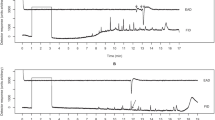
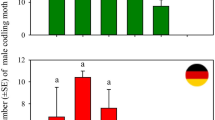
Abstract
The review describes the history of pheromone research in Israel in 1975–2015. The research focused on sex pheromones of moths that were important agricultural pests. Identification, synthesis and field application of sex pheromones was performed. Synthetic procedures of several known sex pheromones were developed. Monitoring and control of key pest moths was evaluated. The interactions of pheromone components of closely related species were studied in field and laboratory experiments. The sex pheromones of three scale insects, two mealybug species and Matsucoccus josephi were studied. New syntheses were developed and the pheromones were implemented in pest management. Structure activity relationship of the pheromonal and kairomonal of the M. josephi pheromone was investigated. Different pherotypes of P. ficus were identified and evaluated. The aggregation pheromone of sap beetles in combination with food baits was evaluated. The aggregation pheromone of the almond bark beetle was identified and a stereospecific synthesis of its enantiomers was developed. Monitoring the pest in stone fruit orchards was implemented. The activity of the pheromone biosynthesis activating neuropeptide (PBAN) was studied in Helicoverpa armigera and Heliothis peltigera. The ligation technique was used to assess the effect of PBAN on the production of female and male pheromones. A structure-activity relationship study of PBAN indicated that shorter peptides display activity as the full length PBAN. A series of linear and cyclic peptide analogs was prepared, resulting in the discovery of a lead antagonist. The research and development activity facilitated the intensive integration of pheromones in the pest management regimes in Israeli agriculture.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altstein, M., & Hariton, A. (2009). Rational design of insect control agents: The PK/PBAN family as a study case. In I. Ishaaya & R. Horowitz (Eds.), Biorational Control of Arthropod Pests: Application and Resistance Management (pp. 49–81). New York: Springer.
Altstein, M., Gazit, Y., & Dunkelblum, E. (1990). Regulation of sex pheromone biosynthesis in Chrysodeixis chalcites and Heliothis peltigera. In: Insect Neurochemistry and Neurophysiology, Edited by Borkovec A.B. & Masler, E.P. pp. 303–307.
Altstein, M., Dunkelblum, E., Gabay, T., Ben-Aziz, O., Schefler, I., & Gazit, Y. (1995). PBAN-Induced sex pheromone biosynthesis in Heliothis peltigera: structure, dose, and time-dependent analysis. Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 30, 307–319.
Altstein, M., Ben-Aziz, O., Daniel, S., Schefler, I., Zeltzer, I., & Gilon, C. (1999). Backbone cyclic peptide antagonists derived from the insect pheromone biosynthetic activating neuropeptide, inhibit sex pheromone biosynthesis in moths. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 274, 17573–17579.
Altstein, M., Ben-Aziz, O., Schefler, I., Zeltzer, I., & Gilon, C. (2000). Advances in the application of neuropeptides in insect control. Crop Protection, 19, 547–555.
Ando, T., Inomata, S., & Yamamoto, M. (2004). Lepidopteran sex pheromones. Topics in Current Chemistry, 239, 51–96.
Anshelevich, L., Kehat, M., Dunkelblum, D., & Greenberg, S. (1993). Sex pheromone traps for monitoring the honeydew moth, Cryptoblabes gnidiella: Effect of pheromone components, pheromone dose, field aging of dispenser, and type of trap on male captures. Phytoparasitica, 21, 189–198.
Argaman, Q. (1990). Rediscription of Maladera matrida (Coleoptera, Scarbaidae, Melolothinae). Israel Journal of Entomology, 88, 21–27.
Bartelt, R. J., Weisleder, D., Dowd, P. F., & Plattner, R. D. (1992). Male-specific tetraene and triene hydrocarbons of Carpophilus hemipterus: structure and pheromonal activity. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 18, 379–402.
Becker, D., & Kimmel, T. (1982). An alternative synthesis of unsaturated aldehydopheromones. Tetrahedron, 38, 1689–1692.
Becker, D., Cyjon, R., Cosse, A., Moore, I., Kimmel, T., & Wysoki, M. (1990). Identification and enantioselective synthesis of (Z,Z)-6,9-cis-(3S,4R)-epoxynonadecadiene, the major sex pheromone component of Boarmia seleneria. Tetrahedron Letters, 31, 4923–4926.
Ben-Yehuda, S., Tolasch, T., Francke, W., Gries, R., Gries, G., Dunkelblum, E., & Mendel, Z. (2002). Aggregation pheromone of the almond bark beetle Scolytus amygdali (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). IOBC wprs Bulletin, 25, 259–270.
Berger, R. S. (1966). Isolation, identification, and synthesis of the sex attractant of the cabbage looper, Trichoplusia ni. Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 59, 767–771.
Bierl-Leonhardt, B. A., Moreno, D. S., Schwarz, M., Fargerlund, J., & Plimmer, J. R. (1981). Isolation, identification and synthesis of the sex pheromone of the citrus mealybug, Planococcus citri (Risso). Tetrahedron Letters, 22, 389–392.
Bjostad, L., Gurevitz, E., Gothilf, S., & Roelofs, W. (1981). Sex attractant for the honeydew moth, Cryptoblabes gnidiella. Phytoparasitica, 9, 95–99.
Blumberg, D., Kehat, M., Goldenberg, S., Bartelt, R. J., & Williams, R. N. (1983). Responses to synthetic aggregation pheromones, host-related volatiles, and their combinations by Carpophilus spp. (Coleoptera: Nitidulidae) in laboratory and field tests. Environmental Entomology, 22, 837–842.
Bober, R., & Rafaeli, A. (2010). Gene-silencing reveals the functional significance of pheromone biosynthesis activating neuropeptide (PBAN-R) in male moth. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107, 16858–16862.
Branco, M., Franco, J. C., Dunkelblum, E., Assael, F., Protasov, A., Ofer, D., & Mendel, Z. (2006). A common mode of attraction of larvae and adults of insect predators to the sex pheromone of their prey (Hemiptera: Matsucoccidae). Bulletin of Entomological Research, 96, 179–185.
Butenandt, A., Beckmann, R., Stamm, D., & Hecker, E. (1959). Über den Sexual-Lockstoff des Seidenspinners Bombyx mori. Reindarstellung und Konstitutionsermittlung. Z Naturforsch, 14b, 283–284.
Cardé, R.T., & Elkinton, J.S. (1984). Field trapping with attractants: Methods and interpretation. Chapter 4, pp 111–129 in Techniques in Pheromone Research. Edit. H.E. Hummel and T.A. Miller, Springer Verlag, New York Berlin, Tokyo.
Cosse, A., Cyjon, R., Moore, I., Wysoki, M., & Becker, D. (1992). Sex pheromone components of the giant looper, Boarmia selenaria Schiff. (Lepidoptera: Geomtridae): identification, synthesis, electrophysiological evaluation and behavioral activity. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 18, 165–181.
Critchley, B. R., Campion, D. G., Cavanagh, G. G., Chameberlain, D. J., & Attique, M. R. (1987). Control of three species of bollworm pests of cotton in Pakistan by a single application of their combined sex pheromone. Tropical Pest Management, 33, 374.
Dunkelblum, E., & Gothilf, S. (1983). Sex pheromone components of the Gamma moth, Autographa gamma (L.) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Z. Naturforsch, 38C, 1011–1014.
Dunkelblum, E., & Kehat, M. (1989). Female sex pheromone components of Heliothis peltigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) Chemical identification from gland extracts and male response. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 15, 2233–2245.
Dunkelblum, E., & Kehat, M. (1992). Sexual behavior of Heliothis peltigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Bulletin of Entomological Research, 82, 13–17.
Dunkelblum, E., & Mazor, M. (1993). Chemical characterization and species specificity of sex pheromones of plusiinae moths in Israel. Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 22, 413–424.
Dunkelblum, E., Gothilf, S., & Kehat, M. (1980). Identification of the sex pheromone of the cotton bollworm Heliothis armigera in Israel. Phytoparasitica, 8, 209–211.
Dunkelblum, E., Gothilf, S., & Kehat, M. (1981). Sex pheromone of the tomato looper, Plusia chalcites (Esp). Journal of Chemical Ecology, 7, 1081–1088.
Dunkelblum, E., Kehat, M., Gothilf, S., Greenberg, S., & Sklarsz, B. (1982). Optimized mixture of sex pheromone components for trapping of male Spodoptera littoralis in Israel. Phytoparasitica, 10, 21–26.
Dunkelblum, E., Kehat, M., Klug, J. T., & Shani, A. (1984). Trimerization of Earias insulana sex pheromone (E,E)-10,12-hexadecadienal, A phenomenon affecting trapping efficiency. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 10, 421–428.
Dunkelblum, E., Snir, R., Gothilf, S., & Harpaz, I. (1987a). Identification of sex pheromone components from pheromone gland volatiles of the tomato looper, Plusia chalcites (Esp). Journal of Chemical Ecology, 13, 991–1003.
Dunkelblum, E., Ben-Dov, Y., Goldschmidt, Z., Wolk, J. A., & Somekh, L. (1987b). Synthesis and field bioassay of some analogs of the sex pheromone of citrus mealybug, Planococcus citri (Risso). Journal of Chemical Ecology, 13, 863–871.
Dunkelblum, E., Mendel, Z., Assael, F., Harel, M., Kerhoas, L., & Einhorn, J. (1993). Identification of the female sex pheromone of the Israeli pine bast scale, Matsucoccus josephi. Tetrahedron Letters, 34, 2805–2808.
Dunkelblum, E., Gries, R., Gries, G., Mori, K., & Mendel, Z. (1995). Chirality of Israeli pine bast scale, Matsucoccus josephi (Homoptera: Matsucoccidae) sex pheromone. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 21, 849–858.
Dunkelblum, E., Mendel, Z., Gries, G., Gries, R., Zegelman, L., Hassner, A., & Mori, K. (1996). Antennal response and field attraction of the predator Elatophilus hebraicus (Hemiptera; Anthocoridae) to sex pheromones and anlogues of three Matsucoccus Spp. (Homoptera: Matsucoccidae). Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 4, 489–494.
Dunkelblum, E., Harel, M., Assael, F., Mori, K., & Mendel, Z. (2000). Specificity of pheromonal and kairomonal response of Israeli pine bast scale, Matsucoccus josephi and its predator Elatophilus hebraicus. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 26, 1649–1657.
Eliyahu, D., Applebaum, S., & Rafaeli, A. (2003). Moth sex-pheromone biosynthesis is inhibited by the herbicide diclofop. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 77, 75–81.
Falach, L., Cojocary, M., & Shani, A. (2003). Evidence for a short-range sex pheromone in female Maladera matrida beetle. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 29, 603–613.
Gaston, L. K., Shorey, H. H., & Sario, S. A. (1967). Insect population control by the use of sex pheromones to inhibit orientation between the sexes. Nature, 213, 1155.
Gazit, Y., Dunkelblum, E., Benichis, M., & Altstein, M. (1990). Effect of synthetic PBAN and derived peptides on sex pheromone biosynthesis in Heliothis peltigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Insect Biochemistry, 20, 853–858.
Gazit, Y., Dunkelblum, E., Ben-Aziz, O., & Altstein, M. (1992). Immunochemical and biological analysis of pheromone biosynthesis activating neuropeptide in Heliothis peltigera. Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 19, 247–260.
Götz, K. (1951). Die Sexualduftstoffe der Lepidopteren. Experientia, 7, 406–418.
Hall, D., Beevor, P. S., Lester, R., & Nesbitt, B. F. (1980). (E,E)-10,12-hexadecadienal: A component of the female sex pheromone of the spiny bollworm, Earias insulana (Boisd.) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Experientia, 36, 152–153.
Hallet, R. H., Gries, G., Bordedn, J. H., Czyzewska, E., Oehlschlager, A. C., Pierce Jr., H. D., Angerilli, N. P. D., & Rauf, A. (1993). Aggregation pheromones of two Asian palm weevils, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus and R. vulneratus. Naturwissenschaften, 80, 328–331.
Halperin, J., Golan, Y., Descoins, Ch., Frerot, B., Shani, A., & Klug, J.T. (1991). Preliminary trials on attraction of Thaumatopea wilkinsoni Tams to the synthetic sex pheromoneof Th. Pityocampa Schiff. La Ya’aran 31, 24–31 (in Hebrew with English abstract).
Hameiri, J., Goren, M., Or, R., Malca, S., & Brener, J. (1991). Pheromone ropes for the control of the pink bollworm in cotton in Bet Shean. Hassadeh, 71, 1153–1154 (in Hebrew with English abstract).
Harari, A. R., Zahavi, T., Gordon, D., Anshelevich, L., Harel, M., Ovadia, S., & Dunkelblum, E. (2007). Pest management programs in vineyards using male mating disruption. Pest Management Science, 63, 769–775.
Hecker, E., & Butenandt, A. (1984). Bombykol revisted – reflections on a pioneering period and on some of its consequences. Chapter 1, pp 1–44 in Techniques in Pheromone Research. Edit. H.E. Hummel and T.A. Miller, Springer Verlag, New York Berlin Heidelberg Tokyo.
Hefetz, A., & Tauber, O. (1990). Male response to the synthetic sex pheromone of Planococcus citri (Risso) (Hom., Pseudococcidae) and its application for population monitoring. Journal of Applied Entomology, 109, 502–506.
Hinkens, D. M., McElfresh, S. J., & Millar, J. G. (2001). Identification and synthesis of the sex pheromone of the vine mealybug, Planococcus ficus. Tetrahedron Letters, 42, 1619–1621.
Hosny, M.M., Isshak, R.R., Nasr El Sayed, A., El-Deeb, Y.A., Critchley, R.R., Topper, C., & Campion, D.G. (1979). Mass trapping for the control of the Egyptian cotton leafworm Spodoptera littoralis (Boisd.) in Egypt. Proccedings 1979 British Crop Protection Conference Pests and Diseases, Brighton, pp. 395–400.
Hummel, H. E., Lyle, K., Gaston, L. K., Shorey, H. H., Kaae, R. S., Byrne, K. J., & Silverstein, R. M. (1973). Clarification of the chemical status of the pink bollworm sex pheromone. Science, 181, 873–875.
Idesis, R., & Shani, A. (1998). Chemical protection of pheromones containing an internal conjugated diene system from isomerization and oxidation. Journal of Chemical Ecology , 14, 1657–1669.
Idesis, R., Klug, J. T., Shani, A., Gothilf, S., & Gurevitz, E. (1982a). Sex pheromone of the European grapevine moth, Lobesia botrana Schiff. (Lepidoptera: Torticidae): synthsis and effect of isomeric purity on biological activity. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 8, 195–200.
Idesis, R., Shani, A., & Klug, J. T. (1982b). Cyclic peroxide: an isolable intermediate in singlet oxygen oxidation of pheromones to the furan system. Chemistry & Industry, 409-410.
Kehat, M., & Dunkelblum, E. (1993). Sex pheromones: Achievements in monitoring and mating disruption of cotton pests in Israel. Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 22, 425–431.
Kehat, M., & Dunkelblum, E. (1990). Behavioral responses of male Heliothis armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) moths in a flight tunnel to combinations of components identified from female sex pheromone glands. Journal of Insect Behavior, 3, 75–83.
Kehat, M., & Gordon, D. (1975). Mating, longevity, fertility and fecundity of the Egyptian cotton leafworm Spodoptera littoralis (Boisd.) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Phytoparasitica, 3, 87–102.
Kehat, M., & Greenberg, S. (1978). Efficiency of the synthetic sex attractant and the effect of trap size on captures of Spodoptera littoralis males in water traps and in dry funnel traps. Phytoparasitica, 6, 79–83.
Kehat, M., Greenberg, S., & Tamaki, Y. (1976). Field evaluation of the synthetic sex pheromone, as attractant for males of the cotton leaf worm, Spodoptera littoralis (Boisd.), in Israel. Applied Entomology and Zoology, 11, 45–52.
Kehat, M., Gothilf, S., Dunkelblum, E., & Greenberg, S. (1979). Communication disruption of the cotton leafworm, Spodoptera littoralis, by using its sex pheromone or other related compounds emitted at different distances from the attractant. Environmental Entomology, 8, 973–975.
Kehat, M., Gothilf, S., Dunkelblum, E., & Greenberg, S. (1980). Field evaluation of the female sex pheromone components of the cotton bollworm, Heliothis armigera. Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata, 27, 188–193.
Kehat, M., Gothilf, S., Dunkelblum, E., & Mazor, M. (1981). Sex pheromone traps as a potential means improving control programs for the spiny bollworm, Earias insulana. Phytoparasitica, 9, 149–151.
Kehat, M., Dunkelblum, E., & Gothilf, S. (1983a). Mating disruption of the cotton leafworm, Spodoptera littoralis, (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), by release of sex pheromone from widely separated Hercon-laminated dispensers. Environmental Entomology, 12, 1265–1269.
Kehat, M., Blumberg, D., & Williams, R. N. (1983b). Seasonal abundance of sap beetles (Coleoptera: Nitidulidae) in date plantations in Israel. Phytoparasitica, 11, 109–112.
Kehat, M., Dunkelblum, E., Gothilf, S., Bar-Shavit, N., & Gordon, D. (1985). Night observations on the cotton leafworm, Spodoptera littoralis: reliability of pheromone traps for population assessment and efficacy of widely separated pheromone dispensers for mating disruption. Phytoparasitica, 13, 215–220.
Kehat, M., Dunkelblum, E., Gothilf, S., Bar-Shavit, N., Gordon, D., & Harel, M. (1986). Mating disruption of the Egyptian cotton leafworm, Spodoptera littoralis, (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), in cotton with polymeric aerosol formulation containing (Z,E)-9,11-tetradecadienyl acetate. Journal of Economic Entomology, 79, 1641–1644.
Kehat, M., Anshelevich, L., & Dunkelblum, E. (1995). Control of codling moth, Cydia pomonella (L.) by mating disruption in apple and pear orchards in Israel. Phytoparasitica, 23, 285–296.
Kehat, M., Anshelevich, L., Gordon, D., Harel, M., & Dunkelblum, E. (1998). Evaluation of Shin-Etsu twist-tie rope dispensers by mating table technique for disrupting mating of the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), and the pink bollworm, Pectinophora gossypiella (Lepidoptera: Gelechidae). Bulletin of Entomological Research, 88, 141–148.
Kehat, M., Anshelevich, L., Gordon, D., Harel, M., Zilberg, L., & Dunkelblum, E. (1999). Effect of density of pheromone sources, dosage and population pressure on mating of pink bollworm, Pectinophora gossypiella (Lepidoptera: Gelechidae). Bulletin of Entomological Research, 89, 339–345.
Klug, J.T., Skorka, J., & Shani, A. (1982). A short synthesis of (E,E)-10,12-hexadecadienal: The main component of the female sex pheromone of the spiny bollworm (Earias insulana). Chemistry & Industry pp. 372-373.
Kol-Maimon, H., Levi-Zada, A., Franco, J. C., Dunkelblum, E., Protasov, A., Eliyahu, M., & Mendel, Z. (2010). Male behaviors reveal multiple pherotypes within vine mealybug Planococcus ficus (Signoret) (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) populations. Naturwissenschaften, 97, 1047–1057.
Kurosawa, S., Takenaka, M., Dunkelblum, E., Mendel, Z., & Mori, K. (2000). Pheromoneal and kairomonal activities can be separated: Synthesis and bioactivity studies of pine bast scale sex pheromones and their analogues. Chembiochem, 1, 56–66.
Levi-Zada, A., Ben-Yehuda, S., Dunkelblum, E., Gindin, G., Fefer, D., Protasov, A., Kuznetsova, T., Manulis-Sasson, S., & Mendel, Z. (2011a). Identification and field bioassay of the sex pheromone of the yellow-legged clearwing Synanthedon vespiformis (Lepidoptera: Sessidae). Chemecology, 21, 227–233.
Levi-Zada, A., Fefer, D., Anshelevitch, L., Litovsky, A., Bengston, M., Gindin, G., & Soroker, V. (2011b). Identification of the sex pheromone of the lesser date moth, Batrachedrae amydraula, using sequential SPME auto-sampling. Tetrahedron Lett.
ers52, 4550-4553.Levi-Zada, A., Nestel, D., Fefer, D., Deloya-Kahane, I., Nemni-Lavy, E., & David, M. (2012). Analyzing diurnal and age-related pheromone emission of the olive fruit fly, Bactrocera oleae (Diptera: Tephritidae) by sequential SPME-GCMS analysis. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 38, 1036–1041.
Levi-Zada, A., Sadovsky, A., Dobrinin, S., David, M., Tichushinski, T., Fefer, D., Greenberg, A., & Blumberg, D. (2013). Reevaluation of the sex pheromone of the lesser date moth, Batrachedra amydraula, using autosampling SPME-GC/MS and field bioassays. Chem, 23, 13–20.
Levi-Zada, A., David, M., Fefer, D., Seplyarsky, V., Sadovsky, A., Dobrinin, S., Ticushinski, T., Harari, D., Blumberg, D., & Dunkelblum, E. (2014a). Circadian release of male-specific components of the greater date moth, Aphomia (Aripensis) sabella, using sequential SPME/GC/MS analysis. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 40, 236–243.
Levi-Zada, A., Fefer, D., David, M., Eliyahu, M., Franco, J. C., Protasov, A., Dunkelblum, E., & Mendel, Z. (2014b). Diel periodicity of pheromone release by females of Planococcus citri and Planococcus ficus and the temporal flight activity of their conspecific males. Naturwissenschaften, 101, 671–678.
Levi-Zada, A., Sadowsky, A., Dobrinin, S., Ticuchinski, T., David, M., Fefer, D., Dunkelblum, E., & Byers, J. A. (2017). Monitoring and mass-trapping methodologies using pheromones: The lesser date moth Batrachedra amydraula. Bulletin of Entomological Research. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007485317000487.
Linn, C. E., Bjostad, L. B., Du, J. W., & Roelofs, W. L. (1984). Redundancy in a chemical signal: Behavioral response of male Trichoplusia ni to a 6-components sex pheromone blend. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 10, 1635–1658.
Mazor, M., & Dunkelblum, E. (1992). Role of sex pheromone components in behavioral reproductive isolation between Autographa gamma (L.) and either Trichoplusia ni (Hubner) or Chrysodeixis chalcites (Esp.) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae: Plusiinae). Journal of Chemical Ecology, 18, 2373–2384.
Mazor, M., & Dunkelblum, E. (1993). Chemical characterization and species specificity of sex pheromones of Plusiinae moths in Israel. Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 22, 413–424.
Mazor, M., Harel, M., Levsky, S., & Dunkelblum, E. (1991). Female sex pheromone components of Conutiplusia circumflexa (L.) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae: Plusiinae). Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata, 60, 167–172.
Mendel, Z. (1988). Attraction of pine bark beetles to the synthetic aggregation pheromone formulation of Orthotomicus erosus and Ips typographus. Phytoparasitica, 16, 109–117.
Mendel, Z., Saphir, N., & Robison, D. (1990a). Mass rearing of the Israeli pine bast scale, Matsucoccus josephi (Homoptera: Margarodidae), with notes on its biology and mating behavior. Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 83, 532–537.
Mendel, Z., Robison, D., & Dunkelblum, E. (1990b). Sexual behavior of Matsucoccus josephi (Homoptera: Margarodidae) Asynchronous adult male emergence and release of female sex pheromone. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 16, 2341–2352.
Mendel, Z., Boneh, O., & Riov, J. (1992). Some foundations for application of aggregation pheromones to control pine bark beetles in Israel. Journal of Applied Entomology, 114, 217–227.
Mendel, Z., Zegelman, L., Hassner, A., Assael, F., Harel, M., Tam, S., & Dunkelblum, E. (1995). Outdoor attractancy of males of Matsucoccus josephi (Homoptera: Matsucoccidae) and Elatophilus hebraicus (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae) to synthetic female sex pheromone of Matsucoccus josephii. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 21, 331–341.
Mendel, Z., Dunkelblum, E., Branco, M., Franco, J. C., Kurosawa, S., & Mori, K. (2003). Synthesis and structure-activity relationship of diene modified analogs of Matsucoccus sex pheromones. Naturwissenschaften, 90, 313–317.
Mendel, Z., Assael, F., & Dunkelblum, E. (2004). Kairomonal attraction of predatory bugs (Heteroptera: Anthocoridae) and brown lacewings (Neuroptera: Hemerobiidae) to sex pheromones of Matsucoccus species (Hemiptera: Matsucoccidae). Biological Control, 30, 134–140.
Mendel, Z., Jasrotia, P., Protasov, A., Kol-Maimon, H., Levi-Zada, A., & Franco, J. C. (2012). Responses of second-instar male nymphs of four mealybug species (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) to conspecific and heterospecific female sex pheromones. Journal of Insect Behavior, 25, 504–513.
Moore, I. (1981). Biological amplification for increasing electroanntenogram between female sex pheromone components of Spodoptera littoralis (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Journal of Chemical Ecology, 7, 791–798.
Mori, K., & Amaike, M. (1994). Synthesis of (2E,5R,6E,8E)-5,7-dimethyl-2,6,8-decatrien-4-one, the major component of the sex pheromone of the Israeli pine bast scale and its antipode. Journal of the Chemical Society, Perkin Transactions 1, 2727–2733.
Nakache, J., Dunkelblum, E., Kehat, M., Anshelevich, L., & Harel, M. (1992). Mating disruption of the spiny bollworm, Earias insulana (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), with Shin Etsu twist-tie ropes in Israel. Bulletin of Entomological Research, 82, 369–373.
Navon, A. (1978). A modified dry pheromone trap for Spodoptera littoralis male moths. Phytoparasitica, 6, 21–24.
Navon, A., Cohen, M., Keren, S., Levski, S., Harel, M., & Dunkelblum, E. (1997). Trapping of the Leopard moth, Zeuzera pyrina L. (Cossidae: Lepidoptera) with sex-pheromone traps fpr monitoring the pest. Experiments in apple and pear orchards, 1995-1996. Alon Hanotea, 51(8), 358–366 (in Hebrew with English abstract).
Nesbit, B. F., Beevor, P. S., Hall, D. R., Lester, R., Sternlicht, M., & Goldenberg, S. (1977). Identification and synthesis of the female sex pheromone of the citrus flower moth, Prays citri. Insect Biochemistry, 7, 355–359.
Nesbitt, B. F., Beevor, P. S., Cole, R. A., Lester, R., & Poppi, R. G. (1973). Sex pheromone of two noctuid moths. Nature: New Biology, 244, 208–209.
Nesbitt, B. F., Beevor, P. S., Hall, D. R., & Lester, R. (1979). Female sex pheromone components of the cotton bollworm, Heliothis armigera. Journal of Insect Physiology, 25, 535–541.
Or, R., Kehat, M., Chen, C., Klein, Z., & Fishler, G. (1986). Determining the efficiency of sex pheromones in controlling the pink bollworm, Pectinophora gossypiella (Saunders) (Lepidoptera: Gelechidae), in cotton fields in Israel. Israel Journal of Entomology, 20, 25–35.
Perez, A. L., Hallet, R. H., Gries, R., Gries, G., Oehlschlager, A. C., & Borden, J. H. (1996). Pheromone chirality of Asian palm weevils Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Oliv.) and R. vulneratus (Panz.) (Coleoptera: Curculiondae). Journal of Chemical Ecology, 22, 357–368.
Piccardi, P., Capizzi, G., Cassani, G., Spinelli, P., Arsura, E., & Masardo, P. (1997). A sex pheromone component of the old world bollworm, Heliothis armigera. Journal of Insect Physiology, 23, 1443–1445.
Rafaeli, A., & Soroker, V. (1989a). Influence of diel rhythm and brain hormone on pheromone production in two lepidopteran species. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 15, 447–455.
Rafaeli, A., & Soroker, V. (1989b). Cyclic AMP mediation of the hormonal stimulation of 14C-acetate incorporation by Heliothis armigera pheromone glands in vitro. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, 65, 43–48.
Rafaeli, A., Soroker, V., Kamensky, B., & Raina, A.K. (1990). Action of pheromone biosynthesis activating neuropeptide on in vitro pheromone glands of Heliothis armigera females. Journal of Insect Physiology, 36, 641–646.
Rafaeli, A., Hirsh, J., Soroker, V., Kamensky, B., & Raina, A. K. (1991). Spatial and temporal distribution of pheromone biosynthesis activating neuropeptide in Helicoverpa (Heliothis) armigera using RIA and in vitro bioassay. Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 18, 119–129.
Raina, A. K., & Klun, J. A. (1984). Brain factor control of sex pheromone production in the female corn earworm moth. Science, 225, 531–532.
Raina, A. K., Jaffe, H., Kempe, T. G., Keim, P., Blacher, R. W., Fales, H. M., Riley, C. T., Klun, J. A., Ridgway, R. L., & Hayes, D. K. (1989). Identification of a neuropeptide hormone thatregulates sex pheromone production in female moths. Science, 244, 796–798.
Reuveny, H., Oppenheim, D., Dunkelblum, E., & Akunis, O. (2001). Control of the codling moth (Cydia pomonella) by mating disruption and monitoring the pest population levels under these conditions. Alon Hanotea, 55, 143–147 (in Hebrew with English abstract).
Reuveny, H., Zada, A., Harari, A., & Oppenheim, D. (2006). Abstract of efficiency of pheromone and egg traps to monitoring the leopard moth Zeuzera pyrina L. Alon Hanotea, 60(8), 18–39 (in Hebrew with English abstract).
Reuveny, H., Oppenheim, D., & Zada, A. (2010). The efficiency of mating disruption technique in controlling the Anarsia lineatella. Alon Hanotea, 64(2), 24–31 (in Hebrew with English abstract).
Rotundo, G., & Tremblay, E. (1980). Evaluation of the daily rate of pheromone release by the females of two mealybug species (Homoptera Coccoidea Pseudococcidae). Boll. Lab Entomol Agric F Silvestri Portici, 37, 167–170.
Shani, A., & Klug, J. T. (1980). Sex pheromone of Egyptian cotton leafworm (Spodopterra littoralis). Its chemical transformation under field conditions. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 6, 875–881.
Shani, A., Klug, J. T., & Skorka, J. (1983). Stereoselective synthesis of Z-13-hexadecen-11-yl acetate, the mjor component of the sex pheromone of the pine processionary moth (Thaumetopea pityocampa). Journal of Chemical Ecology, 9, 863–867.
Sharon, R., Zahavi, T., Sokolsky, T., Sofer-Arad, C., Maor, T., Kedoshim, R., & Harari, A. R. (2016). Mating disruption method against the vine mealybug, Planococcus ficus: effect of sequential treatement on infested vines. Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata, 161, 65–69.
Shorey, H. H. (1977). Manipulation of insect pests of agricultural crops. In H. H. Shorey & J. J. McKelvey (Eds.), Chemical control of insect behavior: theory and application (pp. 353–367). New York: Wiley.
Snir, R., Dunkelblum, E., Gothilf, S., & Harpaz, I. (1986). Sexual behavior and pheromone titre in the tomato looper, Plusia chalcites (ESP.) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Journal of Insect Physiology, 32, 735–739.
Soroker, V., & Rafaeli, A. (1989). In vitro hormonal stimulation of [14C]acetate incorporotaion by Heliothis armigera pheromone glands. Insect Biochemistry, 19, 1–5.
Soroker, V., Blumberg, D., Haberman, A., Hamburger-Rishard, M., Reneh, S., Talebaev, S., Anshelevich, L., & Harari, A. (2005). Current status of red palm weevil infestation in date palm plantations in Israel. Phytoparasitica, 33, 97–106.
Sternlicht, M., Goldenberg, S., Nesbitt, B. F., Hall, D. R., & Lester, R. (1978). Field evaluation of the synthetic female sex pheromone of the citrus flower moth, Prays citri (Mill.) (Lepidoptera: Yponomeutidae), and related compounds. Phytoparasitica, 6, 101–113.
Sternlicht, M., Bar-Zacayi, I., Szivos, Y., & Dunkelblum, E. (1981). Prediction of infestation by and control of the California red scale, Aonidiella auranti (Maskell), through use of its pheromone. Proceedings of the International Society of Citriculture, 2, 695–700.
Sternlicht, M., Barzakay, I., & Tamin, M. (1990). Mangement of Prays citri in lemon orchards by mass trapping of males. Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata, 55, 59–67.
Tamaki, Y., & Yushima, T. (1974). Sex pheromone of the cotton leafworm, Spodoptera littoralis. Journal of Insect Physiology, 20, 1004–1014.
Teich, I., Neumark, S., Jacobson, M., Klug, J. T., & Shani, A. (1979). Mass trapping for the control of the Egyptian cotton leafworm Spodoptera littoralis and large scale synthesis of podlure. In F. J. Ritter (Ed.), Chemical Ecology: Odour Comunication in Animals (pp. 343–350). North Holland Biomedical Press: Elsevier.
Teich, I., Shani, A., & Klug, J. T. (1985). The role of mass trapping of the Egyptian cotton leafworm Spodoptera littoralis (Boisd) in its integrated pest control. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, A20(8), 943–955.
Tonini, C., Cassani, G., Massardo, P., Guliemetti, G., & Castellari, P. L. (1986). Study of female sex pheromone of leopard moth, Zeuzera pyrina L. Isolation and identification of three components. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 12, 1545–1558.
Wolk, J.A., Goldschmidt, Z., & Dunkelblum, E. (1986). A short synthesis of (+)-cis-planococcyl acetate, sex pheromone of the citrus mealybug, Planococcus citri (Risso). Synthesis (pp. 347–348).
Zada, A., & Dunkelblum, E. (2006). A convenient resolution of racemic lavandulol through lipase-catalyzed acylation with succinic anhydride: simple preparation of enantiomerically pure (R)-lavandulol. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry, 17, 230–233.
Zada, A., & Harel, M. (2004). Enzymatic transesterification of racemic lavandulol: preparation of the two enantiomeric alcohols and of the two enantiomers of lavadulyl senecioates. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry, 15, 2339–2343.
Zada, A., Dunkelblum, E., Harel, M., Assael, F., Harel, M., Cojocaru, M., & Mendel, Z. (2003). Sex pheromone of the vine mealybug, Planoccocus ficus in Israel: Occurrence of a second component in a mass-reared population. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 29, 977–988.
Zada, A., Dunkelblum, E., Harel, M., Assael, F., Gross, S., & Mendel, Z. (2004a). Sex pheromone of the citrus mealybug, Planococcus citri: Synthesis and optimization of trap parameters. Journal of Economic Entomology, 97, 361–368.
Zada, A., Ben-Yehuda, S., Dunkelblum, E., Harel, M., Assael, F., & Mendel, Z. (2004b). Synthesis and biological activity of the four stereoisomers of 4-methyl-3-heptanol: main component of the aggregation pheromone of Scolytus amygdali. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 30, 631–641.
Zada, A., Dunkelblum, E., Assael, F., Franco, J. C., da Silva, E. B., Protasov, A., & Mendel, Z. (2008). Attraction of Planococcus ficus males to racemic and chiral pheromone baits: flight activity and bait longevity. Journal of Applied Entomology, 132, 480–489.
Zegelman, L., Hassner, A., Mendel, Z., & Dunkelblum, E. (1993). Synthesis and field bioassay of the Israeli pine bast scale, Matsucoccus joephi, female sex pheromone. Tetrahedron Letters, 34, 5641–5644.
Zeltzer, I., Gilon, C., Ben-Aziz, O., Schefler, I., & Altstein, M. (2000). Discovery of a linear lead antagonist to the insect pheromone biosynthesis activating neuropeptide (PBAN). Peptides, 21, 1457–1465.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all reviewers for their constructive and helpful remarks.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dedicated to the late Dr. Moshe Kehat
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dunkelblum, E., Levi-Zada, A. Pheromone Research and Development in Israel 1975–2015. Phytoparasitica 45, 619–637 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-017-0617-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-017-0617-7