Abstract
Proteus mirabilis is a common cause of infectious urolithiasis. The first stage in the formation of urinary stones is the crystallization of mineral salts in the urine induced by urease activity of this microorganism. Lactobacillus spp. are an important component of the human microbiota and in large quantities occur in foods. Regardless of their origin, those with probiotic properties are proposed as an alternative to antibiotic therapy in the treatment of urinary tract infections. The aim of the study was to check the effect of selected Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus brevis strains on crystallization caused by P. mirabilis in an in vitro experiment. It has been confirmed that selected Lactobacillus strains have antibacterial properties and colonize the urinary tract epithelium. During 24-h incubation of bacterial cultures, containing P. mirabilis and individual Lactobacillus strains, in synthetic urine, bacterial viability (CFU/mL), pH, and crystallization were determined. Crystallization was assessed quantitatively and qualitatively using AAS and XRD techniques as well as phase-contrast microscopy. It has been shown that in the presence of selected Lactobacillus strains, the culture pH increases faster, especially after 8 h of incubation, compared with the pure P. mirabilis culture. An increase in pH reduces the viability of P. mirabilis; however, in the presence of some lactobacilli, the uropathogen grows more intensively. The presence of Lactobacillus also affected crystallization by increasing its intensity, and the resulting crystals were larger in size. Tested L. plantarum and L. brevis strains could therefore accelerate the formation of urinary stones and development of infection.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Proteus spp. belong to the family Morganellaceae and occur both in the natural environment and as a part of the microflora of humans and animals [1, 36]. These bacilli which are found in water, soil, and manure play an important role in decomposing the organic matter of animal origin. However, first of all, they are known for their pathogenicity. Proteus spp., mainly Proteus mirabilis, play a particularly important role in urinary tract infections (UTI), primarily in long-term catheterized patients or patients with functional and structural abnormalities of the urinary tract. Proteus infections are known to be frequently persistent and difficult to treat and can lead to several complications such as bacteriuria, acute or chronic pyelonephritis, and urinary stone formation [5]. Urolithiasis resulting from urinary tract infections, called also infectious urinary stones, is distinguished by several features from metabolic urolithiasis. These stones are formed as a result of infection caused by urease-producing bacteria and made off struvite (magnesium ammonium phosphate) and apatite (calcium phosphate, mainly carbonate apatite) [10, 15]. They are not very common compared to other types of urinary stones (about 10–15% of all urinary calculi); however, they pose a serious health problem because of difficulties in treating and preventing relapse [30]. Among urease-producing uropathogens, P. mirabilis is most frequently isolated from such stones [32, 42]. The process of kidney stones formation consists of three main stages: supersaturation of urine salts, formation of crystals, and their retention in the urinary tract [8]. Each stage in the process of infectious stones formation is a result of the presence of bacteria in the urinary tract. Supersaturation and crystallization of mineral salts are connected with the urease activity. Urease hydrolyzes urea to ammonia and carbamate, which is unstable and forms carbonic acid and ammonia. An increase in urine pH and the reactions occurring as a result of urea hydrolysis cause an increase in the concentration of ions: NH4+, PO43−, and CO32−, which in the presence of calcium and magnesium ions in the urine leads to precipitation of phosphate salt and promotes crystallization of struvite (MgNH4PO4 × 6 H2O) and carbonate apatite (Ca10(PO4)6 × CO3) [34, 35]. Further stages are the growth of crystals and retention of their aggregates in the urinary tract in which bacterial extracellular polysaccharides (lipopolysaccharide; LPS, capsular polysaccharide; CPS) and various host factors released from the inflammatory response are involved [30, 39]. Treating patients with infectious urolithiasis is complex and includes stone removal (percutaneous nephrolithotomy “PCNL”; shockwave lithotripsy “SWL”), pathogen elimination, and relapse prevention [15]. Antibiotic therapy is carried out for up to 3 months to eliminate bacteria from the urinary tract. The antibiotic is chosen according to the sensitivity of bacteria, but in the case of this type of infection, it is recommended to administer of fluoroquinolones [10, 15, 20]. To prevent recurrence, the treatment is supplemented by acidifying the urine, administering bacterial urease inhibitors (e.g., acetohydroxamic acid), and an appropriate diet [10, 38]. Infectious urolithiasis is more common in people who are more likely to get urinary tract infections, due to urinary tract abnormalities or predisposition to this kind of infections. It is more common among women than men because of their higher susceptibility. On the other hand, among children, boys have struvite stones more often than girls [35]. It seems that the most important procedure in the treatment and prevention of infectious urolithiasis is combating both infection and crystallization. In the fight against infection, other alternative antibacterial agents are used in addition to antibiotics. Recently, much attention has been paid to the use of probiotic concepts or only their products in the treatment of patients with chronic urinary tract infections [16, 17]. The efficacy of probiotics against various uropathogens such as Proteus spp., K. pneumoniae, E. coli, or E. faecalis was confirmed by in vitro and in vivo studies [14, 17, 23, 41]. Antagonistic effect on uropathogens has been proven for many types of probiotic microorganisms among others Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, Saccharomyces, Pediococcus, and Bacillus [2, 18, 23, 25]. Of the genus Lactobacillus, many species isolated from various sources such as genitourinary tract, faces, and fermented food exhibit antagonistic activity against uropathogens, for example, L. gasseri, L. crispatus, L. rhamnosus, L. plantarum, L. brevis, and L. acidophilus [23, 26, 33, 41]. Their use in women with bacterial vaginosis and recurrent UTI also brings positive effects [7]. The human body is intentionally colonized by administering selected probiotic organisms but also by consuming food containing these bacteria. The mechanism preventing the development of urinary tract infections by Lactobacillus spp. consists mainly in the production of substances with antibacterial activity, inhibiting adhesion and immunomodulatory activity [29, 41]. Among the antibacterial substances produced by Lactobacillus spp., besides lactic acid, should be mentioned: biosurfactants, hydrogen peroxide, bacteriocins, and other organic acids [41].
The effect of Lactobacillus on the viability or virulence factors of uropathogens has been established so far, but it has not been investigated how these microorganisms affect one of the complications of urinary tract infections, which is the development of infectious urolithiasis. The purpose of this work was to determine the effect of Lactobacillus brevis and Lactobacillus plantarum on the crystallization caused by Proteus mirabilis, which initiates the formation of urinary stones.
Material and Methods
Bacterial Strains
Lactobacillus strains were isolated from fermented cucumbers, which are the most popular fermented foods consumed in Poland. Juice of fermented cucumbers was seeded on MRS agar (De Man, Rogosa and Sharpe agar, BTL, Warsaw, Poland) and incubated in aerobic condition for 24 h at 37 °C. Bacteria were isolated and identified from selected colonies. Isolates which were Gram-positive and catalase-negative rods were further identified using API 50CHL (bio-Merieux, Marcy l’Etoile, France) and MALDI-TOF MS analysis (Bruker, Billerica, Massachusetts, USA). Of 26 isolates, 4 strains of Lactobacillus plantarum and 4 strains of Lactobacillus brevis were selected for further study. One of the selection criteria was the growth capacity of these strains in the presence of bile salts and gastric juice which was checked by methods described by Li et al. [22].
P. mirabilis (strain C7) was derived from encrusted biofilm formed on urinary catheters of long-term catheterized patients and was deposited in the bacterial strain collection at the Department of Biology of Bacteria, the University of Lodz. The method of isolation of this strain and its characteristics had been described in our previous study [31].
Adhesion Assay
The ability of the Lactobacillus strains to adhere to both intestinal (Caco-2) and urinary (Hu609) epithelial cells was determined. In this assay, the cells were grown in a suitable medium line, in the case of Caco-2, it was Dulbecco’s medium; for Hu 609, RPMI 1640 medium was used. Media were supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal calf serum (FCS, Lonza, Walkersville, MS, USA), 2 mM ultraglutamine (Lonza), 100 IU/mL penicillin, and 100 μg/mL streptomycin (Polfa Tarchomin, Warsaw, Poland). For the adhesion assay, all types of epithelial cells (1 × 105 cells per well) were seeded into 24-well plates and grown for 24 h in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2 at 37 °C in culture medium supplemented only with 10% fetal bovine serum (FCS, Lonza) and 2 mM ultraglutamine (Lonza). Afterwards, the cells were infected with 1-mL bacterial suspension (108 CFU/mL in culture medium with 10% FBS + 2 mM ultraglutamine) (Lonza). After 3-h incubation (37 °C, 5% CO2), the suspension was aspirated, and the cells were washed three times with PBS (pH 7.3) to remove free bacteria. To establish the number of adherent bacteria, a monolayer was lysed using 1% Triton X-100. After that, 1/10 dilution of the suspension was seeded on MRS plates and incubated for 24 h at 37 °C. The results are expressed as bacterial colony-forming units (CFU) recovered per milliliter.
Antibacterial Activity
The antimicrobial activity of Lactobacillus strains was checked by broth microdilution method. Cultures of Lactobacillus (MRS broth for 48 h at 37 °C) were centrifuged 8000×g for 20 min at 4 °C. The supernatant without the bacteria was recovered and separated into two aliquots. One of them was untreated; the second supernatant was neutralized to pH 6.5 with 1 N sodium hydroxide (NaOH). In the case of untreated supernatants, the pH ranged between 3.42 and 3.86. The supernatants were sterilized by filtration through Minisart® (Sartorius, Goettingen, Germany) syringe filters 0.2 μm. The antibacterial activity of Lactobacillus was checked against P. mirabilis C7. The strain was cultured in TSB medium (tryptic soy broth, BTL, Warsaw, Poland) for 24 h at 37 °C. In the experiment, the dilutions of supernatants were prepared in F-bottom 96-well plates. To each well, 100 μl of bacterial suspension (105 CFU/mL) in TSB to 100-μl tested supernatant was added. As controls, 200 μl TSB (negative control) and 200 μl bacterial suspension in TSB of the tested bacterial strains (positive control) were used. Inhibition of bacterial growth was detected by measuring turbidity at 600 nm using a microplate reader Multiskan Ex (Labsystems, Helsinki, Finland).
Analysis of the Influence of Lactobacillus on the Crystallization Caused by P. mirabilis
The effect of Lactobacillus on crystallization caused by P. mirabilis was analyzed in eight independent tests. The first probe (control) contained only P. mirabilis, in the remaining seven tests, P. mirabilis bacteria were incubated simultaneously with individually tested strains of Lactobacillus. Lactobacillus strains were cultured on MRS medium (De Man, Rogosa and Sharpe broth, BTL, Warsaw, Poland) for 48 h at 37 °C, while P. mirabilis was grown in a TSB medium (tryptic soy broth, Warsaw, BTL, Poland) for 18 h at 37 °C. Before each experiment, a suspension of both or only one species in 20 mL of synthetic urine was prepared. The number of bacteria per milliliter was determined spectrophotometrically at 600 nm (Ultrospec 2000, Pharmacia Biotech, Vienna, Austria), where the density of the suspension was adjusted to 1–5 × 105 bacteria per milliliter. Synthetic urine is a composition which corresponds to the mean concentration of the mineral components found during a 24-h period in normal human urine and was used in in vitro studies of uropathogens [19, 44]. The solution was prepared using the modified method previously described by McLean et al. [30] and consisted of the following components (g/L): urea (CH4N2O)—25.0, sodium chloride (NaCl)—4.6, potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH2PO4)—2.8, sodium sulfate (Na2SO4)—2.3, potassium chloride (KCl)—1.6, ammonium chloride (NH4Cl)—1.0, creatine (C4H9N3O2)—1.1, calcium chloride dihydrate (CaCl2 × 2H2O)—0.651, magnesium chloride hexahydrate (MgCl2 × 6H2O)—0.651, sodium citrate (Na3C6H5O7)—0.65, sodium oxalate (Na2C2O4)—0.02 (Sigma, Poznan, Poland), and tryptic soy broth, 10.0 (BTL, Warsaw, Poland). After adjusting the pH to 5.8, the synthetic urine solution was sterilized by passing through a 0.2-μm pore-size filter (Minisart® Sartorius, Goettingen, Germany).
Bacterial suspension in synthetic urine was incubated without mixing for 24 h at 37 °C. At the beginning of the experiment (0 h) and after 5, 8, and 24 h, incubation pH, bacterial viability, and the degree of crystallization were evaluated in all cultures. A pure culture of P. mirabilis was used as a control system in all mentioned test. The numbers of bacteria in pure and mixed cultures, defined as CFU/mL (colony forming units per milliliter), were determined on McConkey medium (BTL, Warsaw, Poland) and MRS agar for P. mirabilis and Lactobacillus, respectively.
Crystallization was determined by spectrophotometric measurements, microscopic observation using direct phase-contrast microscopy (Nikon Eclipse 2000S, Tokyo, Japan), and its intensity was tested by chemical analysis. The turbidity of bacterial suspension in synthetic urine as an absorbance of light at 600 nm wavelength was measured (Ultrospec 2000, Pharmacia Biotech, Uppsala, Sweden). For chemical analyses, a sample (1 mL) of crystals with a bacterial suspension was centrifuged at 8000×g for 10 min. The obtained pellet was suspended in aqueous solution of nitric acid (30% HNO3, POCh, Gliwice, Poland) and incubated for 60 min at 100 °C. After mineralization, calcium and magnesium concentrations were determined by atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS, SpectrAA-300 Varian, Palo Alto, USA). X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) was used for phase identification of a crystalline material. Analysis was performed on X’pert PRO MPD (PANalytical) diffractometer where CuKα radiation monochromatized by nickel filter was applied. Measurements were done in the range of 2θ angles from 3 to 90° with a continuous scan (step 0.0167°) where the measurement time of one step was 30 s. The X’Pert High Score Plus PANanalytical (Almelo, The Netherlands) software was used for indexing peaks in the XRD pattern.
For the evaluation of bacterial extracellular protein and polysaccharide content, 1 mL of each sample was taken at 0, 5, 8, and 24 h of incubation and centrifuged at 8000×g for 10 min in room temperature. Protein concentrations were determined by the method of Lowry et al. [24] using bovine serum albumin as a standard. The phenol-sulfuric acid method described by Masuko et al. [27] with glucose as a standard was selected for carbohydrate determination.
Statistics
The data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD) of three to five independent experiments. Statistical analyses were based on the Mann-Whitney U test performed using Statistica software version 13.3 pl (StatSoft, Krakow, Poland). The results were considered to be statistically significant at p < 0.05. Statistical differences between groups are indicated in the text.
Results
Lactobacillus strains Characteristics
Eight strains selected for this study were characterized in terms of their antibacterial activity and ability to colonize the epithelium both of the urinary tract and the digestive system. As shown in Table 1, the tested strains showed the ability to adhere both to the Caco-2 and Hu 609 lines. The number of bacteria adhering to the urinary epithelium was varied and ranged from 14.3 to 136.85 × 105 CFU/mL. Similarly, in the case of the Caco-2 line, the number of adherent bacteria was 19.0 to 330.4 × 105 CFU/mL. Only S18K7 and S21K7 strains strongly adhered to both Caco-2 and Hu 609 lines. As for the antibacterial activity, untreated supernatants of all Lactobacillus strains inhibited the growth of P. mirabilis C7. After the neutralization of the pH of 1 N NaOH, the inhibitory activity remained in the supernatants of the L. brevis strains S1K1, S20K3, and S21K5 and only in one strain of L. plantarum S23K2, which indicated the presence of antibacterial agents other than organic acids.
Effect of Lactobacillus on Bacterial Growth and Crystallization Caused by P. mirabilis in Synthetic Urine
Growth of Bacteria
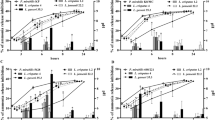
In the crystallization experiment, Lactobacillus strains were simultaneously incubated with the P. mirabilis strain in synthetic urine. Changes in P. mirabilis growth intensity during incubation are shown in Fig. 1. The initial suspension for P. mirabilis was 1–1.4 × 106 CFU/mL, and for Lactobacillus spp., it was between 0.9 and 1.6 × 106 CFU/mL depending on the experiment. With the time of incubation, the number of P. mirabilis cells increased reaching in 5 h in mixed cultures with Lactobacillus, the values were from 12.6 × 106 CFU/mL (L. plantarum S23K2) to 38 × 106 CFU/mL for the co-culture with L. plantarum S2K18. At that point of the experiment, P. mirabilis growth was higher in the presence of lactobacilli compared with the growth in the pure culture, but this difference was not statistically significant in each case (Fig. 1). Up to 8 h of incubation, the most intensive growth of P. mirabilis was observed reaching the values in the range of 102– 266 × 106 CFU/mL both in the mixed cultures and in the pure culture. The number of P. mirabilis cells did not differ between the mixed and pure cultures as it was seen in 5 h, except for the co-culture with L. plantarum S21K7 and L. brevis S1K1 and S21K5, where P. mirabilis grew more intensively. At that point, the culture pH was already very high (Table 2), and the viability of the bacteria started to decrease. After 24 h of incubation, the number of Proteus bacilli in the culture varied considerably depending on the Lactobacillus strain with which it was grown. In the case of the co-culture with L. plantarum S23K2 and S21K7, the number of P. mirabilis cells was lower and reached 1.48 × 106 and 1.2 × 106 CFU/mL, respectively, in comparison with the pure P. mirabilis culture (4.36 × 106 CFU/mL). On the other hand, L. brevis S1K1 and S21K5 promoted the growth of P. mirabilis in the same conditions because the number of P. mirabilis bacteria reached 12.5 × 106 and 11.5 × 106 CFU/mL, respectively. All Lactobacillus strains tested in mixed cultures with P. mirabilis survived until the end of the experiment, and the kinetics of growth of the lactobacilli was similar to that of P. mirabilis. The number of bacteria increased until 8 h of incubation, when it reached the highest value (6.04–46.33 × 106 CFU/mL), and then it decreased, and in 24 h, there were about 105. The S18K2 strain exhibited the most intensive growth, while the S20K3 strain probably survived, but its cells did not divide in this environment.
Growth of P mirabilis and Lactobacillus spp. in mixed cultures during incubation in synthetic urine after 5 h (a), 8 h (b), and 24 h (c). The values represent means ± SD of 5 experiments. *p ≤ 0.05 comparing P. mirabilis cells number in mixed cultures with those in pure culture; black bars—number of P mirabilis cells, white bars—Lactobacillus cells number
Changes in pH During the Co-Culture of P. mirabilis with Lactobacillus Spp.
During the growth of P. mirabilis in synthetic urine, the pH increases due to the hydrolysis of urea. In this experiment, the pH changes in the pure culture of P. mirabilis were compared to those observed in the mixed cultures (P. mirabilis + Lactobacillus sp.). The starting urine pH ranged from 6.16 to 6.53 and increasing all the time; in 24 h, it reached a value close to 10 (Table 2). After 5 h, an increase in pH was already observed; the highest value to about 7 was noted for samples with the mixed cultures of P. mirabilis from L. plantarum S2K18 and S21K7 and L. brevis S18K7. After 8 h of incubation, the differences between the samples were more visible. In most cases, the pH in the mixed cultures was higher than that in the pure cultures. The exception was the cultures with L. plantarum S23K2 and L. plantarum S18K2 where the pH value was close to that of the pH of the pure culture. At the end of the experiment, significantly lower pH values compared with the P. mirabilis culture were noted in co-cultures with 3 L. brevis strains S20K3, S21K5, and S1K1.
Effect of Lactobacillus Spp. on the Crystallization Caused by Proteus mirabilis
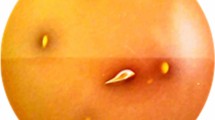
Along with the increase in pH resulting from the decomposition of urea, calcium and magnesium phosphates fall out of the urine solution and, at a later stage, crystallize as apatite and struvite. Apatites (calcium phosphates) appear when the pH exceeds 6.8 while struvite (ammonium magnesium phosphate) when the pH exceeds 7.5. Crystallization can be evaluated spectrophotometrically because it is accompanied by an increase in turbidity of suspension. As shown in Fig. 2a, b, the time course of the curves is very similar for all samples tested including the control and mixed cultures of P. mirabilis with L. plantarum or L. brevis. The increase occurred from 5 h reaching the maximum value in 8 h and then the absorbance slowly decreased. In 8- and 24-h incubations, differences in the intensity of crystallization between mixed cultures and control were visible. In the case of the culture containing L. brevis, the absorption for 3 strains was below this value for the pure culture of P. mirabilis. For the L. plantarum cultures, this tendency was opposite; the absorbance for most suspensions was equal to or higher than the absorbance of the pure culture. The samples were submitted to a more detailed analysis at 0, 5, 8, and 24 h. Microscopic observation showed that the first small crystals appeared at about 5 h of the experiment (Fig. 3). After 8 h of incubation, amorphous apatite precipitates and struvite crystals with typical hemimorphic morphology of coffin-lid shape along with bacterial cells were observed in all samples. Crystallization occurred all the time, and after 24 h, an increase in the number and size of single crystals was noted. For the P. mirabilis monoculture and the mixed culture of P. mirabilis and L. plantarum S23K2, dendrite crystals, demonstrating faster growth, were also visible. It is interesting that in most samples from the mixed cultures both in 5 h and 24 h, the crystals were larger in size compared to the pure P. mirabilis culture, which was especially visible when L. plantarum S2K18 and L. brevis S20K3 and S1K1 were present in the culture. An attempt was made to determine the presence of proteins and polysaccharides in post-culture supernatants by identifying the factor responsible for the formation of larger crystals. However, the concentrations of polysaccharides and proteins were comparable in all tests (Fig. 2c). The concentration of polysaccharides was 1315.6 μg/mL at Oh, and from 5 h, it began to decline to average values of 1050.3 μg/mL and 1198.4 μg/mL for P. mirabilis culture and mixed cultures. respectively, reaching the lowest level at 24 h, where the decrease was about 30% (921.5 μg/mL and 915.3 μg/mL for “P. mirabilis” and “P. mirabilis + Lactobacillus”, respectively) compared with the initial value in the cultures. Similarly, the protein concentration was the highest at 0 h (8703.3 μg/mL); from 8 h, it began to decline till the end of the experiment (6596.2 μg/mL (P. mirabilis) and 6325.3 μg/mL (P. mirabilis + Lactobacillus). The decrease in the content of polysaccharides and proteins in the supernatants compared with the sterile medium results from the use of these components by bacteria as a source of carbon and energy. This indicated a similar metabolic activity of bacteria in all cultures tested rather than the secretion of substances that could modulate the crystallization process. The intensity of crystallization was also quantified by analyzing the calcium and magnesium levels in the samples. As shown in Table 3, the levels of these cations did not differ significantly between 0- and 5-h incubation, which indicated a very low level of salt crystallization and confirmed the results of the previous analyses at 5 h. Calcium and magnesium levels significantly (on average 10 times) increased after 8 h of incubation. The content of these ions in the formed crystals was higher in the mixed cultures than in the pure culture, and only in the case of the P. mirabilis + L. plantarum S23K2 sample, it was comparable with the culture containing P. mirabilis alone. The intensity of crystallization increased with the incubation time, but not as intensely as between 5 and 8 h of incubation, reaching values between 41.12 and 56.11 μg/mL for calcium and 35.42 and 53.08 μg/mL for magnesium at the end of the experiment. To confirm the composition of the crystalline components in the samples, XRD analysis was performed after 24-h incubation. As shown in Fig. 2d, in 2 samples with P. mirabilis and P. mirabilis with L. plantarum S23K2 (a representative sample for the mixed cultures), the obtained samples had a crystalline character and the diffraction pattern was similar. The dominant components such as struvite and hydroxyapatite were also found in both types of culture. The only significant difference in the phase composition of both samples was the presence of a small amount of hydrated calcium phosphate in the sample containing P. mirabilis alone.
Crystallization intensity in P. mirabilis culture and mixture of P. mirabilis with L. plantarum (a), and L. brevis (b) evaluated spectrophotometrically; changes in concentration of sugar and proteins in supernatants of pure and mixed cultures during incubation time (values for mixed cultures are the average of all samples from Lactobacillus spp.); su synthetic urine, P.m. P mirabilis culture, P.m. + L- (c) and comparison of X-ray diffraction pattern of the sample from P. mirabilis culture with the samples from culture of P. mirabilis + L. plantarum S23K2 (difference samples are marked X) (d)
Discussion
In recent years, interest in the use of probiotic strains for the treatment or prevention of urinary tract infections has increased. To date, the results are not clear as to the effectiveness of the antibacterial effect of probiotics, and this is probably the result of the selection of concepts and the route of administration to patients. Strains used for treatment are usually isolated from human stool, or in the case of women, they come from the genitourinary tract [17, 41]. However, food-derived strains with high antibacterial properties might also play an important role. Manzoor et al. [26] showed antimicrobial activity of Lactobacillus spp. strains including L. plantarum and L. brevis isolated from local food against antibiotic resistant uropathogens including E. coli, K. pneumoniae, and E. faecalis. Similarly, Liu et al. [23] evaluated the effect of lactic acid bacteria isolated from fermented food on uropathogenic E. coli and showed that in both in vitro and in vivo conditions, the ability of the pathogen to adhere and its growth in the presence of LAB decreased. Lactobacillus spp. are also the main component of urobiome, i.e., the microbiome of the urinary tract, where they play an important role in maintaining the homeostasis of this environment [4, 21]. Their elimination from natural flora results in greater susceptibility to infection and the development of other diseases of the genitourinary system. The aim of this study was examining the effect of two Lactobacillus species, Lactobacillus plantarum, and Lactobacillus brevis, derived from fermented foods on crystallization induced by P. mirabilis during urinary tract infection. Strains with different antimicrobial activity were selected for the study. We assumed that those exhibiting antimicrobial properties would either act in a bactericidal manner on the P. mirabilis or inhibit the activity of its virulence factors, thus affecting crystallization. However, none of them inhibited the growth of P. mirabilis in synthetic urine or crystallization. This may be due to the inhibition of the ability to synthesize antibacterial compounds by Lactobacillus spp. in synthetic urine or to the reduced activity of Lactobacillus-produced organic acids caused by the high urine pH. Based on their experience, Yang et al. [46] showed that the ability to produce bacteriocins depends on the pH, temperature, and composition of the substrate. In addition, Mataragas et al. [28] stated that the highest bacteriocin production occurs not under optimal growth conditions but with reduced temperature and pH. In our experiments, Lactobacillus not only did not inhibit growth but even caused a significantly larger growth in P. mirabilis compared with the control. This is not the first case where co-cultivation promotes the growth of one or all microorganisms in the co-culture. Alteri et al. [3] studied in vivo co-infections E. coli and P. mirabilis on a mouse model. Based on their research results, they concluded that in mixed infection, both E. coli and P. mirabilis colonize the urinary tract of mice better than in mono infection, which results from the metabolic properties of these microorganisms consisting in the complementary use of carbon sources. Similar results were obtained in our earlier studies where a better growth of P. mirabilis in vitro in synthetic urine was observed in the presence of other uropathogens including E. coli [43]. Therefore, it cannot be ruled out that in this case, P. mirabilis uses other sources of carbon and energy than Lactobacillus, or Lactobacillus provides nutrients for P. mirabilis. Even more interesting is the growth of Lactobacillus in our experimental condition, although L. plantarum and L. brevis grow in human urine, and they are isolated from the urinary tract; in this case, during the growth of P. mirabilis, the pH of synthetic urine increases significantly (up to 10), which is not typical for this group of bacteria. Sawatari and Yokota [37] studied the effect of alkaline stress on the growth, physiology, and metabolism of lactobacilli isolated from various sources including human feces, saliva, or food. Maximum pH allowing the growth of these lactobacilli ranged between 6.7 and 8.9, with pH values of 8.5 for strains derived from plants (L. casei, L. paracasei subsp. tolerans, L. paracasei subsp. paracasei, L. curvatus, L. pentosus, and L. plantarum). They found that lactobacilli growth in an alkaline environment depended on the alkali tolerance of the cellular metabolism, especially on the glycolysis reactions. It is possible that these mechanisms of survival in the alkaline environment also occurred in the strains used for the present study.
The aim of this work was to find a Lactobacillus strain whose properties would allow inhibiting the growth of P. mirabilis and/or crystallization of mineral salts of urine induced by these bacteria. However, as previously mentioned, Lactobacillus enhanced the growth of P. mirabilis, and some of the tested strains increased crystallization. The increase in the intensity of crystallization was manifested by both the formation of bigger crystals and the crystallization of larger amounts of calcium and magnesium phosphates. The intensity of crystallization in such conditions may depend on the rate of pH increase, which affects the degree of supersaturation of urine [9]. The increase in the concentration of ammonium ions and pH play a key role in inducing struvite and apatite crystallization, and in the presence of the appropriate concentration of calcium and magnesium, ions also have an impact on the crystallization rate [40]. This is confirmed by our results; in mixed cultures of P. mirabilis with Lactobacillus (except for cultures with Lactobacillus S23K2 and S18K2) at the 8 h of incubation, both the pH and the amount of crystallized calcium and magnesium salts were higher than in with P. mirabilis monoculture. The intensity of crystallization also depends on the presence of bacterial factors, such as extracellular polysaccharides or other macromolecules. Bacterial macromolecules having different binding capacity for calcium and magnesium cations can accelerate or inhibit crystallization [13]. These compounds possessing a strong affinity bind cations from the environment and act as crystallization inhibitors; on the other hand, ones with weak affinity easily release cations promoting their accumulation and subsequent crystallization [13, 45]. Like other bacteria, due to the presence of cell wall components, e.g., teichoic acids, proteins, and polysaccharides, lactic acid bacteria may have a surface charge that allows interaction with ions contained in the environment. In addition, exopolysaccharides as hetero- and homopolysaccharides are produced in the environment in very large quantities by many Lactobacillus strains including L. brevis and L. plantarum [12]. The ability to bind calcium ions by Lactobacillus exopolysaccharides has been experimentally confirmed by Astasov-Frauenhoffer et al. [6] in studies on the role of exopolysaccharides of Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus paracasei in binding calcium in cariogenic biofilms. Taking this into account, it was verified whether there is a difference in the level of macromolecules such as proteins and polysaccharides in the culture medium. Unfortunately, no differences in total amount of polysaccharides and proteins between samples from P. mirabilis monocultures and co-culture with different Lactobacillus strains were shown. The participation of extracellular macromolecules as well as those associated with the surface of lactobacilli in crystallization cannot be excluded, but it requires more detailed analysis, especially since there is evidence that the proteins of this microbial group participate in crystallization. Borah et al. [11] have shown that the acidic proteins of L. plantarum, L. acidophilus, and Pediococcus acidilactici affect crystallization by providing nucleation centers and changing the morphology of calcium and barium salt crystals.
In summary, it has been shown that P. mirabilis, co-cultured with L. plantarum and L. brevis strains derived from food and with potential to colonize the urinary tract, shows better viability and resistance to high pH. Such conditions also proved to be conducive to crystallization of calcium and magnesium salts induced by P. mirabilis. These interactions between microorganisms along with an explanation of the effect on the intensity of crystallization require further investigation; however, at this stage, it indicates that without knowing exactly the complexity of the interaction of microorganisms from different environments, it is not safe to introduce bacteria into the human body as a means of preventing or treating diseases.
References
Adeolu M, Alnajar S, Naushad S, Gupta R (2016) Genome-based phylogeny and taxonomy of the ‘Enterobacteriales’: proposal for Enterobacterales ord. nov. divided into the families Enterobacteriaceae, Erwiniaceae fam. nov., Pectobacteriaceae fam. nov., Yersiniaceae fam. nov., Hafniaceae fam. nov., Morganellaceae fam. nov., and Budviciaceae fam. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:5575–5599. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001485
Algburi A, Alazzawi SA, Al-Ezzy AIA, Weeks R, Chistyakov V, Chikindas ML (2020) Potential probiotics Bacillus subtilis KATMIRA1933 and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens B-1895 co-aggregate with clinical isolates of Proteus mirabilis and prevent biofilm formation. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-020-09631-0
Alteri CHJ, Himpsl SD, Mobley HLT (2015) Preferential use of central metabolism in vivo reveals a nutritional basis for polymicrobial infection. PLoS Pathog 11:e1004601. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1004601
Aragón IM, Herrera-Imbroda B, Queipo Ortuño M, Castillo E, Del Moral J, Gomez-Millan J, Yucel Lara Cabanas MF (2018) The urinary tract microbiome in health and disease. Eur Urol Focus 4:128–1384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euf.2016.11.001
Armbruster CE, Mobley HLT, Pearson MM (2018) Pathogenesis of Proteus mirabilis infection. EcoSal Plus 8. https://doi.org/10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0009-2017
Astasov-Frauenhoffer M, Varenganayil MM, Decho AW, Waltimo T, Braissant O (2017) Exopolysaccharides regulate calcium flow in cariogenic biofilms. PLoS One 12(10):e0186256. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0186256
Barrons R, Tassone D (2008) Use of Lactobacillus probiotics for bacterial genitourinary infections in women: a review. Clin Ther 30:453–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinthera.2008.03.013
Basavaraj DR, Biyani CHS, Browning AJ, Cartledge JJ (2007) The role of urinary kidney stone inhibitors and promoters in the pathogenesis of calcium containing renal stones. EAU-EBU Update Series 5:126–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eeus.2007.03.002
Bayuseno AP, Perwitasari DS, Muryanto S, Tauviqirrahman M, Jamaria J (2020) Kinetics and morphological characteristics of struvite (MgNH4PO4.6H2O) under the influence of maleic acid. Heliyon 6(3):e03533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03533
Bichler KH, Eipper E, Naber K, Braun V, Zimmermann R, Lahme S (2002) Urinary infection stones. Int J Antimicrob Agents 19:488–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0924-8579(02)00088-2
Borah BM, Singh AK, Ramesh A, Das G (2009) Lactic acid bacterial extract as a biogenic mineral growth. J Cryst Growth 311:2664–2672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2009.02.015
Ciszek-Lenda M (2011) Biological functions of exopolysaccharides from probiotic bacteria. Centr Eur J Immunol 36:51–55
Dumanski AJ, Hedelin H, Edin-Liljegren A, Beauchemin D, McLean RJ (1994) Unique ability of the Proteus mirabilis capsule to enhance mineral growth in infectious urinary calculi. Infect Immun 62:2998–3003
Ezeonu IM, Louis GO, Eze CA, Chah KF, Ugwu NE (2020) Direct instillation of Lactobacillus plantarum into rat bladder inhibits urinary tract infection (UTI) and protects the integrity of urinary organs. Microbiol Res Int 8:1–9. https://doi.org/10.30918/MRI.81.19.036
Flannigan R, Choy WH, Chew B, Lange D (2014) Renal struvite stones—pathogenesis, microbiology, and management strategies. Nat Rev Urol 11:333–341. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrurol.2014.99
Gupta V, Deepika N, Prathiba G (2017) Recurrent urinary tract infections in women: how promising is the use of probiotics? Indian J Med Microbiol 35:347–354 http://www.ijmm.org/text.asp?2017/35/3/347/216616
Hoesl CE, Altwein JE (2005) The probiotic approach: an alternative treatment option in urology. Eur Urol 47:288–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2004.09.011
Hütt P, Shchepetova J, Lõivukene K, Kullisaar T, Mikelsaar M (2006) Antagonistic activity of probiotic Lactobacilli and Bifidobacteria against entero- and uropathogens. J Appl Microbiol 100:1324–1332. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2006.02857.x
Ipe D, Ulett G (2016) Evaluation of the in vitro growth of urinary tract infection-causing gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria in a proposed synthetic human urine (SHU) medium. J Microbiol Methods 127:164–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2016.06.013
Kang C-I, Kim J, Park D, Kim B-N, Ha U-S, Lee S-J, Yeo J, Min S, Lee H, Wie S-H (2018) Clinical practice guidelines for the antibiotic treatment of community-acquired urinary tract infections. Infect Chemother 50:67–100. https://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2018.50.1.67
Kim J-M, Park Y-J (2018) Lactobacillus and urine microbiome in association with urinary tract infections and bacterial vaginosis. Urogenit Tract Infec 13:7–13. https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2018.13.1.7
Li Q, Liu X, Dong M, Zhou J, Wang Y (2015) Adhesion and probiotic properties of Lactobacillus planatrum isolated from Chinese traditional fermented soybean paste. Glob Adv Res J Food Sci Technol 4:1–9
Liu Y-H, Ho C-Y, Huang C-C, Tsai C-C (2016) Inhibitory effect of lactic acid bacteria on uropathogenic Escherichia coli-induced urinary tract infection. J Prob Health 4:2. https://doi.org/10.4172/2329-8901.1000144
Lowry O, Rosenbrough N, Lewis-Farr A, Randall R (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Madden-Fuentes RJ, Arshad M, Ross SS, Seed PC (2015) Fluoroquinolone-probiotic combination therapy to treat recurrent urinary tract infections in children. Clin Ther 37:2143–2147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinthera.2015.06.018
Manzoor A, Ul-Hag I, Baig S, Qazi JI, Seratlic S (2016) Efficacy of locally isolated lactic acid bacteria against antibiotic-resistance uropathogens. Jundishapur J Microbiol 9:e18952. https://doi.org/10.5812/jjm.18952
Masuko T, Minami A, Iwasaki N, Majima T, Nishimura SI, Lee YC (2005) Carbohydrate analysis by a phenol-sulphuric acid method in microplate format. Anal Biochem 339:69–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2004.12.001
Mataragas M, Metaxopoulos J, Galiotou M, Drosinos EH (2003) Influence of pH and temperature on growth and bacteriocin production by Leuconostoc mesenteroides L124 and Lactobacillus curvatus L442. Meat Sci 64:265–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0309-1740(02)00188-2
Matsuzaki T, Chin J (2000) Modulating immune responses with probiotic bacteria. Immunol Cell Biol 78:67–73. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1440-1711.2000.00887.x
McLean RJC, Nickel JC, Cheng K-J, Costerton JW (1988) The ecology and pathogenicity of urease-producing bacteria in the urinary tract. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol 16:37–79. https://doi.org/10.3109/10408418809104467
Moryl M, Torzewska A, Jałmużna P, Różalski A (2013) Analysis of Proteus mirabilis distribution in multi-species biofilms on urinary catheters and determination of bacteria resistance to antimicrobial agents. Pol J Microbiol 62:377–384
Naas T, Al-Agili S, Bashir O (2001) Urinary calculi: bacteriological and chemical association. East Mediterr Health J 7:763–770
Okereke HC, Achi OK, Ekwenye UN, Orji FA (2012) Antimicrobial properties of probiotic bacteria from various sources. Afr J Biotechnol 11:9416–9421. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB11.3334
Prywer J, Torzewska A (2009) Bacterially induced struvite growth from synthetic urine: experimental and theoretical characterization of crystal morphology. Cryst Growth Des 9:3538–3543. https://doi.org/10.1021/cg900281g
Rodman JS (1999) Struvite stones. Nephron 81:50–59. https://doi.org/10.1159/000046299
Różalski A, Sidorczyk Z, Kotełko K (1997) Potential virulence factors of Proteus bacilli. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 61:65–89
Sawatari Y, Yokota A (2007) Diversity and mechanisms of alkali tolerance in lactobacilli. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:3909–3915. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02834-06
Sayer JA, Moochhala SH, Thomas DJ (2010) The medical management of urolithiasis. Brit J Med Surg Urol 3:87–95
Schaffer JN, Norsworthy AN, Sun T-T, Pearson MM (2016) P. mirabilis clusters initiate stone formation. PNAS 113:4494–4499. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1601720113
Shaddel S, Grini T, Andreassen J-P, Østerhus SW, Ucar S (2020) Crystallization kinetics and growth of struvite crystals by seawater versus magnesium chloride as magnesium source: towards enhancing sustainability and economics of struvite crystallization. Chemosphere 256:126968. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126968
Shim YH, Lee SJ, Lee JW (2016) Antimicrobial activity of lactobacillus strains against uropathogens. Pediatr Int 58:1009–1013. https://doi.org/10.1111/ped.12949
Tavichakorntrakool R, Prasongwattana V, Sungkeeree S, Saisud P, Sribenjalux P, Pimratana C, Bovornpadungkitti S, Sriboonlue P, Thongboonkerd V (2012) Extensive characterizations of bacteria isolated from catheterized urine and stone matrices in patients with nephrolithiasis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 27:4125–4130. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfs057
Torzewska A, Bednarska K, Różalski A (2019) Influence of various uropathogens on crystallization of urine mineral components caused by Proteus mirabilis. Res Microbiol 170:80–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resmic.2018.11.005
Torzewska A, Różalski A (2014) Inhibition of crystallization caused by Proteus mirabilis during the development of infectious urolithiasis by various phenolic substances. Microbiol Res 169:579–584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2013.09.020
Torzewska A, Stączek P, Róźalski A (2003) Crystallization of urine mineral components may depend on the chemical nature of Proteus endotoxin polysaccharides. J Med Microbiol 52:471–477. https://doi.org/10.1099/jmm.0.05161-0
Yang E, Fan L, Yan J, Jiang Y, Doucette C, Fillmore S, Walker B (2018) Influence of culture media, pH and temperature on growth and bacteriocin production of bacteriocinogenic lactic acid bacteria. AMB Express 8:10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-018-0536-0
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Torzewska, A., Wiewiura, P., Brodecka, D. et al. Potentially Probiotic Lactobacillus Strains Derived from Food Intensify Crystallization Caused by Proteus mirabilis in Urine. Probiotics & Antimicro. Prot. 13, 441–452 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-020-09689-w
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-020-09689-w