Abstract
Objective
The objective of this study was to identify the nutritional status of hospitalized elderly and verify if calf circumference can be a tool to monitor nutritional status in this population.
Methods
A total of 170 inpatients (79 men and 91 women) aged more than 60 years were assessed. Anthropometric and dietary assessments were done according to standard procedures. The software STATISTICA 6.0 was used for the statistical analysis. The confidence interval was set at 95% and significance level at 5% (p<0.05).
Results
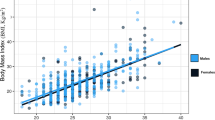
Body mass index assessment revealed a high rate of underweight patients (45.3%), and arm circumference and triceps skinfold revealed a high prevalence of depletion. Males had more lean mass according to the mid-arm muscle circumference (p=0.017) and mid-arm muscle area (p=0.01), and females presented higher triceps skinfold values (p<0.001). There was a positive correlation between calf circumference and Body Mass Index (p<0.001), arm circumference (p=0.001), triceps skinfold (p=0.001), mid-arm muscle circumference (p=0.001), and mid-arm muscle area (p=0.001).
Conclusion
This study found a positive correlation between calf circumference and nutritional status of assessed patients indicating that this measurement can be used as a complementary tool for monitoring the nutritional status of elderly inpatients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amaral ACS, Coeli CM, Costa MCE, Cardoso VS, Toledo ALA, Fernandes CR. Perfil de morbidade e de mortalidade de pacientes idosos hospitalizados. Cad Saude Publica 2004; 20(6): 1617–1626.
Campanella LCA, Farias MB, Breitkopf T, Almeida CB, Mendes L, Fenilli M, Silva AA, Relação entre padrão alimentar e estado nutricional de idosos hospitalizados. Rev Bras Nutr Clin 2007; 22(2):100–106
Vannucchi H, Cunha DF, Bernardes MM, Unamuno MDL. Avaliação dos níveis séricos das vitaminas A, E, C e B2, de carotenóides e zinco, em idosos hospitalizados. Rev Saude Publica 1994; 28(2): 121–126.
Sampaio LR. Avaliação nutricional e envelhecimento. Rev Nutr 2004; 17(4): 507–514.
Perissinotto E, Pisent C, Sergi G, Grigoletto F, Enzi G. Anthropometric measurements in the elderly: Age and gender differences. Br J Nutr 2002; 87:177–186.
Barbosa AR, Souza JMP, Lebrão ML, Laurenti R, Marucci MFN. Anthropometry of elderly residents in the city of São Paulo, Brazil. Cad. Saude Publica 2005; 21(6):1929–1938.
Hughes VA, Roubenoff R, Wood M, Frontera WR, Evans WJ, Fiatarone-Singh MA. Anthropometric assessment of 10-y changes in body composition in the elderly. Am J Clin Nutr 2004; 80:475–482.
Tavares EL, Anjos LA. Perfil antropométrico da população idosa brasileira. Resultados da Pesquisa Nacional sobre Saúde e Nutrição. Cad Saude Publica 1999; 15:759–768.
Kuczmarski MF, Kuczmarski RJ, Najjar M. Descriptive anthropometric reference data for older Americans. J Am Diet Assoc 2000; 100:59–66.
Velasquez-Alva MC, Irigoyen CME, Zepeda ZM, Sanchez MVM, Garcia JL, Cisneros MP, et al. Anthropometric measurements of sixty-year and older Mexican urban group. J Nutr Health Aging 2003; 7:1–5.
Santos JL, Albala C, Lera L, Garcia C, Arroyo P, Perez-Bravo F, et al. Anthropometric measurements in the elderly population of Santiago, Chile. Nutr 2004; 20:452–457.
Menezes TN, Marucci MFN. Antropometria de idosos residentes em instituições geriátricas, Fortaleza, CE. Rev Saude Publica 2005; 39(2):169–175.
Khadivzadeh T. Mid upper arm and calf circumferences as indicators of nutritional status in women of reproductive age. East Mediterr Health J 2002; 8(4–5):612–618.
World Health Organization. Physical status: the use and interpretation of anthropometry: report of a WHO Expert Committee. Geneva: WHO; 1995.
Frisancho AR. Anthropometric standards for the assessment of growth and nutritional status. Michigan: The University of Michigan Press; 1990.
Burr ML, Phillips MK. Anthropometric norms in the elderly. Br J Nutr 1984; 51:165–169.
Lipschitz DA. Screening for nutritional status in the elderly. Prim Care 1994; 22(1): 55–67.
Universidade Federal de São Paulo. Escola Paulista de Medicina. Programa de Apoio a Nutrição (NUTWIN) — programa de computador, versão 1.5. São Paulo: UNIFESP/ EPM; 2002.
Núcleo de Estudos e Pesquisa em Alimentos — NEPA. Tabela brasileira de composição de alimento — TACO (versão — 1). Campinas: NEPA-UNICAMP; 2004.
Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística. Tabela de Composição de Alimentos. 5. ed. Rio de Janeiro; 1999.
Philippi ST. Tabela de Composição de Alimentos: Suporte para decisão nutricional. 2a ed. São Paulo: Coronário; 2002.
Food and Nutrition Board. Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes for energy, carbohydrates, fiber, fat, fatty acids, cholesterol, protein and amino acids (macronutrients). Washington: National Academy Press; 2002.
Gaino NM, Leandro-Merhi VA, Oliveira MRM, Idosos hospitalizados: estado nutricional, dieta, doença e tempo de internação. Rev Bras Nutr Clin 2007; 22(4):273–279.
Anselmo MAC, Burini RC, Angeleli AYO, Mota NGS, Campana AO. Assessment of nutritional status of healthy middle class young and adult subjects living in Botucatu, State of S. Paulo, Brazil: energy and protein intakes, anthropometric and blood biochemical estimations and immunocompetence tests. Rev Saude Publica 1992;26: 46–53.
Batista-Filho M, Anete R. Nutritional transition in Brazil: geographic and temporal trends. Cad Saude Publica 2003; 19(5): 1445–1451
Waitzberg DL, Caiaffa WT, Correia MITD. Hospital malnutrition: the Brazilian national survey (IBRANUTRI): a study of 4,000 patients. Nutr 2001; 17(7): 573–580.
Tuck JP, Enid MH. A comparison of mid upper arm circumference, body mass index and weight loss as indices of undernutrition in acutely hospitalized patients. Clin Nutr 2003; 22(3):307–312.
Cuppari L. Avaliação nutricional. In: Cuppari L. Nutrição: nutrição clínica no adulto. São Paulo: Manole; 2002.
Duerksen DR, Yeo TA, Siemens JL, O’Connor MP. The validity and reproducibility of clinical assessment of nutritional status in the elderly. Nutr 2000; 16(9):740–744.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Portero-McLellan, K.C., Staudt, C., Silva, F.R.F. et al. The use of calf circumference measurement as an anthropometric tool to monitor nutritional status in elderly inpatients. J Nutr Health Aging 14, 266–270 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-010-0059-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-010-0059-0