Abstract
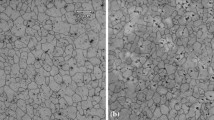
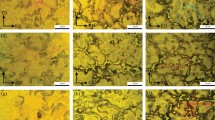
The effects of Sr and Y on microstructure, tensile property and free bulge formability of AZ31 alloy sheet produced by twin-roll casting and sequential hot rolling were investigated to improve the mechanical properties and formability of the AZ31 alloy. Sr and Y addition can form Al4Sr, Al2Y and Al3Y phases which can impede dislocation movement and promote dynamic recrystallization during the rolling deformation and decrease the lattice resistance to dislocation motion by decreasing Al solubility in the alloy, resulting in finer grains, lower dislocation density and no twinning generating in the twin-roll casting and sequential hot rolling (TRC-HR) AZ31–1.3Sr–1.0Y alloy. The maximum stress and elongation of the alloy increase significantly after adding Sr and Y. The average cavity and grain sizes of the TRC-HR AZ31–1.3Sr–1.0Y alloy are smaller, resulting in higher elongation in the alloy. The addition of Y and Sr can effectively improve the free bulge formability and the thickness uniform of the alloy. The Al4Sr, Al2Y and Al3Y phases can inhibit the grain growth by obstructing dislocation motion or grain boundary slip, resulting in smaller grain size of AZ31–1.3Sr–1.0Y alloy bulge parts.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Friedrich H, Schumann S. Research for a “new age of magnesium” in the automotive industry. J Mater Process Technol. 2001;117(3):276.
Xu W, Birbilis N, Sha G, Wang Y, Daniels JE, Xiao Y, Ferry M. A high-specific-strength and corrosion-resistant magnesium alloy. Nat Mater. 2015;14(12):1229.
Feng S, Liu W, Zhao J, Wu GH, Zhang HH, Ding WJ. Effect of extrusion ratio on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg–8Li–3Al–2Zn–0.5Y alloy with duplex structure. Mater Sci Eng A. 2017;692(4):9.
Wu HR, Du WB, Li SB, Liu K, Wang ZH. Microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ31 magnesium alloy reinforced by I-phase. Rare Met. 2019;38(6):733.
Zhang K, Li X, Li Y, Yuan J, Liu X, Wang S. Effect of heat treatment on mechanical properties of ZM51 magnesium alloy. Chin J Rare Met. 2019;43(6):585.
Mordike BL, Ebert T. Magnesium: properties—applications—potential. Mater Sci Eng A. 2001;302(1):37.
Liu Y, Wei Y. A polycrystal based numerical investigation on the temperature dependence of slip resistance and texture evolution in magnesium alloy AZ31B. Int J Plast. 2014;55(2):80.
Ali Y, Qiu D, Jiang B, Pan FS, Zhang MX. Current research progress in grain refinement of cast magnesium alloys: a review article. J Alloys Compd. 2015;619(1):639.
Stjohn DH, Ma Q, Easton MA, Cao P, Hildebrand Z. Grain refinement of magnesium alloys. Metall Mater Trans A. 2005;53(7):841.
Ai X, Quan G. Effect of Ti on the mechanical properties and corrosion of cast AZ91 magnesium alloy. Open Mater Sci J. 2012;6(1):6.
Choi JY, Kim WJ. Significant effects of adding trace amounts of Ti on the microstructure and corrosion properties of Mg–6Al–1Zn magnesium alloy. J Alloys Compd. 2014;614(2):49.
Lee TJ, Kim WJ. The significant effect of adding trace amounts of Ti on the high-temperature deformation behavior of fine-grained Mg–6Al–1Zn magnesium alloys. J Alloys Compd. 2014;617(12):352.
Qian M, StJohn DH. Grain nucleation and formation in Mg–Zr alloys. Int J Cast Met Res. 2009;22(1–4):256.
Masoudpanah SM, Mahmudi R. Effects of rare-earth elements and Ca additions on the microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ31 magnesium alloy processed by ECAP. Mater Sci Eng A. 2009;526(16):3685.
Liu SF, Li B, Wang XH, Su W, Han H. Refinement effect of cerium, calcium and strontium in AZ91 magnesium alloy. J Mater Process Technol. 2009;209(8):3999.
Hirai K, Somekawa H, Takigawa Y, Higashi K. Effects of Ca and Sr addition on mechanical properties of a cast AZ91 magnesium alloy at room and elevated temperature. Mater Sci Eng A. 2005;403(1):276.
Harandia SE, Mirshahi M, Koleini S, Idris HM, Jafari H, Kadir MRA. Effect of calcium content on the microstructure, hardness and in vitro corrosion behavior of biodegradable Mg–Ca binary alloy. Mater Res. 2012;16(1):11.
Yan L, Xiao L. Deformation behavior of a coarse-grained Mg-8Al-1.5Ca-0.2Sr magnesium alloy at elevated temperatures. J Mater Eng Perform. 2018;27(2):905.
Kim SH, Bae SW, Lee SW, Moon BG, Kim HS, Kim YM, Yoon J, Park SH. Microstructural evolution and improvement in mechanical properties of extruded AZ31 alloy by combined addition of Ca and Y. Mater Sci Eng A. 2018;725(5):309.
Srinivasan A, Pillai UTS, Swaminathan J, Das SK, Pai BC. Observations of microstructural refinement in Mg–Al–Si alloys containing strontium. J Mater Sci. 2006;41(18):6087.
Chen S, Dong X, Ma R, Zhang L, Wang H, Fan Z. Effects of Cu on microstructure, mechanical properties and damping capacity of high damping Mg–1% Mn based alloy. Mater Sci Eng A. 2012;551(31):87.
Lee S, Lee SH, Kim DH. Effect of Y, Sr and Nd additions on the microstructure and microfracture mechanism of squeeze-cast AZ91-X magnesium alloys. Metall Mater Trans A. 1998;29(4):1221.
Yang M, Pan F, Cheng R, Shen J. Comparison about effects of Sb, Sn and Sr on as-cast microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ61–0.7Si magnesium alloy. Mater Sci Eng A. 2008;489(1–2):413.
Zhang W, Li M, Chen Q, Hu W, Zhang W, Xin W. Effects of Sr and Sn on microstructure and corrosion resistance of Mg–Zr–Ca magnesium alloy for biomedical applications. Mater Des. 2012;39(8):379.
Chen G, Peng XD, Fan PG, Xie W, Wei Q, Ma H, Yang Y. Effects of Sr and Y on microstructure and corrosion resistance of AZ31 magnesium alloy. Trans Nonferr Metal Soc. 2011;21(4):725.
Bettles CJ, Gibson MA, Zhu SM. Microstructure and mechanical behaviour of an elevated temperature Mg-rare earth based alloy. Mater Sci Eng A. 2009;505(1):6.
Tao W. Influence of rare earth elements on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-Li alloys. J Rare Earths. 2006;24(6):797.
Zhang Y, Zeng XQ, Liu LF, Lu C, Zhou HT, Li Q, Zhu YP. Effects of yttrium on microstructure and mechanical properties of hot-extruded Mg-Zn-Y-Zr alloys. Mater Sci Eng A. 2004;373(1):320.
Kashefi N, Mahmudi R. The microstructure and impression creep behavior of cast AZ80 magnesium alloy with yttrium additions. Mater Des. 2012;39(8):200.
Wang Y, Liao X, Zhu Y. Grain refinement and growth induced by severe plastic deformation. Int J Mater Res. 2009;100(12):1632.
Kondoh K, Tsuzuki R, Du W, Kamado S. Materials and processing designs for magnesium alloys–grain refining by repeated plastic working and solid-state synthesis of Mg2Si (review). Adv Technol Mater Mater Process. 2004;6(2):328.
Kang SH, Lee YS, Lee JH. Effect of grain refinement of magnesium alloy AZ31 by severe plastic deformation on material characteristics. J Mater Process Technol. 2008;201(1):436.
Liang D, Cowley CB. The twin-roll strip casting of magnesium. JOM. 2004;56(5):26.
Watari H, Haga T, Koga N, Davey K. Feasibility study of twin roll casting process for magnesium alloys. J Mater Process Technol. 2007;192(10):300.
Yu YD, Hu Q, Jiang P. Microstructures and mechanical properties of AZ31 + Sr + Y magnesium alloy sheets produced by twin-roll casting and sequential hot rolling. Adv Mater Res. 2013;765–767(3):3176.
Sadeghi A, Pekguleryuz M. Recrystallization and texture evolution of Mg-3%Al-1%Zn-(0.4-0.8)%Sr alloys during extrusion. Mater Sci Eng A. 2011;528(4–5):1678.
Sadeghi A, Hoseini M, Pekguleryuz M. Effect of Sr addition on texture evolution of Mg-3Al-1Zn (AZ31) alloy during extrusion. Mater Sci Eng A. 2011;528(3):3096.
Yu Y, Jiang P, Li C, Lin K. Deformation behaviour of AZ31 magnesium alloy sheets produced by twin-roll casting and sequential hot rolling. Adv Mater Res. 2011;299–300(19):368.
Kaibyshev R, Kazakulov I, Gromov D, Musin F, Lesuer DR, Nieh TG. Superplasticity in a 2219 aluminum alloy. Scr Mater. 2001;44(10):2411.
Zhang K, Yan H. Deformation behavior of fine-grained 5083Al alloy at elevated temperature. Trans Nonferr Metal Soc. 2009;19(s2):s307.
Sun PH, Wu HY, Tsai HH, Huang CC, Tzou MD. Effect of pressurization profile on the deformation characteristics of fine-grained AZ31B Mg alloy sheet during gas blow forming. J Mater Process Technol. 2010;210(12):1673.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51705038 and 51875053) and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province of China (No. BK20150268).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, P., Li, LB., Yu, YD. et al. Microstructure, tensile properties and free bulge formability of Sr- and Y-containing AZ31 alloy sheet produced by twin-roll casting and sequential hot rolling. Rare Met. 39, 1202–1209 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01381-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01381-w