Abstract
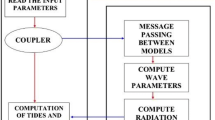
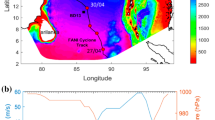
A storm surge is a complex phenomenon in which current, tide, and waves interact with each other. Even if the wind is the main force of driving the surge, waves and tide are also key factors that affect the momentum and mass transport during the storm surge. Although, the Iranian Makran coastal region in the Gulf of Oman is vulnerable to storms and coastal hazards, the interaction of waves on the storm surge has not yet been studied in this region. This paper aims to investigate tropical cyclone-induced waves and storm surges in the Gulf of Oman through the wave-tide-circulation coupled system. The simulations were carried out using the two-way coupling of wave and hydrodynamic models (MIKE 21 SW + MIKE 3 HD) to compute the wave characteristics and water levels during the super cyclone Gonu, which were validated with the field measurements. Model results, and in particular the water level and significant wave height, agreed well with the observations during the Gonu storm’s period. Also, the influences of the key factors interaction (wind, atmospheric pressure, and wave) on a storm surge in the Iranian Makran coasts were evaluated. First, there is a peak surge caused by winds, after that the surges induced by the wave and atmospheric pressure. The wind, pressure, and wave have a contribution of 77.9%, 22.3%, and 10.3%, respectively, in inducing the peak surge of the storm. Key findings of this study indicate the importance of wave-induced setup due to radiation stress as well as the role of the coupled model inaccurate storm surge simulation.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al Najar KA, Salvekar PS (2010) Understanding the tropical cyclone Gonu. In: Charabi Y (ed) Indian ocean tropical cyclones and climate change. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 359–369. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-3109-9
Allahdadi MN, Chaichitehrani N, Allahyar M, McGee L (2017) Wave spectral patterns during a historical cyclone: a numerical model for cyclone gonu in the northern Oman Sea. Open J Fluid Dyn 7:131. https://doi.org/10.4236/ojfd.2017.72009
Allahdadi MN, Chaichitehrani N, Jose F, Nasrollahi A, Afshar A, Allahyar M (2018) Cyclone-generated Storm Surge in the Northern Gulf of Oman: a field data analysis during Cyclone Gonu. Am J Fluid Dyn 8:10–18. https://doi.org/10.5923/j.ajfd.20180801.02
Bertin X, Bruneau N, Breilh J-F, Fortunato AB, Karpytchev M (2012) Importance of wave age and resonance in storm surges: the case Xynthia, Bay of Biscay. Ocean Model 42:16–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocemod.2011.11.001
Brown JM, Wolf J (2009) Coupled wave and surge modelling for the eastern Irish Sea and implications for model wind-stress. Cont Shelf Res 29:1329–1342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2009.03.004
Cavaleri L, Sclavo M (2006) The Calibration of wind and wave model data in the Mediterranean Sea. Coast Eng 53:613–627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coastaleng.2005.12.006
Cavaleri L, Alves J-HGM, Ardhuin F, Babanin A, Banner M, Belibassakis K, Benoit M, Donelan M, Groeneweg J, Herbers THC, Hwang P, Janssen PAEM, Janssen T, Lavrenov IV, Magne R, Monbaliu J, Onorato M, Polnikov V, Resio D, Rogers WE, Sheremet A, McKee Smith J, Tolman HL, van Vledder G, Wolf J, Young I (2007) Wave modelling—the state of the art. Prog Oceanogr 75:603–674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pocean.2007.05.005
DHI (2017a) MIKE zero toolbox. Danish Hydraulic Institute, Hørsholm
DHI (2017b) MIKE 21 & MIKE 3 flow model fm, hydrodynamics and transport module, scientific documentation. Danish Hydraulic Institute, Hørsholm
DHI (2017c) MIKE 21, spectral wave module, scientific documentation. Danish Hydraulic Institute, Hørsholm
Dibajnia M, Soltanpour M, Nairn R, Allahyar M (2010) Cyclone Gonu: the most intense tropical cyclone on record in the Arabian Sea. In: Charabi Y (ed) Indian ocean tropical cyclones and climate change. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 149–157. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-3109-9
Egbert GD, Erofeeva SY (2002) Efficient inverse modeling of barotropic ocean tides. J Atmos Ocean Technol 19:183–204. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0426(2002)019%3c0183:EIMOBO%3e2.0.CO;2
Feng X, Yin B, Yang D, William P (2011) The effect of wave-induced radiation stress on storm surge during Typhoon Saomai (2006). Acta Oceanol Sin 30:20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-011-0115-6
Fritz HM, Blount C, Albusaidi FB, Al-Harthy AHM (2010) Cyclone Gonu storm surge in the Gulf of Oman. In: Charabi Y (ed) Indian ocean tropical cyclones and climate change. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 255–263. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-3109-9
Golshani A, Taebi S (2008) Numerical modeling and warning procedure for Gonu super cyclone along Iranian Coastlines. In: Wallendorf L, Ewing L, Jones C, Jaffe B (eds) Solutions to Coastal Disasters 2008. American Society of Civil Engineers, Reston, pp 268–275. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-3109-9
Hassannezhad M, Soltanpour M, Haghighi S (2011) 2D hydrodynamic modeling and measurements of Chabahar Bay. J Coast Res SI 64:1043–1047
He Z, Tang Y, Xia Y, Chen B, Xu J, Yu Z, Li L (2020) Interaction impacts of tides, waves and winds on storm surge in a channel-island system: observational and numerical study in Yangshan Harbor. Ocean Dyn 70:307–325. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10236-019-01328-5
Jayakrishnan PR, Babu CA (2013) Study of the oceanic heat budget components over the Arabian Sea during the formation and evolution of super cyclone. Gonu Atmos Clim Sci 3:282. https://doi.org/10.4236/acs.2013.33030
JTWC (2019) The joint typhoon warning center tropical cyclone best-tracks, 1945–2019. The Joint Typhoon Warning Center, Naval Meteorology and Oceanography Command, Mississippi
Kim SY, Yasuda T, Mase H (2008) Numerical analysis of effects of tidal variations on storm surges and waves. Appl Ocean Res 30:311–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apor.2009.02.003
Krishna KM, Rao SR (2009) Study of the intensity of super cyclonic storm GONU using satellite observations. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 11:108–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2008.11.001
Kumar VS, Singh J, Pednekar P, Gowthaman R (2011) Waves in the nearshore waters of northern Arabian Sea during the summer monsoon. Ocean Eng 38:382–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2010.11.009
Lee HS (2015) Evaluation of WAVEWATCH III performance with wind input and dissipation source terms using wave buoy measurements for October 2006 along the east Korean coast in the East Sea. Ocean Eng 100:67–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2015.03.009
Lee HS, Yamashita T, Hsu JR-C, Ding F (2013) Integrated modeling of the dynamic meteorological and sea surface conditions during the passage of Typhoon Morakot. Dyn Atmos Ocean 59:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dynatmoce.2012.09.002
Li Y, Feng H, Vigouroux G, Yuan D, Zhang G, Ma X, Kl L (2020) Storm surges in the Bohai Sea: the role of waves and tides. Water 12:1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051509
Mashhadi L, Zaker NH, Soltanpour M, Moghimi S (2013) Study of the Gonu tropical cyclone in the Arabian Sea. J Coast Res 31:616–623. https://doi.org/10.2112/JCOASTRES-D-13-00017.1
Mastenbroek C, Burgers G, Janssen P (1993) The dynamical coupling of a wave model and a storm surge model through the atmospheric boundary layer. J Phys Oceanogr 23:1856–1866. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0485(1993)023%3c1856:TDCOAW%3e2.0.CO;2
Mellor GL (2008) The depth-dependent current and wave interaction equations: a revision. J Phys Oceanogr 38:2587–2596. https://doi.org/10.1175/2008JPO3971.1
Meza-Padilla R, Appendini CM, Pedrozo-Acuña A (2015) Hurricane-induced waves and storm surge modeling for the Mexican coast. Ocean Dyn 65:1199–1211. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10236-015-0861-7
Moon I-J (2005) Impact of a coupled ocean wave–tide–circulation system on coastal modeling. Ocean Model 8:203–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocemod.2004.02.001
Moon I-J, Ginis I, Hara T (2008) Impact of the reduced drag coefficient on ocean wave modeling under hurricane conditions. Mon Weather Rev 136:1217–1223. https://doi.org/10.1175/2007MWR2131.1
Olabarrieta M, Warner JC, Armstrong B, Zambon JB, He R (2012) Ocean–atmosphere dynamics during Hurricane Ida and Nor’Ida: an application of the coupled ocean–atmosphere–wave–sediment transport (COAWST) modeling system. Ocean Model 43:112–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocemod.2011.12.008
Olfateh M, Callaghan DP, Nielsen P, Baldock TE (2017) Tropical cyclone wind field asymmetry—development and evaluation of a new parametric model. J Geophys Res-Ocean 122:458–469. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016JC012237
Pan Y, Chen Y, Li J, Ding X (2016) Improvement of wind field hindcasts for tropical cyclones. Water Sci Eng 9:58–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wse.2016.02.002
Rautenbach C, Daniels T, Vos M, Barnes MA (2020) A coupled wave, tide and storm surge operational forecasting system for South Africa: validation and physical description. Nat Hazards 103:1407–1439. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-020-04042-4
Rhome JR, Raman S (2006) Environmental influences on tropical cyclone structure and intensity: a review of past and present literature. Indian J Geo-Mar Sci 35(2):61–74
Roland A, Cucco A, Ferrarin C, Hsu T-W, Liau J-M, Ou S-H, Umgiesser G, Zanke U (2009) On the development and verification of a 2-D coupled wave-current model on unstructured meshes. J Mar Syst 78:S244–S254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmarsys.2009.01.026
Saha S, Moorthi S, Pan H-L et al (2010) The NCEP climate forecast system reanalysis. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 91:1015–1058. https://doi.org/10.1175/2010BAMS3001.1
Sarker MA (2018) Numerical modelling of waves and surge from Cyclone Chapala (2015) in the Arabian Sea. Ocean Eng 158:299–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2018.04.014
Shao Z, Liang B, Li H, Wu G, Wu Z (2018) Blended wind fields for wave modeling of tropical cyclones in the South China Sea and East China Sea. Appl Ocean Res 71:20–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apor.2017.11.012
Signell RP, Carniel S, Cavaleri L, Chiggiato J, Doyle JD, Pullen J, Sclavo M (2005) Assessment of wind quality for oceanographic modelling in semi-enclosed basins. J Mar Syst 53:217–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmarsys.2004.03.006
Smith WHF, Sandwell DT (1997) Global sea floor topography from satellite altimetry and ship depth soundings. Science 277:1956–1962. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.277.5334.1956
Sørensen OR, Kofoed-Hansen H, Rugbjerg M, Sørensen LS (2005) A third-generation spectral wave model using an unstructured finite volume technique. In: Smith JM (ed) Coastal engineering 2004, vol 4. World Scientific, Singapore, pp 894–906. https://doi.org/10.1142/9789812701916_0071
Takagaki N, Komori S, Suzuki N, Iwano K, Kuramoto T, Shimada S, Kurose R, Takahashi K (2012) Strong correlation between the drag coefficient and the shape of the wind sea spectrum over a broad range of wind speeds. Geophys Res Lett 39(23):L23604. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012GL053988
Wang Z, DiMarco SF, Stössel MM, Zhang X, Howard MK, Vall K (2012) Oscillation responses to tropical Cyclone Gonu in northern Arabian Sea from a moored observing system. Deep-Sea Res Pt I 64:129–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr.2012.02.005
Webster PJ, Holland GJ, Curry JA, Chang H-R (2005) Changes in tropical cyclone number, duration, and intensity in a warming environment. Science 309:1844–1846. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1116448
Wijnands JS, Qian G, Kuleshov Y (2016) Spline-based modelling of near-surface wind speeds in tropical cyclones. Appl Math Model 40:8685–8707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2016.05.013
Willmott CJ (1981) On the validation of models. Phys Geogr 2:184–194. https://doi.org/10.1080/02723646.1981.10642213
Willmott CJ (1982) Some comments on the evaluation of model performance. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 63:1309–1313. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0477(1982)063%3c1309:SCOTEO%3e2.0.CO;2
WMO (2009) WWRP 2010–2—1st WMO International Conference on Indian Ocean Tropical Cyclones and Climate Change. World Meteorological Organization (WMO), WMO/TD-No. 1541
Wolf J (2009) Coastal flooding: impacts of coupled wave–surge–tide models. Nat Hazards 49:241–260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-008-9316-5
Wu J (1980) Wind-stress coefficients over sea surface near neutral conditions—a revisit. J Phys Oceanogr 10:727–740. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0485(1980)010%3c0727:WSCOSS%3e2.0.CO;2
Wu J (1994) The sea surface is aerodynamically rough even under light winds. Bound Lay Meteorol 69:149–158. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00713300
Acknowledgements
Parallel processes conducted in this study were carried out using the cluster system of the Atmospheric Science and Meteorological Research Center (ASMERC) of the I. R. of IRAN Meteorological Organization (IRIMO); also, to validate the results of the model, the field data measured by the monitoring and modeling study of the Iranian coasts and supported by the I. R. IRAN Ports and Maritime Organization (PMO) was used; the authors of the article express their gratitude to these organizations. This research received no specific grant from any funding agency, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siahsarani, A., Karami Khaniki, A., Aliakbari Bidokhti, AA. et al. Numerical Modeling of Tropical Cyclone-Induced Storm Surge in the Gulf of Oman Using a Storm Surge–Wave–Tide Coupled Model. Ocean Sci. J. 56, 225–240 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12601-021-00027-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12601-021-00027-x