Abstract
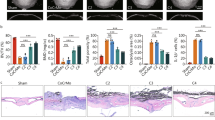
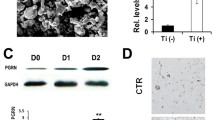
Wear particles generated from total joint replacements induce chronic osteolysis mediated by inflammatory upregulation, which leads to implant failure. Recent studies have suggested an important role of the gut microbiota in modulating the host’s metabolism and immune system, leading to alterations in bone mass. Following gavage with P. histicola, micro-CT and HE staining revealed that osteolysis was significantly reduced in titanium (Ti)-treated mice. Immunofluorescence analysis revealed an increased macrophage (M)1/M2 ratio in the guts of Ti-treated mice, which decreased when P. histicola was added. P. histicola was also found to upregulate the tight junction proteins ZO-1, occludin, claudin-1, and MUC2 in the gut, reduce the levels of inflammatory factors IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α, primarily in the ileum and colon, and decrease the expression of IL-1β and TNF-α and increase the level of IL-10 in the serum and cranium. Furthermore, P. histicola treatment resulted in a significant downregulation of CTX-1, RANKL, and RANKL/OPG. These findings demonstrate that P. histicola significantly mitigates osteolysis in Ti-treated mice by improving intestinal microbiota that repairs intestinal leakage and reduces systemic and local inflammation which in turn inhibits RANKL expression for bone resorption. P. histicola treatment may thus be therapeutically beneficial for particle-induced osteolysis.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The original contributions presented in the study are publicly available. This data can be found here: https://www.jianguoyun.com/p/DYtOBHgQh8LpCRizwN8EIAA.
References
Learmonth ID, Young C, Rorabeck C (2007) The operation of the century: total hip replacement. Lancet 370(9597):1508–1519
Menikheim SD, Lavik EB (2020) Self-healing biomaterials: the next generation is nano. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol 12(6):e1641
Zhao Z, Wang C, Xu Y, Wang X, Jia B, Yu T et al (2021) Effects of the local bone renin-angiotensin system on titanium-particle-induced periprosthetic osteolysis. Front Pharmacol 12:684375
Teitelbaum SL (2006) Osteoclasts; culprits in inflammatory osteolysis. Arthritis Res Ther 8(1):201
Almeida M, Laurent MR, Dubois V, Claessens F, O’Brien CA, Bouillon R et al (2017) Estrogens and androgens in skeletal physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol Rev 97(1):135–187
Boyce BF, Xing L (2007) Biology of RANK, RANKL, and osteoprotegerin. Arthritis Res Ther 9(Suppl 1):S1
Li Y, Lin S, Liu P, Huang J, Qiu J, Wen Z et al (2021) Carnosol suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis and attenuates titanium particles-induced osteolysis. J Cell Physiol 236(3):1950–1966
Zaiss MM, Jones RM, Schett G, Pacifici R (2019) The gut-bone axis: how bacterial metabolites bridge the distance. J Clin Invest 129(8):3018–3028
Bear TLK, Dalziel JE, Coad J, Roy NC, Butts CA, Gopal PK (2020) The role of the gut microbiota in dietary interventions for depression and anxiety. Adv Nutr 11(4):890–907
Jandhyala SM, Talukdar R, Subramanyam C, Vuyyuru H, Sasikala M, Reddy DN (2015) Role of the normal gut microbiota. World J Gastroenterol 21(29):8787–803.
Kim S, Jazwinski SM (2018) The gut microbiota and healthy aging: a mini-review. Gerontology 64(6):513–520
Scher JU, Ubeda C, Artacho A, Attur M, Isaac S, Reddy SM et al (2015) Decreased bacterial diversity characterizes the altered gut microbiota in patients with psoriatic arthritis, resembling dysbiosis in inflammatory bowel disease. Arthritis Rheumatol 67(1):128–139
Hu S, Xue Y, He J, Chen C, Sun J, Jin Y et al (2021) Irisin recouples osteogenesis and osteoclastogenesis to protect wear-particle-induced osteolysis by suppressing oxidative stress and RANKL production. Biomater Sci 9(17):5791–5801
Wang Z, Chen K, Wu C, Chen J, Pan H, Liu Y et al (2021) An emerging role of Prevotella histicola on estrogen deficiency-induced bone loss through the gut microbiota-bone axis in postmenopausal women and in ovariectomized mice. Am J Clin Nutr 114(4):1304–1313
Shah HN, Collins DM (1990) Prevotella, a new genus to include Bacteroides melaninogenicus and related species formerly classified in the genus Bacteroides. Int J Syst Bacteriol 40(2):205–208
Marietta EV, Murray JA, Luckey DH, Jeraldo PR, Lamba A, Patel R et al (2016) Suppression of inflammatory arthritis by human gut-derived Prevotella histicola in humanized mice. Arthritis Rheumatol 68(12):2878–2888
Semlitsch MF, Weber H, Streicher RM, Schon R (1992) Joint replacement components made of hot-forged and surface-treated Ti-6Al-7Nb alloy. Biomaterials 13(11):781–788
Eger M, Hiram-Bab S, Liron T, Sterer N, Carmi Y, Kohavi D et al (2018) Mechanism and prevention of titanium particle-induced inflammation and osteolysis. Front Immunol 9:2963
Qiu J, Peng P, Xin M, Wen Z, Chen Z, Lin S et al (2020) ZBTB20-mediated titanium particle-induced peri-implant osteolysis by promoting macrophage inflammatory responses. Biomater Sci 8(11):3147–3163
Lin T, Yan SG, Cai XZ, Ying ZM (2012) Bisphosphonates for periprosthetic bone loss after joint arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of 14 randomized controlled trials. Osteoporos Int 23(6):1823–1834
Prieto-Alhambra D, Javaid MK, Judge A, Maskell J, Cooper C, Arden NK et al (2015) Hormone replacement therapy and mid-term implant survival following knee or hip arthroplasty for osteoarthritis: a population-based cohort study. Ann Rheum Dis 74(3):557–563
Nystrom A, Kiritopoulos D, Ullmark G, Sorensen J, Petren-Mallmin M, Milbrink J et al (2020) Denosumab prevents early periprosthetic bone loss after uncemented total hip arthroplasty: results from a randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Bone Miner Res 35(2):239–247
Song S, Guo Y, Yang Y, Fu D (2022) Advances in pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies for osteoporosis. Pharmacol Ther 237:108168
Zhang YW, Cao MM, Li YJ, Dai GC, Lu PP, Zhang M et al (2022) The regulative effect and repercussion of probiotics and prebiotics on osteoporosis: involvement of brain-gut-bone axis. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 1–19
Wang Z, Xue K, Bai M, Deng Z, Gan J, Zhou G et al (2017) Probiotics protect mice from CoCrMo particles-induced osteolysis. Int J Nanomedicine 12:5387–5397
Ferrari SL (2018) Osteoporosis: romosozumab to rebuild the foundations of bone strength. Nat Rev Rheumatol 14(3):128
Zhu X, Zhang Y, Yang H, He F, Lin J (2020) Melatonin suppresses Ti-particle-induced inflammatory osteolysis via activation of the Nrf2/catalase signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 88:106847
Xu Q, Chen G, Xu H, Xia G, Zhu M, Zhan H et al (2021) Celastrol attenuates RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in vitro and reduces titanium particle-induced osteolysis and ovariectomy-induced bone loss in vivo. Front Pharmacol 12:682541
Ikebuchi Y, Aoki S, Honma M, Hayashi M, Sugamori Y, Khan M et al (2018) Coupling of bone resorption and formation by RANKL reverse signalling. Nature 561(7722):195–200
Infante M, Fabi A, Cognetti F, Gorini S, Caprio M, Fabbri A (2019) RANKL/RANK/OPG system beyond bone remodeling: involvement in breast cancer and clinical perspectives. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38(1):12
Mundy GR (2007) Osteoporosis and inflammation. Nutr Rev 65(12 Pt 2):S147–S151
Yamaguchi M, Fukasawa S (2021) Is inflammation a friend or foe for orthodontic treatment?: inflammation in orthodontically induced inflammatory root resorption and accelerating tooth movement. Int J Mol Sci 22(5)
Yokota K, Sato K, Miyazaki T, Aizaki Y, Tanaka S, Sekikawa M et al (2021) Characterization and function of tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6-induced osteoclasts in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 73(7):1145–1154
Hotchkiss KM, Reddy GB, Hyzy SL, Schwartz Z, Boyan BD, Olivares-Navarrete R (2016) Titanium surface characteristics, including topography and wettability, alter macrophage activation. Acta Biomater 31:425–434
Merino JJ, Cabana-Munoz ME, Toledano Gasca A, Garcimartin A, Benedi J, Camacho-Alonso F et al (2019) Elevated systemic L-kynurenine/L-tryptophan ratio and increased IL-1 beta and chemokine (CX3CL1, MCP-1) proinflammatory mediators in patients with long-term titanium dental implants. J Clin Med 8(9)
Wu Y, He F, Zhang C, Zhang Q, Su X, Zhu X et al (2021) Melatonin alleviates titanium nanoparticles induced osteolysis via activation of butyrate/GPR109A signaling pathway. J Nanobiotechnology 19(1):170
Cao X, Han Y, Gu M, Du H, Song M, Zhu X et al (2020) Foodborne titanium dioxide nanoparticles induce stronger adverse effects in obese mice than non-obese mice: gut microbiota dysbiosis, colonic inflammation, and proteome alterations. Small 16(36):e2001858
Wang Y, Ablimit N, Zhang Y, Li J, Wang X, Liu J et al (2021) Novel beta-mannanase/GLP-1 fusion peptide high effectively ameliorates obesity in a mouse model by modifying balance of gut microbiota. Int J Biol Macromol 191:753–763
Pittayanon R, Lau JT, Leontiadis GI, Tse F, Yuan Y, Surette M et al (2020) Differences in gut microbiota in patients with vs without inflammatory bowel diseases: a systematic review. Gastroenterology 158(4):930–946e1
Xie Y, Sun J, Hu C, Ruan B, Zhu B (2021) Oral microbiota is associated with immune recovery in human immunodeficiency virus-infected individuals. Front Microbiol 12:794746
Paharik AE, Horswill AR (2016) The Staphylococcal biofilm: adhesins, regulation, and host response. Microbiol Spectr 4(2)
Funding
This work was supported by the Basic Public Welfare Research Project of Zhejiang Natural Science Foundation of China (LGF19H070004), and the Wenzhou Science and Technology Bureau (Y20210418).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YL was responsible for the study concept and design. FH and HP collected the data. ZT analyzed and interpreted the data. LC and TL drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original contributions presented in the study are publicly available. This data can be found here: https://www.jianguoyun.com/p/DYtOBHgQh8LpCRizwN8EIAA
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, F., Pan, H., Tan, Z. et al. Prevotella histicola Prevented Particle-Induced Osteolysis via Gut Microbiota-Dependent Modulation of Inflammation in Ti-Treated Mice. Probiotics & Antimicro. Prot. 16, 383–393 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-023-10057-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-023-10057-7