Abstract
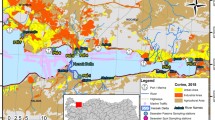
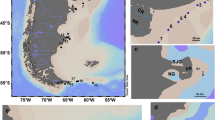
A high-speed rotation-type passive sampling device (HSR-PSD) was designed to effectively measure the freely dissolved hydrophobic organic contaminants in an aquatic environment, and the operating conditions of the HSR-PSD were optimized. In addition to the HSR-PSD, a conventional high-volume water sampler was applied to the Yellow Sea near Korea, and the distributions of three environmental phases of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) were investigated. The HSR-PSD, operating for under 12 h at 1000 rpm, can measure the freely dissolved concentrations of PAHs up to log KOW = 6. Total freely dissolved PAH concentrations obtained from the HSR-PSD were from 0.67 to 1.9 ng/L in the Yellow Sea. The PAH levels were higher by one order of magnitude than those in other oceans. Concentrations of PAHs in dissolved and particulate phases ranged from 10 to 20 ng/L and from 0.0062 to 0.060 ng/L, respectively. Unlike the spatial distribution of dissolved PAHs, the concentrations of freely dissolved PAHs in water and predicted PAHs in fish are higher in the central regions than in coastal areas of the Yellow Sea. Locations with high bioavailable PAHs are adjacent to identified potential sources, demonstrating that PAHs, in the freely dissolved phase, tend to be more consistently distributed near to potential sources than those in the dissolved phase.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan IJ, Nilsson HC, Tjensvoll I, Bradshaw C, Næs K (2011) Mobile passive samplers: Concept for a novel mode of exposure. Environ Pollut 159:2393–2397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.06.039
Apell JN, Gschwend PM (2014) Validating the use of performance reference compounds in passive samplers to assess porewater concentrations in sediment beds. Environ Sci Technol 48:10301–10307. https://doi.org/10.1021/es502694g
Apell JN, Tcaciuc AP, Gschwend PM (2016) Understanding the rates of nonpolar organic chemical accumulation into passive samplers deployed in the environment: Guidance for passive sampler deployments. Integr Environ Assess Manag 12:486–492. https://doi.org/10.1002/ieam.1697
Bao LJ, Xu SP, Liang Y, Zeng EY (2012) Development of a low-density polyethylene-containing passive sampler for measuring dissolved hydrophobic organic compounds in open waters. Environ Toxicol Chem 31:1012–1018. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.1788
Bao LJ, Wu X, Jia F, Zeng EY, Gan J (2016) Isotopic exchange on solid-phase micro extraction fiber in sediment under stagnant conditions: Implications for field application of performance reference compound calibration. Environ Toxicol Chem 35:1978–1985. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.3345
Bian C, Jiang W, Greatbatch RJ (2013) An exploratory model study of sediment transport sources and deposits in the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea, and East China Sea. J Geophys Res Ocean 118:5908–5923. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013JC009116
Booij K, Smedes F (2010) An improved method for estimating in situ sampling rates of nonpolar passive samplers. Environ Sci Technol 44:6789–6794. https://doi.org/10.1021/es101321v
Booij K, Smedes F, Van Weerlee EM (2002) Spiking of performance reference compounds in low density polyethylene and silicone passive water samplers. Chemosphere 46:1157–1161. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(01)00200-4
Booij K, Hofmans HE, Fischer CV, Van Weerlee EM (2003) Temperature-dependent uptake rates of nonpolar organic compounds by semipermeable membrane devices and low-density polyethylene membranes. Environ Sci Technol 37:361–366. https://doi.org/10.1021/es025739i
Booij K, van Bommel R, van Aken HM, van Haren H, Brummer GJA, Ridderinkhof H (2014) Passive sampling of nonpolar contaminants at three deep-ocean sites. Environ Pollut 195:101–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2014.08.013
Burgess RM (2012) Guidelines for using passive samplers to monitor organic contaminants at superfund sediment sites. US Environmental Protection Agency, Washington DC
Burgess RM, Driscoll SBK, Burton GA, Ghosh U, Gschwend PM, Reible D, Ahn S, Thompson T (2017) Laboratory, field, and analytical procedures for using passive sampling in the evaluation of contaminated sediments: user’s manual. US Environmental Protection Agency, Alexandria
Burkhard LP (2000) Estimating dissolved organic carbon partition coefficients for nonionic organic chemicals. Environ Sci Technol 34:4663–4668. https://doi.org/10.1021/es001269l
Cai M, Duan M, Guo J, Liu M, Qi A, Lin Y, Liang J (2018) PAHs in the Northern South China Sea: Horizontal transport and downward export on the continental shelf. Mar Chem 202:121–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2018.03.004
Chen Y, Lin T, Tang J, Xie Z, Tian C, Li J, Zhang G (2016) Exchange of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons across the air-water interface in the Bohai and Yellow Seas. Atmos Environ 141:153–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2016.06.039
Cornelissen G, Pettersen A, Broman D, Mayer P, Breedveld GD (2008) Field testing of equilibrium passive samplers to determine freely dissolved native polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon concentrations. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:499–508. https://doi.org/10.1897/07-253.1
Emelogu ES, Pollard P, Dymond P, Robinson CD, Webster L, McKenzie C, Dobson J, Bresnan E, Moffat CF (2013) Occurrence and potential combined toxicity of dissolved organic contaminants in the Forth estuary and Firth of Forth, Scotland assessed using passive samplers and an algal toxicity test. Sci Total Environ 461–462:230–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.05.011
Fernandez LA, Lao W, Maruya KA, White C, Burgess RM (2012) Passive sampling to measure baseline dissolved persistent organic pollutant concentrations in the water column of the Palos Verdes shelf superfund site. Environ Sci Technol 46:11937–11947. https://doi.org/10.1021/es302139y
Fernandez LA, Lao W, Maruya KA, Burgess RM (2014) Calculating the diffusive flux of persistent organic pollutants between sediments and the water column on the palos verdes shelf superfund site using polymeric passive samplers. Environ Sci Technol 48:3925–3934. https://doi.org/10.1021/es404475c
Guo W, He M, Yang Z, Lin C, Quan X, Wang H (2007) Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water, suspended particulate matter and sediment from Daliao River watershed, China. Chemosphere 68:93–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.12.072
Huckins JN, Pettey JD, Booij K (2006) Monitors of organic chemicals in the environment. Springer, New York, p 223
ITRC (2011) Incorporating bioavailability considerations into the evaluation of contaminated sediment sites (CS-1). Guid Doc ITRC 297
Jang YL, Lee HJ, Jeong H, Jeong DY, Kim NY, Kim GB (2021) Determination of freely dissolved pahs in seawater around the korean peninsula using high speed rotation-type passive sampling device. J Korean Soc Oceanogr 26:37–48. https://doi.org/10.7850/jkso.2021.26.1.037
Jia XM, Li JY, Tian SY (2017) Assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) ecological risk in surface seawater from the west Bohai Bay, China. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 82:012040
Joyce AS, Burgess RM (2018) Using performance reference compounds to compare mass transfer calibration methodologies in passive samplers deployed in the water column. Environ Toxicol Chem 37:2089–2097. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.4167
Joyce AS, Pirogovsky MS, Adams RG, Lao W, Tsukada D, Cash CL, Haw JF, Maruya KA (2015) Using performance reference compound-corrected polyethylene passive samplers and caged bivalves to measure hydrophobic contaminants of concern in urban coastal seawaters. Chemosphere 127:10–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.12.067
Ju JH, Lee IS, Sim WJ, Eun H, Oh JE (2009) Analysis and evaluation of chlorinated persistent organic compounds and PAHs in sludge in Korea. Chemosphere 74:441–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.09.059
Kim NY, Jang YL, Jeong H, Jeong DY, Kim GB (2020) Applicability of vinyl wrap (linear low density polyethylene) as a new passive sampler : measurement of freely dissolved polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the offshore. J Korean Soc Mar Environ Energy 23:277–285. https://doi.org/10.7846/jkosmee.2020.23.4.277
Kuivikko M, Sorsa K, Kukkonen JVK, Akkanen J, Kotiaho T, Vähätalo AV (2010) Partitioning of tetra- and pentabromo diphenyl ether and benzo[a]pyrene among water and dissolved and particulate organic carbon along a salinity gradient in coastal waters. Environ Toxicol Chem 29:2443–2449. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.308
Lao W, Maruya KA, Tsukada D (2019) An exponential model based new approach for correcting aqueous concentrations of hydrophobic organic chemicals measured by polyethylene passive samplers. Sci Total Environ 646:11–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.192
Lin Y, Deng W, Li S, Li J, Wang G, Zhang D, Li X (2017) Congener profiles, distribution, sources and ecological risk of parent and alkyl-PAHs in surface sediments of Southern Yellow Sea, China. Sci Total Environ 580:1309–1317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.12.094
Lohmann R (2012) Critical review of low-density polyethylene’s partitioning and diffusion coefficients for trace organic contaminants and implications for its use as a passive sampler. Environ Sci Technol 46:606–618. https://doi.org/10.1021/es202702y
Lohmann R, Muir D (2010) Response to comment on “global aquatic sampling (aqua-gaps): using passive samplers to monitor pops in the waters of the world.” Environ Sci Technol 44:4386. https://doi.org/10.1021/es101053m
Lohmann R, Dapsis M, Morgan EJ, Dekany V, Luey PJ (2011) Determining air-water exchange, spatial and temporal trends of freely dissolved PAHs in an urban estuary using passive polyethylene samplers. Environ Sci Technol 45:2655–2662. https://doi.org/10.1021/es1025883
Lohmann R, Klanova J, Kukucka P, Yonis S, Bollinger K (2012) PCBs and OCPs on a east-to-west transect: The importance of major currents and net volatilization for PCBs in the atlantic ocean. Environ Sci Technol 46:10471–10479. https://doi.org/10.1021/es203459e
Lohmann R, Klanova J, Pribylova P, Liskova H, Yonis S, Bollinger K (2013) PAHs on a west-to-east transect across the tropical Atlantic Ocean. Environ Sci Technol 47:2570–2578. https://doi.org/10.1021/es304764e
Lohmann R, Markham E, Klanova J, Kukucka P, Pribylova P, Gong X, Pockalny R, Yanishevsky T, Wanger CC, Sunderland EM (2020) Trends of diverse POPs in air and water across the western atlantic ocean: strong gradients in the ocean but not in the air. Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c04611
Mei X, Li R, Zhang X, Liu J, Wang Z, Lan X, Liu J, Sun R (2016) Evolution of the yellow sea warm current and the yellow sea cold water mass since the middle pleistocene. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 442:48–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2015.11.018
MOE (2008) The Yellow Sea pollution and surveillance system for persistent organic pollutants. Korea, Ministry of Environment, p 439
Monteyne E, Roose P, Janssen CR (2013) Application of a silicone rubber passive sampling technique for monitoring PAHs and PCBs at three Belgian coastal harbours. Chemosphere 91:390–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.11.074
Moschet C, Vermeirssen ELM, Seiz R, Pfefferli H, Hollender J (2014) Picogram per liter detections of pyrethroids and organophosphates in surface waters using passive sampling. Water Res 66:411–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.08.032
Novák J, Vrana B, Rusina T, Okonski K, Grabic R, Neale PA, Escher BI, Macová M, Ait-Aissa S, Creusot N, Allan I, Hilscherová K (2018) Effect-based monitoring of the Danube River using mobile passive sampling. Sci Total Environ 636:1608–1619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.02.201
Ohura T, Sakakibara H, Watanabe I, Shim WJ, Manage PM, Guruge KS (2015) Spatial and vertical distributions of sedimentary halogenated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in moderately polluted areas of Asia. Environ Pollut 196:331–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2014.10.028
Perron MM, Burgess RM, Suuberg EM, Cantwell MG, Pennell KG (2013) Performance of passive samplers for monitoring estuarine water column concentrations: 1. Contaminants of Concern Environ Toxicol Chem 32:2182–2189. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.2321
Perugini M, Visciano P, Giammarino A, Manera M, Nardo WD, Amorena M (2007) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in marine organisms from the Adriatic Sea, Italy. Chemosphere 66:1904–1910. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.07.079
Qiao M, Qi W, Liu H, Qu J (2014) Oxygenated, nitrated, methyl and parent polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in rivers of Haihe River System, China: Occurrence, possible formation, and source and fate in a water-shortage area. Sci Total Environ 481:178–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.02.050
Qin Z, Bragg L, Ouyang G, Niri VH, Pawliszyn J (2009) Solid-phase microextraction under controlled agitation conditions for rapid on-site sampling of organic pollutants in water. J Chromatogr A 1216:6979–6985. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2009.08.052
Rusina TP, Smedes F, Koblizkova M, Klanova J (2010) Calibration of silicone rubber passive samplers: experimental and modeled relations between sampling rate and compound properties. Environ Sci Technol 44:362–367. https://doi.org/10.1021/es900938r
Sacks VP, Lohmann R (2011) Development and use of polyethylene passive samplers to detect triclosans and alkylphenols in an Urban estuary. Environ Sci Technol 45:2270–2277. https://doi.org/10.1021/es1040865
Sacks VP, Lohmann R (2012) Freely dissolved PBDEs in water and porewater of an urban estuary. Environ Pollut 162:287–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.11.028
Stout SA, Magar VS, Uhler RM, Ickes J, Abbott J, Brenner R (2001) Characterization of naturally-occurring and anthropogenic pahs in urban sediments—wycoff/eagle harbor superfund site. Environ Forensics 2:287–300. https://doi.org/10.1080/713848281
Sun C, Soltwedel T, Bauerfeind E, Adelman DA, Lohmann R (2016) Depth profiles of persistent organic pollutants in the north and tropical atlantic ocean. Environ Sci Technol 50:6172–6179. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b05891
Tidwell LG, Allan SE, O’Connell SG, Hobbie KA, Smith BW, Anderson KA (2016) PAH and OPAH Flux during the Deepwater Horizon Incident. Environ Sci Technol 50:7489–7497. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b02784
Verbruggen, EMJ (2012) Environmental risk limits for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs): For direct aquatic, benthic, and terrestrial toxicity. RIVM report 607711007/2012; 2012, 339 p.
Vrana B, Mills GA, Allan IJ, Dominiak E, Svensson K, Knutsson J, Morrison G, Greenwood R (2005) Passive sampling techniques for monitoring pollutants in water. TrAC - Trends Anal Chem 24:845–868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2005.06.006
Vrana B, Smedes F, Allan I, Rusina T, Okonski K, Hilscherová K, Novák J, Tarábek P, Slobodník J (2018) Mobile dynamic passive sampling of trace organic compounds: evaluation of sampler performance in the Danube River. Sci Total Environ 636:1597–1607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.242
Vrana B, Rusina T, Okonski K, Prokeš R, Carlsson P, Kopp R, Smedes F (2019) Chasing equilibrium passive sampling of hydrophobic organic compounds in water. Sci Total Environ 664:424–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.242
Wang Q, Peng F, Chen Y, Jin L, Lin J, Zhao X, Yin J, Li JY (2019a) Heavy metals and PAHs in an open fishing area of the East China Sea. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:21140–21150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05355-z
Wang A, Ralston DK, Bi N, Cheng Z, Wu X, Wang H (2019b) Seasonal variation in sediment transport and deposition on a muddy clinoform in the Yellow Sea. Cont Shelf Res 179:37–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2019.04.009
Wang P, Mi W, Xie Z, Tang J, Apel C, Joerss H, Ebinghaus R, Zhang Q (2020) Overall comparison and source identification of PAHs in the sediments of European Baltic and North Seas, Chinese Bohai and Yellow Seas. Sci Total Environ 737:139535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139535
Xia X, Zhai Y, Dong J (2013) Contribution ratio of freely to total dissolved concentrations of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in natural river waters. Chemosphere 90:1785–1793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.08.021
Ya M, Wang X, Wu Y, Li Y, Yan J, Fang C, Zhao Y, Qian R, Lin X (2017a) Seasonal variation of terrigenous polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons along the marginal seas of china: input, phase partitioning, and ocean-current transport. Environ Sci Technol 51:9072–9079. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b02755
Ya M, Wu Y, Li Y, Wang X (2017b) Transport of terrigenous polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons affected by the coastal upwelling in the northwestern coast of South China Sea. Environ Pollut 229:60–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.05.054
Ya M, Xu L, Wu Y, Li Y, Zhao S, Wang X (2018) Fossil fuel-derived polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the taiwan strait, china, and fluxes across the air-water interface. Environ Sci Technol 52:7307–7316. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b01331
Yates K, Pollard P, Davies I, Webster L, Moffat C (2013) Silicone rubber passive samplers for measuring pore water and exchangeable concentrations of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons concentrations in sediments. Sci Total Environ 463–464:988–996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.06.035
Yu H, Guo T, Wu Z, Lin T, Hu L, Guo Z (2021) Distribution and gas-particle partitioning of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons over the East China Sea and Yellow Sea in spring: Role of atmospheric transport transition. Sci Total Environ 762:143071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143071
Zhang Z, Hibberd A, Zhou JL (2008) Analysis of emerging contaminants in sewage effluent and river water: comparison between spot and passive sampling. Anal Chim Acta 607:37–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2007.11.024
Zhao D, Zhang P, Ge L, Zheng GJ, Wang X, Liu W, Yao Z (2018a) The legacy of organochlorinated pesticides (OCPs), polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in Chinese coastal seawater monitored by semi-permeable membrane devices (SPMDs). Mar Pollut Bull 137:222–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.10.004
Zhao W, Cai M, Adelman D, Khairy M, August P, Lohmann R (2018b) Land-use-based sources and trends of dissolved PBDEs and PAHs in an urbanized watershed using passive polyethylene samplers. Environ Pollut 238:573–580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.02.057
Zhou JL, Maskaoui K (2003) Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water and surface sediments from Daya Bay, China. Environ Pollut 121:269–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(02)00215-4
Acknowledgements
This research was a part of the projects titled 'Determination of freely dissolved POPs using high-speed rotation-type passive sampler (TE99882)' and 'Development of Technology for Impact Assessment and Management of HNS discharged from Marine Industrial Facilities', funded by the Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries, Korea. This research was also supported by the project titled 'Techniques development for management and evaluation of biofouling on ship hulls (20210651)', funded by the Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries, Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jang, Y.L., Jeong, H., Kim, N.Y. et al. Distribution of Freely Dissolved Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Yellow Sea: Application of Improved Passive Sampling Technique. Ocean Sci. J. 57, 314–323 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12601-021-00039-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12601-021-00039-7