Mediterranean dietary pattern and prediction of all-cause mortality in a US population: results from the NIH-AARP Diet and Health Study. Arch Intern Med. 2007 Dec 10;167(22):2461–8.
Trichopoulou A, Bamia C, Trichopoulos D. Mediterranean diet and survival among patients with coronary heart disease in Greece. Arch Intern Med. 2005 Apr 25;165(8):929–35.
Trichopoulou A, Vasilopoulou E. Mediterranean diet and longevity. Br J Nutr. 2000 Dec;84 Suppl 2:S205–9.
Knoops KTB, de Groot LCPGM, Kromhout D, Perrin A-E, Moreiras-Varela O, Menotti A, et al. Mediterranean diet, lifestyle factors, and 10-year mortality in elderly European men and women: the HALE project. JAMA. 2004 Sep 22;292(12):1433–9.
Keys A, Menotti A, Karvonen MJ, Aravanis C, Blackburn H, Buzina R, et al. The diet and 15-year death rate in the seven countries study. Am J Epidemiol. 1986 Dec;124(6):903–15.
St-Onge M-P. Relationship between body composition changes and changes in physical function and metabolic risk factors in aging. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2005 Sep;8(5):523–8.
Guralnik JM, Branch LG, Cummings SR, Curb JD. Physical performance measures in aging research. J Gerontol. 1989 Sep;44(5):M141–6.
Gallucci M, Ongaro F, Meggiolaro S, Antuono P, Gustafson DR, Forloni GL, et al. Factors related to disability: evidence from the “Treviso Longeva (TRELONG) study.” Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2011 Jun;52(3):309–16.
Guralnik J, Fried L, Simonsick E, Kasper J, Lafferty M. Women’s Health and Aging Study–health and social characteristics of olderwomenwith disability. 1995.
Guralnik JM, Ferrucci L, Pieper CF, Leveille SG, Markides KS, Ostir GV, et al. Lower extremity function and subsequent disability: consistency across studies, predictive models, and value of gait speed alone compared with the short physical performance battery. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2000 Apr;55(4):M221–31.
Fogel JF, Hyman RB, Rock B, Wolf-Klein G. Predictors of hospital length of stay and nursing home placement in an elderly medical population. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2000 Oct;1(5):202–10.
Guralnik JM, Simonsick EM, Ferrucci L, Glynn RJ, Berkman LF, Blazer DG, et al. A short physical performance battery assessing lower extremity function: association with self-reported disability and prediction of mortality and nursing home admission. J Gerontol. 1994 Mar;49(2):M85–94.
Studenski S, Perera S, Wallace D, Chandler JM, Duncan PW, Rooney E, et al. Physical performance measures in the clinical setting. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2003 Mar;51(3):314–22.
Inouye SK, Peduzzi PN, Robison JT, Hughes JS, Horwitz RI, Concato J. Importance of functional measures in predicting mortality among older hospitalized patients. JAMA. 1998 Apr 15;279(15):1187–93.
Gallucci M, Mazzuco S, Ongaro F, Di Giorgi E, Mecocci P, Cesari M, et al. Body mass index, lifestyles, physical performance and cognitive decline: the “Treviso Longeva (TRELONG)” study. J Nutr Health Aging. 2013 Apr;17(4):378–84.
Katz S, Ford AB, Moskowitz RW, Jackson BA, Jaffe MW. Studies of illness in the aged. The index of adl: a standardized measure of biological and psychosocial function. JAMA J Am Med Assoc. 1963 Sep 21;185:914–9.
Lawton MP, Brody EM. Assessment of older people: self-maintaining and instrumental activities of daily living. The Gerontologist. 1969;9(3):179–86.
Brach JS, VanSwearingen JM, Newman AB, Kriska AM. Identifying early decline of physical function in community-dwelling older women: performance-based and selfreport measures. Phys Ther. 2002 Apr;82(4):320–8.
Thomas DR, Marren K, Banks W, Morley J. Do objective measurements of physical function in ambulatory nursing home women improve assessment of functional status? J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2007 Sep;8(7):469–76.
Rantanen T, Guralnik JM, Foley D, Masaki K, Leveille S, Curb JD, et al. Midlife hand grip strength as a predictor of old age disability. JAMA. 1999 Feb 10;281(6):558–60.
Cesari M, Onder G, Zamboni V, Manini T, Shorr RI, Russo A, et al. Physical function and self-rated health status as predictors of mortality: results from longitudinal analysis in the ilSIRENTE study. BMC Geriatr. 2008;8:34.
Cesari M, Onder G, Russo A, Zamboni V, Barillaro C, Ferrucci L, et al. Comorbidity and physical function: results from the aging and longevity study in the Sirente geographic area (ilSIRENTE study). Gerontology. 2006;52(1):24–32.
Cesari M, Penninx BWJH, Pahor M, Lauretani F, Corsi AM, Rhys Williams G, et al. Inflammatory markers and physical performance in older persons: the InCHIANTI study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2004 Mar;59(3):242–8.
Syddall H, Cooper C, Martin F, Briggs R, Aihie Sayer A. Is grip strength a useful single marker of frailty? Age Ageing. 2003 Nov;32(6):650–6.
Gallucci M, Ongaro F, Bresolin F, Bernardi U, Salvato C, Minello A, et al. The Treviso Longeva (Trelong) study: a biomedical, demographic, economic and social investigation on people 70 years and over in a typical town of North-East of Italy. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2007;44 Suppl 1:173–92.
Massy-Westropp NM, Gill TK, Taylor AW, Bohannon RW, Hill CL. Hand Grip Strength: age and gender stratified normative data in a population-based study. BMC Res Notes. 2011 Apr 14;4:127.
Mathiowetz V. Comparison of Rolyan and Jamar dynamometers for measuring grip strength. Occup Ther Int. 2002;9(3):201–9.
Smidt N, van der Windt DA, Assendelft WJ, Mourits AJ, Devillé WL, de Winter AF, et al. Interobserver reproducibility of the assessment of severity of complaints, grip strength, and pressure pain threshold in patients with lateral epicondylitis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2002 Aug;83(8):1145–50.
Rumawas ME, Dwyer JT, McKeown NM, Meigs JB, Rogers G, Jacques PF. The development of the Mediterranean-style dietary pattern score and its application to the American diet in the Framingham Offspring Cohort. J Nutr. 2009 Jun;139(6):1150–6.
Willett WC, Sacks F, Trichopoulou A, Drescher G, Ferro-Luzzi A, Helsing E, et al. Mediterranean diet pyramid: a cultural model for healthy eating. Am J Clin Nutr. 1995 Jun;61(6 Suppl):1402S–1406S.
Khan AM. R-software: A Newer Tool in Epidemiological Data Analysis. Indian J Community Med Off Publ Indian Assoc Prev Soc Med. 2013 Jan;38(1):56–8.
Milaneschi Y, Bandinelli S, Corsi AM, Lauretani F, Paolisso G, Dominguez LJ, et al. Mediterranean diet and mobility decline in older persons. Exp Gerontol. 2011 Apr;46(4):303–8.
Shahar DR, Houston DK, Hue TF, Lee J-S, Sahyoun NR, Tylavsky FA, et al. Adherence to mediterranean diet and decline in walking speed over 8 years in community-dwelling older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2012 Oct;60(10):1881–8.
Bartali B, Frongillo EA, Bandinelli S, Lauretani F, Semba RD, Fried LP, et al. Low nutrient intake is an essential component of frailty in older persons. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2006 Jun;61(6):589–93.
Bartali B, Frongillo EA, Guralnik JM, Stipanuk MH, Allore HG, Cherubini A, et al. Serum micronutrient concentrations and decline in physical function among older persons. JAMA. 2008 Jan 23;299(3):308–15.
Cesari M, Pahor M, Bartali B, Cherubini A, Penninx BWJH, Williams GR, et al. Antioxidants and physical performance in elderly persons: the Invecchiare in Chianti (InCHIANTI) study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004 Feb;79(2):289–94.
Lauretani F, Semba RD, Bandinelli S, Dayhoff-Brannigan M, Giacomini V, Corsi AM, et al. Low plasma carotenoids and skeletal muscle strength decline over 6 years. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2008 Apr;63(4):376–83.
Lauretani F, Semba RD, Bandinelli S, Dayhoff-Brannigan M, Lauretani F, Corsi AM, et al. Carotenoids as protection against disability in older persons. Rejuvenation Res. 2008 Jun;11(3):557–63.
Semba RD, Varadhan R, Bartali B, Ferrucci L, Ricks MO, Blaum C, et al. Low serum carotenoids and development of severe walking disability among older women living in the community: the women’s health and aging study I. Age Ageing. 2007 Jan;36(1):62–7.
Mayne ST. Antioxidant nutrients and chronic disease: use of biomarkers of exposure and oxidative stress status in epidemiologic research. J Nutr. 2003 Mar;133 Suppl 3:933S–940S.
Esposito K, Marfella R, Ciotola M, Di Palo C, Giugliano F, Giugliano G, et al. Effect of a mediterranean-style diet on endothelial dysfunction and markers of vascular inflammation in the metabolic syndrome: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2004 Sep 22;292(12):1440–6.
Estruch R, Martínez-González MA, Corella D, Salas-Salvadó J, Ruiz-Gutiérrez V, Covas MI, et al. Effects of a Mediterranean-style diet on cardiovascular risk factors: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2006 Jul 4;145(1):1–11.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fougère, B., Mazzuco, S., Spagnolo, P. et al. Association between the Mediterranean-style dietary pattern score and physical performance: Results from TRELONG study. J Nutr Health Aging 20, 415–419 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-015-0588-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-015-0588-7