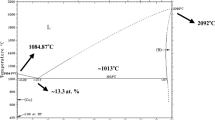
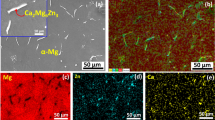
Abstract
The microstructure and properties of as-cast Zr-2.5Nb-1X (X = Ru, Mo, Ta and Si) alloy are screened to explore novel biomedical zirconium alloys for magnetic resonance applications. Corresponding microstructure and phase transformation were characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and transmission electron microscope (TEM). Hardness test, magnetic detection and electrochemical corrosion measurements are taken to present properties. The results show that all alloys consist of α-Zr, β-Zr and ω-Zr. α-Zr and β-Zr mainly exist in the form of parallel and intersecting plates, and nanoscale ω-Zr is dispersed in β-Zr plate. Especially, blocky ω-Zr with needle-like α-Zr is only found in plate-free blocks of Zr-2.5Nb-1Mo/Ru alloy. The orientation relationship (OR) between α- Zr and ω-Zr follows \( \left[ {11\bar{2}0} \right]_{\upalpha} \)//\( \left[ {1\bar{1}01} \right]_{\upomega} \) and \( \left( {0001} \right)_{\upalpha} \)//(\( \left[ {\bar{1}011} \right]_{\upomega} \) 011)ω. Combining this OR with the OR between β-Zr and ω-Zr, the transformation relationship between β-Zr/ω-Zr and α-Zr is also discussed. Zr-2.5Nb-1Ru alloy with high corrosion potential (− 0.500 V), low corrosion rate (0.949 μm·year–1) and low magnetic susceptibility (92 × 10−6) shows great potential to be a novel biomedical implant with magnetic resonance imaging compatibility. Based on the experimental results, the possible relationship among alloying elements, microstructure and properties has been established in these Zr-2.5Nb-1X alloys.
Graphical abstract

摘要
为了探索用于磁共振领域的新型生物医用锆合金,铸态Zr-2.5Nb-1X(X= Ru, Mo, Ta and Si)合金的微观组织和性能 被浏览。对应的微观结构和相变被X 射线、扫描电镜和透射电镜表征。硬度,磁学性能和电化学腐蚀性能被用来 呈现合金的性能。结果显示所有的合金均含有α-Zr、 β-Zr 和ω-Zr。α-Zr 和β-Zr 通常以平行和交错板条的形式存 在,纳米尺度的ω-Zr 弥散分布在β-Zr 板条内。特别地,在Zr-2.5Nb-1Mo/Ru 合金中发现了含有针状α-Zr 的块状 ω-Zr。α-Zr 和ω-Zr 的取向关系遵循[11"2" ̅0]α // [1"1" ̅01]ω and (0001)α // ("1" ̅011)ω。结合该种取向以及β-Zr 和 ω-Zr 的取向,讨论了α-Zr 与 β-Zr 和ω-Zr 之间的转变关系。由于拥有高的腐蚀电位、低的腐蚀速率和低的磁化 率,Zr-2.5Nb-1Ru 在新型磁兼容生物植入物显示出巨大潜力。基于Zr-2.5Nb-1X 合金的实验结果,合金元素、微 观组织和性能三者之间可能存在的关系被建立。









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Olsrud J, Latt J, Brockstedt S, Romner B, Bjorkman-Burtscher IM. Magnetic resonance imaging artifacts caused by aneurysm clips and shunt valves: dependence on field strength (1.5 and 3 T) and imaging parameters. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2005;22(3):433. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.20391.
Shafiei F, Honda E, Takahashi H, Sasaki T. Artifacts from dental casting alloys in magnetic resonance imaging. J Dent Res. 2003;82(8):602. https://doi.org/10.1177/154405910308200806.
Bui FM, Bott K, Mintchev MP. A quantitative study of the pixel-shifting, blurring and nonlinear distortions in MRI images caused by the presence of metal implants. J Med Eng Technol. 2000;24(1):20. https://doi.org/10.1080/030919000294003.
Matsuura H, Inoue T, Konno H, Sasaki M, Ogasawara K, Ogawa A. Quantification of susceptibility artifacts produced on high-field magnetic resonance images by various biomaterials used for neurosurgical implants. Techn J Neurosurg. 2002;97(6):1472. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2002.97.6.1472.
Matsuura H, Inoue T, Ogasawara K, Sasaki M, Konno H, Kuzu Y, Nishimoto H, Ogawa A. Quantitative analysis of magnetic resonance imaging susceptibility artifacts caused by neurosurgical biomaterials: comparison fo 0.5, 1.5, and 3.0 Tesla magnetic fields. Neurol Med Chir. 2005;45(3):395. https://doi.org/10.2176/nmc.45.395.
Mehjabeen A, Song T, Xu W, Tang HP, Qian M. Zirconium alloys for orthopaedic and dental applications. Adv Eng Mater. 2018;20(9):1800207. https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.201800207.
Chen Q, Thouas GA. Metallic implant biomaterials. Mater Sci Eng R. 2015;87:1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mser.2014.10.001.
Niinomi M. Recent metallic materials for biomedical applications. Metall Mater Trans A. 2002;33(3):477. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-002-0109-2.
Hernigou P, Mathieu G, Poignard A, Manicom O, Filippini P, Demoura A. Oxinium, a new alternative femoral bearing surface option for hip replacement. Eur J Orthop Surg Tr. 2007;17(3):243. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-006-0180-2.
Imai H, Tanaka Y, Nomura N, Tsutsumi Y, Doi H, Kanno Z, Ohno K, Ono T, Hanawa T. Three-dimensional quantification of susceptibility artifacts from various metals in magnetic resonance images. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(9):8433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2013.05.017.
Kondo R, Nomura N, Suyalatu TY, Doi H, Hanawa T. Microstructure and mechanical properties of as-cast Zr-Nb alloys. Acta Biomater. 2011;7(12):4278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2011.07.020.
Zhou FY, Wang BL, Qiu KJ, Lin WJ, Li L, Wang YB, Nie FL, Zheng YF. Microstructure, corrosion behavior and cytotoxicity of Zr–Nb alloys for biomedical application. Mater Sci Eng C. 2012;32(4):851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2012.02.002.
Yang HL, Juaim AN, Zou L, Zhu MZ, Chen XN, Ma CX, Zhou XW. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of newly developed Zr-30Ta and Zr-25Ta-5Ti alloys against implant-associated infection. Rare Metals. 2022;41(12):4176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-022-02144-5.
Li Y, Yang C, Zhao H, Qu S, Li X, Li Y. New developments of Ti-based alloys for biomedical applications. Materials. 2014;7(3):1709. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7031709.
Zhou YL, Niinomi M, Akahori T, Fukui H, Toda H. Corrosion resistance and biocompatibility of Ti–Ta alloys for biomedical applications. Mater Sci Eng A. 2005;398(1–2):28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2005.03.032.
Zhou YL, Niinomi M, Akahori T. Effects of Ta content on Young’s mo dulus and tensile properties of binary Ti–Ta alloys for biomedical applications. Mater Sci Eng A. 2004;371(1–2):283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2003.12.011.
Rosalbino F, Maccio D, Giannoni P, Quarto R, Saccone A. Study of the in vitro corrosion behavior and biocompatibility of Zr-2.5Nb and Zr-1.5Nb-1Ta (at%) crystalline alloys. J Mater Sci Mater M. 2011;22(5):1293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-011-4301-z.
Tsuno AT, Tanaka Y, Kondo R, Nomura N, Tsutsumi Y, Hanawa T. Effect of Ta content on the magnetic susceptibility of Zr–Ta binary alloys preventing artefacts for MRI. Adv Mater Process Te. 2016;2(4):606. https://doi.org/10.1080/2374068x.2016.1247336.
Wataha JC. Biocompatibility of dental casting alloys: a review. J Prosthet Dent. 2000;83(2):223. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-3913(00)80016-5.
Atsuta M, Matsumura H, Tanaka T. Bonding fixed prosthodontic composite resin and precious metal alloys with the use of a vinyl-thiol primer and an adhesive opaque resin. J Prosthet Dent. 1992;67(3):296. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3913(92)90233-z.
Schutz RW. Ruthenium enhanced titanium alloys. Platin Met Rev. 1996;40:54.
Li HF, Zhou FY, Li L, Zheng YF. Design and development of novel MRI compatible zirconium-ruthenium alloys with ultralow magnetic susceptibility. Sci Rep. 2016;6:24414. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep24414.
Suyalatu KR, Tsutsumi Y, Doi H, Nomura N, Hanawa T. Effects of phase constitution on magnetic susceptibility and mechanical properties of Zr-rich Zr-Mo alloys. Acta Biomater. 2011;7(12):4259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2011.07.005.
Suyalatu N, Nomura K, Oya Y, Tanaka R, Kondo H, Doi Y, Tsutsumi TH. Microstructure and magnetic susceptibility of as-cast Zr-Mo alloys. Acta Biomater. 2010;6(3):1033. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2009.09.013.
Zhou FY, Wang BL, Qiu KJ, Li L, Lin JP, Li HF, Zheng YF. Microstructure, mechanical property, corrosion behavior, and in vitro biocompatibility of Zr-Mo alloys. J Biomed Mater Res B. 2013;101(2):237. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.b.32833.
Okamoto H. The Si-Zr (silicon-zirconium) system. J Phase Equilib. 1990;11(5):513. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02898272.
Bandyopadhyay D. The Ti-Si-C system (titanium-silicon-carbon). J Phase Equilib Diff. 2004;25(5):415. https://doi.org/10.1361/15477030420890.
Kim HS, Kim WY, Lim SH. Microstructure and elastic modulus of Ti–Nb–Si ternary alloys for biomedical applications. Scr Mater. 2006;54(5):887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2005.11.001.
Zhan YZ, Zhang XJ, Hu J, Guo QH, Du Y. Evolution of the microstructure and hardness of the Ti–Si alloys during high temperature heat-treatment. J Alloys Compd. 2009;479(1–2):246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.01.017.
Li CL, Zhan YZ, Jiang WP. Zr–Si biomaterials with high strength and low elastic modulus. Mater Design. 2011;32(8–9):4598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2011.03.072.
Kondo R, Shimizu R, Nomura N, Doi H, Suyalatu Tsutsumi Y, Mitsuishi K, Shimojo M, Noda K, Hanawa T. Effect of cold rolling on the magnetic susceptibility of Zr-14Nb alloy. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(3):5795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2012.10.046.
Chai LJ, Chen K, Wang SY, Xia JY, Wang TT, Yang ZN. Microstructural characteristics of as-forged and β -air-cooled Zr–2.5 Nb alloy. T Nonferr Metal Soc. 2018;28(7):1321. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1003-6326(18)64769-7.
Banerjee S, Krishnan R. Martensitic transformation in zirconium-niobium alloys. Acta Metall. 1971;19(12):1317. https://doi.org/10.1016/0001-6160(71)90068-x.
Tao BR, Qiu RS, Luan BF, Fang Q, Deng C, Liu YS. Structural characterization of 101¯1 twin in a Zr alloy after β quenching. Mater Lett. 2018;223:231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2018.04.053.
Taluts NI, Dobromyslov AV, Elkin VA. Structural and phase transformations in quenched and aged Zr–Ru alloys. J Alloys Compd. 1999;282(1–2):187. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0925-8388(98)00851-2.
Ramos AS, Nunes CA, Coelho GC. On the peritectoid Ti3Si formation in Ti-Si alloys. Mater Charact. 2006;56(2):107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2005.09.009.
Hsu HC, Wu SC, Hsu SK, Li YC, Ho WF. Structure and mechanical properties of as-cast Ti-Si alloys. Intermetallics. 2014;47:11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2013.12.004.
Okunishi E, Kawai T, Mitsuhara M, Farjami S, Itakura M, Hara T, Nishida M. HAADF-STEM studies of athermal and isothermal ω-phases in β-Zr alloy. J Alloys Compd. 2013;577:S713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.12.115.
Adachi N, Todaka Y, Suzuki H, Umemoto M. Orientation relationship between α-phase and high-pressure ω-phase of pure group IV transition metals. Scr Mater. 2015;98:1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2014.10.029.
Rabinkin A, Talianker M, Botstein O. Crystallography and a model of the α → ω phase transformation in zirconium. Acta Metall. 1981;29(4):691. https://doi.org/10.1016/0001-6160(81)90152-8.
Usikov MP, Zilbershtein VA. The orientation relationship between the α- and ω-phases of titanium and zirconium. Phys Status Solidi A. 1973;19(1):53. https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa.2210190103.
Low TSE, Brown DW, Welk BA, Cerreta EK, Okasinski JS, Niezgoda SR. Isothermal annealing of shocked zirconium: Stability of the two-phase α/ω microstructure. Acta Mater. 2015;91:101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2015.03.031.
Trinkle DR, Hennig RG, Srinivasan SG, Hatch DM, Jones MD, Stokes HT, Albers RC, Wilkins JW. New mechanism for the alpha to omega martensitic transformation in pure titanium. Phys Rev Lett. 2003;91(2):025701. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.91.025701.
Kilmametov AR, Ivanisenko Y, Mazilkin AA, Straumal BB, Gornakova AS, Fabrichnaya OB, Kriegel MJ, Rafaja D, Hahn H. The α→ω and β→ω phase transformations in Ti–Fe alloys under high-pressure torsion. Acta Mater. 2018;144:337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2017.10.051.
Zong HX, Ding XD, Lookman T, Sun J. Twin boundary activated α → ω phase transformation in titanium under shock compression. Acta Mater. 2016;115:1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2016.05.037.
Tan XN, Qiu RS, Liu YS, Bi FX, Zhang JL, Tao BR, Liu Q. Nanoscale face-centered-cubic zirconium dispersed in omega zirconium. Philos Mag Lett. 2022;102(7):220. https://doi.org/10.1080/09500839.2022.2077999.
Schenck JF. The role of magnetic susceptibility in magnetic resonance imaging: MRI magnetic compatibility of the first and second kinds. Med Phys. 1996;23(6):815. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.597854.
Wang Z, Fu BG, Wang YF, Dong TS, Li JK, Li GL, Zhao XB, Liu JH, Zhang GX. Effect of Cu content on the precipitation behaviors, mechanical and corrosion properties of as-cast Ti-Cu alloys. Materials. 2022;15(5):1969. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15051696.
Gao L, Ding XD, Lookman T, Sun J, Salje EKH. Metastable phase transformation and hcp-ω transformation pathways in Ti and Zr under high hydrostatic pressures. Appl Phys Lett. 2016;109(3):031912. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4959864.
Sikka SK, Vohra YK, Chidambaram R. Omega phase in materials. Prog Mater Sci. 1982;27(3–4):245. https://doi.org/10.1016/0079-6425(82)90002-0.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51421001) and the Program of the Ministry of Education of China for Introducing Talents of Discipline to Universities (No. B16007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, XN., Li, FT., Liu, YS. et al. Microstructure and properties of as-cast Zr-2.5Nb-1X (X = Ru, Mo, Ta and Si) alloys for biomedical application. Rare Met. 42, 3497–3509 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-023-02291-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-023-02291-3