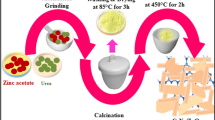
Abstract
Because of the impressive evolution of the drug-resistant bacteria, the development of efficient, antibiotic-free agent is in great urgency. Herein, an efficient antibacterial agent, CuS@HKUST-polydopamine (PDA), was exquisitely designed, where the Cu-based metal-organic framework (MOF)—HKUST nanoparticles served as the porous frame, and the CuS was synthesized within the structure of the MOF through the process of in situ sulfuration, followed with polydopamine (PDA) covering the nanoparticles. The structure of the HKUST preventing the aggregation of the CuS nanoparticles, which improved their photothermal and photocatalytic properties. After covering with PDA, the nanoparticles’ abilities to produce heat and free radicals were further enhanced. This was because that the PDA itself could transform light into heat, which not only benefited the photothermal property, but also improved the photocatalytic property of the nanoparticles by accelerating the charge mobility. Moreover, the PDA could also transfer the photo-induced electrons fast and thus prevented the recombination of the photo-generated electron–hole pairs, which resulted in the enhanced ability to produce free radicals. As a result, under light irradiation, the antibacterial efficiency of the CuS@HKUST-PDA against Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) and Escherichia coli (E. coli) could reach 99.77% and 99.57%. Hence, the synthesized CuS@HKUST-PDA can be promising for anti-infection and sterilization application without using antibiotics.
Graphical abstract

摘要
由于耐药菌的飞速进化, 研发有效的, 非抗生素类的抗菌剂迫在眉睫。本文设计了一种高效的抗菌剂——CuS@HKUST-聚多巴胺(PDA)。这种复合材料使用铜基金属-有机框架结构 (MOF)——HKUST作为多孔框架, 通过原位硫化的方法在HKUST颗粒中原位生成CuS纳米颗粒, 并使用聚多巴胺 (PDA) 包覆纳米颗粒。HKUST的多孔结构可以有效防止CuS纳米颗粒之间的团聚, 并避免由此导致的光热转换效率降低。当纳米颗粒表面包裹一层PDA后, 复合纳米颗粒在光照下产生热量和自由基的能力均会明显增强。这主要是由以下几方面原因造成的: 首先, PDA自身可以将光转换为热量, 提高复合材料的光热转换能力; 同时高热也可以提高电子的流动性, 进而增强复合纳米材料的光动力性能。此外, PDA可以快速转移光致电子,阻碍电子-空穴的复合, 进一步提高纳米颗粒在光照下产生自由基的能力。在光照下, CuS@HKUST-PDA对金黄色葡萄球菌和大肠杆菌的抗菌率分别可以达到99.77%和99.57%。因此, CuS@HKUST-PDA纳米颗粒作为非抗生素类抗菌剂在抗感染和食品杀菌等方面有较大的潜力。








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu X, Li X, Shan Y, Yin Y, Liu C, Lin Z, Kumar SS. CuS nanoparticles anchored to g-C3N4 nanosheets for photothermal ablation of bacteria. RSC Adv. 2020;10(21):12183.
Farrow C, McBean E, Huang G, Yang AL, Wu YC, Liu Z, Dai ZN, Cawte T, Li YP. Ceramic water filters: a point-of-use water treatment technology to remove bacteria from drinking water in Longhai city, Fujian province, China. J Environ Inform. 2018;32(2):63.
Brown ED, Wright GD. Antibacterial drug discovery in the resistance era. Nature. 2016;529(7586):336.
Theuretzbacher U, Outterson K, Engel A, Karlen A. The global preclinical antibacterial pipeline. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2020;18(5):275.
Levy SB, Marshall B. Antibacterial resistance worldwide: causes, challenges and responses. Nat Med. 2004;10(12 Suppl):S122.
Dai B, Yu Y, Chen Y, Huang H, Lu C, Kou J, Zhao Y, Xu Z. Construction of self-healing internal electric field for sustainably enhanced photocatalysis. Adv Funct Mater. 2019;29(16):1807934.
Gao L, Cui X, Wang Z, Sewell C, Li Z, Liang S, Zhang M, Li J, Hu Y, Lin Z. Operando unraveling photothermal-promoted dynamic active-sites generation in NiFe2O4 for markedly enhanced oxygen evolution. PNAS. 2021;118(7):e2023421118.
Lin Y, Han D, Li Y, Tan L, Liu X, Cui Z, Yang X, Li Z, Liang Y, Zhu S, Wu S. Ag2S@WS2 heterostructure for rapid bacteria-killing using near-infrared light. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng. 2019;7(17):14982.
Ren Y, Liu H, Liu X, Zheng Y, Li Z, Li C, Yeung K, Zhu S, Liang Y, Cui Z, Wu S. Photoresponsive materials for antibacterial applications. Cell Rep Phys Sci. 2020;1(11):100245.
Han D, Li Y, Liu X, Li B, Han Y, Zheng Y, Yeung KWK, Li C, Cui Z, Liang Y, Li Z, Zhu S, Wang X, Wu S. Rapid bacteria trapping and killing of metal-organic frameworks strengthened photo-responsive hydrogel for rapid tissue repair of bacterial infected wounds. Chem Eng J. 2020;396:125194.
Ding H, Han D, Han Y, Liang Y, Liu X, Li Z, Zhu S, Wu S. Visible light responsive CuS/ protonated g-C3N4 heterostructure for rapid sterilization. J Hazard Mater. 2020;393:122423.
Li Y, Liu X, Tan L, Cui Z, Yang X, Zheng Y, Yeung KWK, Chu PK, Wu S. Rapid sterilization and accelerated wound healing using Zn2+ and graphene oxide modified g-C3N4 under dual light irradiation. Adv Funct Mater. 2018;28(30):1800299.
Zhao Y, Liu J, Han M, Yang G, Ma L, Wang Y. Two comparable Ba-MOFs with similar linkers for enhanced CO2 capture and separation by introducing N-rich groups. Mater Rare Met. 2021;40(2):499.
Li Y, Yang Y, Huang J, Wang L, She H, Zhong J, Wang Q. Preparation of CuS/BiVO4 thin film and its efficaciously photoelectrochemical performance in hydrogen generation. Rare Met. 2019;38(5):428.
Yu P, Han Y, Han D, Liu X, Liang Y, Li Z, Zhu S, Wu S. In-situ sulfuration of Cu-based metal-organic framework for rapid near-infrared light sterilization. J Hazard Mater. 2020;390:122126.
Tan H, Li Q, Zhou Z, Ma C, Song Y, Xu F, Wang L. A sensitive fluorescent assay for thiamine based on metal-organic frameworks with intrinsic peroxidase-like activity. Anal Chim Acta. 2015;856:90.
Yu S, Li G, Liu R, Ma D, Xue W. Dendritic Fe3O4@poly(dopamine)@PAMAM nanocomposite as controllable NO-releasing material: a synergistic photothermal and NO antibacterial study. Adv Funct Mater. 2018;28(20):1707440.
Kim Y, Coy E, Kim H, Mrowczynski R, Torruella P, Jeong D, Choi KS, Jang JH, Song MY, Jang D, Peiro F, Jurga S, Kim HJ. Efficient photocatalytic production of hydrogen by exploiting the polydopamine-semiconductor interface. Appl Catal B. 2021;280:119423.
Han D, Ma M, Han Y, Cui Z, Liang Y, Liu X, Li Z, Zhu S, Wu S. Eco-friendly hybrids of carbon quantum dots modified MoS2 for rapid microbial inactivation by strengthened photocatalysis. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng. 2019;8(1):534.
Tian N, Gao Y, Wu J, Luo S, Dai W. Water-resistant HKUST-1 functionalized with polydimethylsiloxane for efficient rubidium ion capture. New J Chem. 2019;43(39):15539.
Wang C, Qian X, An X. In situ green preparation and antibacterial activity of copper-based metal-organic frameworks/cellulose fibers (HKUST-1/CF) composite. Cellulose. 2015;22(6):3789.
Mosleh S, Rahimi MR, Ghaedi M, Dashtian K, Hajati S. Photocatalytic degradation of binary mixture of toxic dyes by HKUST-1 MOF and HKUST-1-SBA-15 in a rotating packed bed reactor under blue LED illumination: central composite design optimization. RSC Adv. 2016;6(21):17204.
Gupta VK, Pathania D, Agarwal S, Singh P. Adsorptional photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue onto pectin-CuS nanocomposite under solar light. J Hazard Mater. 2012;243:179.
Han D, Li Y, Liu X, Yeung KWK, Zheng Y, Cui Z, Liang Y, Li Z, Zhu S, Wang X, Wu S. Photothermy-strengthened photocatalytic activity of polydopamine-modified metal-organic frameworks for rapid therapy of bacteria-infected wounds. J Mater Sci Technol. 2021;62:83.
Feng M, Yu S, Wu P, Wang Z, Liu S, Fu J. Rapid, high-efficient and selective removal of cationic dyes from wastewater using hollow polydopamine microcapsules: isotherm, kinetics, thermodynamics and mechanism. Appl Surf Sci. 2021;542:148633.
Cui X, Sun X, Liu L, Huang Q, Yang H, Chen C, Nie S, Zhao Z, Zhao Z. In-situ fabrication of cellulose foam HKUST-1 and surface modification with polysaccharides for enhanced selective adsorption of toluene and acidic dipeptides. Chem Eng J. 2019;369:898.
Song C, Wang X, Zhang J, Chen X, Li C. Enhanced performance of direct Z-scheme CuS-WO3 system towards photocatalytic decomposition of organic pollutants under visible light. Appl Surf Sci. 2017;425:788.
Qin Y, Kong X, Lei D, Lei X. Facial grinding method for synthesis of high-purity CuS nanosheets. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2018;57(8):2759.
Álvarez JR, Sánchez-González E, Pérez E, Schneider-Revueltas E, Martínez A, Tejeda-Cruz A, Islas-Jácome A, González-Zamora E, Ibarra IA. Structure stability of HKUST-1 towards water and ethanol and their effect on its CO2 capture properties. Dalton Trans. 2017;46(28):9192.
Liu Y, Ai K, Lu L. Polydopamine and its derivative materials: Synthesis and promising applications in energy, environmental, and biomedical fields. Chem Rev. 2014;114(9):5057.
Li L, Rashidi LH, Yao M, Ma L, Chen L, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Chen W. CuS nanoagents for photodynamic and photothermal therapies: phenomena and possible mechanisms. Photodiagn Photodyn Ther. 2017;19:5.
Li M, Liu X, Tan L, Cui Z, Yang X, Li Z, Zheng Y, Yeung K, Chu PK, Wu S. Noninvasive rapid bacteria-killing and acceleration of wound healing through photothermal/photodynamic/copper ion synergistic action of a hybrid hydrogel. Biomater Sci. 2018;6(8):2110.
Ding X, Liu J, Li J, Wang F, Wang Y, Song S, Zhang H. Polydopamine coated manganese oxide nanoparticles with ultrahigh relaxivity as nanotheranostic agents for magnetic resonance imaging guided synergetic chemo-/photothermal therapy. Chem Sci. 2016;7(11):6695.
Chen Y, Ai K, Liu J, Ren X, Jiang C, Lu L. Polydopamine-based coordination nanocomplex for T1/T2 dual mode magnetic resonance imaging-guided chemo-photothermal synergistic therapy. Biomaterials. 2016;77:198.
Zou Y, Wu T, Li N, Guo X, Li Y. Photothermal-enhanced synthetic melanin inks for near-infrared imaging. Polymer. 2020;186:122042.
Tian Y, Zhang J, Tang S, Zhou L, Yang W. Polypyrrole composite nanoparticles with morphology-dependent photothermal effect and immunological responses. Small. 2016;12(6):721.
Hou L, Shan X, Hao L, Feng Q, Zhang Z. Copper sulfide nanoparticle-based localized drug delivery system as an effective cancer synergistic treatment and theranostic platform. Acta Biomater. 2017;54:307.
Xu W, Zhu S, Liang Y, Li Z, Cui Z, Yang X, Inoue A. Nanoporous CuS with excellent photocatalytic property. Sci Rep. 2015;5(1):1.
Hou L, Zhang M, Guan Z, Li Q, Yang J. Effect of annealing ambience on the formation of surface/bulk oxygen vacancies in TiO2 for photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Appl Surf Sci. 2018;428:640.
Sun X, Yan L, Xu R, Xu M, Zhu Y. Surface modification of TiO2 with polydopamine and its effect on photocatalytic degradation mechanism. Colloids Surf A. 2019;570:199.
Zhang C, Yang H, Wan L, Liang H, Li H, Xu Z. Polydopamine-coated porous substrates as a platform for mineralized β-FeOOH nanorods with photocatalysis under sunlight. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(21):11567.
Huo R, Yang X, Yang J, Yang S, Xu Y. Self-assembly synthesis of BiVO4/polydopamine/g-C3N4 with enhanced visible light photocatalytic performance. Mater Res Bull. 2018;98:225.
Wang X, He Y, Hu Y, Jin G, Jiang B, Huang Y. Photothermal-conversion-enhanced photocatalytic activity of flower-like CuS superparticles under solar light irradiation. Sol Energy. 2018;170:586.
Dai B, Fang J, Yu Y, Sun M, Huang H, Lu C, Kou J, Zhao Y, Xu Z. Construction of infrared-light-responsive photoinduced carriers driver for enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Adv Mater. 2020;32(12):1906361.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by Jilin Provincial Science and Technology Project (No. YDZJ202101ZYTS054), the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (No. 51925104) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51871162).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, DL., Yu, PL., Liu, XM. et al. Polydopamine modified CuS@HKUST for rapid sterilization through enhanced photothermal property and photocatalytic ability. Rare Met. 41, 663–672 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-021-01786-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-021-01786-1