Abstract
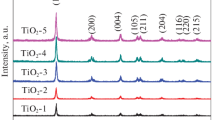
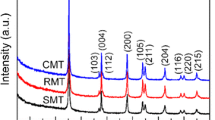
Titania nanowires (TiO2-NW) with tunable aspect ratios and morphologies were directly synthesized using a simple alcohol-thermal technique. Specifically, ethanol and acetic acid were used as solvents and lithium ion was used as the capping agent to promote the conversion of titanium butoxide into TiO2-NW. The morphologies and crystal phases of TiO2-NW were determined by the molar ratio of solvents and the content (mol%) of lithium ion. The band gap of TiO2-NW with pure anatase phase is slightly bigger than that of TiO2-NW with a mixture of anatase and rutile phases. All TiO2-NW could achieve effective decolorization of methyl blue (the decolorization rate is over 95%) after 35-min ultraviolet (UV) irradiation.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xia M, Zhang Q, Pan P, Zhong X, Long H, Tong X, Liu G. Enhanced surface photovoltaic properties of TiO2 nanowires doped by Ag nanoparticles. Mater Lett. 2015;160(Supplement C):544.
Wang X, Li Z, Shi J, Yu Y. One-dimensional titanium dioxide nanomaterials: nanowires, nanorods, and nanobelts. Chem Rev. 2014;114(19):9346.
Zander Z, Yagloski R, DeCoste J, Zhang D, DeLacy BG. One-pot synthesis of high aspect ratio titanium dioxide nanorods using oxalic acid as a complexing agent. Mater Lett. 2016;163(Supplement C):39.
Xu Z, Kan Y, Liu C. Aspect ratio control and photocatalytic properties analysis of anatase TiO2 nanoparticles. Mater Res Bull. 2018;107:80.
Wang J, Wang C, Zhu S, Luo X, Li Z, Xu L. Benzohydroxamic acid photodegradation by prepared Ce modified TiO2. Chin J Rare Metals. 2018;42(4):393.
Wang J, Lou C, Chen X, Hu F, Yan B, Zhang M. Preparation and optical properties of inverse opal titanium dioxide. Chin J Rare Metals. 2018;42(8):850.
Lee K, Mazare A, Schmuki P. One-dimensional titanium dioxide nanomaterials: nanotubes. Chem Rev. 2014;114(19):9385.
Luan S, Qu D, An L, Jiang W, Gao X, Hua S, Miao X, Wen Y, Sun Z. Enhancing photocatalytic performance by constructing ultrafine TiO2 nanorods/g-C3N4 nanosheets heterojunction for water treatment. Sci Bull. 2018;63(11):683.
Han B, Kim SJ, Hwang BM, Kim SB, Park KW. Single-crystalline rutile TiO2 nanowires for improved lithium ion intercalation properties. J Power Sources. 2013;222(Supplement C):225.
Xu ZX, Yang JT, Liu K, Guo XQ. Shape evolution behavior of anatase titania nanocrystals via the Solvothermal method. Acta Phys Chim Sin. 2016;32(2):581.
Wu HB, Chen JS, Lou XW, Hng HH. Asymmetric anatase TiO2 nanocrystals with exposed high-index facets and their excellent lithium storage properties. Nanoscale. 2011;3(10):4082.
Dai L, Sow CH, Lim CT, Cheong WCD, Tan VBC. Numerical investigations into the tensile behavior of TiO2 nanowires: structural deformation, mechanical properties, and size effects. Nano Lett. 2009;9(2):576.
Sadeghzadeh Attar A, Hassani Z. Fabrication and growth mechanism of single-crystalline rutile TiO2 nanowires by liquid-phase deposition process in a porous alumina template. J Mater Sci Technol. 2015;31(8):828.
Yuan L, Meng S, Zhou Y, Yue Z. Controlled synthesis of anatase TiO2 nanotube and nanowire arrays via AAO template-based hydrolysis. J Mater Chem A. 2013;1(7):2552.
Hwang YJ, Hahn C, Liu B, Yang P. Photoelectrochemical properties of TiO2 nanowire arrays: a study of the dependence on length and atomic layer deposition coating. ACS Nano. 2012;6(6):5060.
Cheng Z, Wang W, Yang L, Xu Z, Ji Z, Huang S. Preparation of La–TiO2 and photocatalytic degradation of petrochemical secondary effluent. Chin J Rare Metals. 2018;42(9):950.
Kang SH, Choi SH, Kang MS, Kim JY, Kim HS, Hyeon T, Sung YE. Nanorod-based dye-sensitized solar cells with improved charge collection efficiency. Adv Mater. 2008;20(1):54.
Dong S, Ding X, Guo T, Yue X, Han X, Sun J. Self-assembled hollow sphere shaped Bi2WO6/RGO composites for efficient sunlight-driven photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants. Chem Eng J. 2017;316:778.
Tao RH, Wu JM, Xue HX, Song XM, Pan X, Fang XQ, Fang XD, Dai SY. A novel approach to titania nanowire arrays as photoanodes of back-illuminated dye-sensitized solar cells. J Power Sources. 2010;195(9):2989.
Guoxin H, Xu Z. Monodisperse iron oxide nanoparticle-reduced graphene oxide composites formed by self-assembly in aqueous phase. Fuller Nanotub Carbon Nanostruct. 2015;23(4):283.
Li X, Zhang H, Huang J, Luo J, Feng Z, Wang X. Folded nano-porous graphene-like carbon nitride with significantly improved visible-light photocatalytic activity for dye degradation. Ceram Int. 2017;43(17):15785.
Wu HB, Hng HH, Lou XW. Direct synthesis of anatase TiO2 nanowires with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Adv Mater. 2012;24(19):2567.
Gu X, Wang B, Zhang Q, Zhao Y, Qiang Y. Preparation of ultrathin TiO2 single-crystal nanowires for high performance dye sensitized solar cells. J Mater Sci Mater Electron. 2013;24(2):520.
Tang HL, Ren Y, Wei SH, Liu G, Xu XX. Preparation of 3D ordered mesoporous anatase TiO2 and their photocatalytic activity. Rare Metals. 2019;1:6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-019-01211-8.
Kim CS, Moon BK, Park JH, Tae Chung S, Son SM. Synthesis of nanocrystalline TiO2 in toluene by a solvothermal route. J Cryst Growth. 2003;254(3):405.
Liu X, Zhang F, Huang R, Pan C, Zhu J. Capping modes in PVP-directed silver nanocrystal growth: multi-twinned nanorods versus single-crystalline nano-hexapods. Cryst Growth Des. 2008;8(6):1916.
Jiang XC, Xiong SX, Tian ZA, Chen CY, Chen WM, Yu AB. Twinned structure and growth of V-shaped silver nanowires generated by a polyol–thermal approach. J Phys Chem C. 2011;115(5):1800.
Spurr RA, Myers H. Quantitative analysis of anatase–rutile mixtures with an X-ray diffractometer. Anal Chem. 1957;29(5):760.
Kumar PS, Nizar SAS, Sundaramurthy J, Ragupathy P, Thavasi V, Mhaisalkar SG, Ramakrishna S. Tunable hierarchical TiO2 nanostructures by controlled annealing of electrospun fibers: formation mechanism, morphology, crystallographic phase and photoelectrochemical performance analysis. J Mater Chem. 2011;21(26):9784.
Li H, Shen X, Liu Y, Wang L, Lei J, Zhang J. Facile phase control for hydrothermal synthesis of anatase–rutile TiO2 with enhanced photocatalytic activity. J Alloys Compd. 2015;646:380.
Scanlon DO, Dunnill CW, Buckeridge J, Shevlin SA, Logsdail AJ, Woodley SM, Catlow CRA, Powell MJ, Palgrave RG, Parkin IP, Watson GW, Keal TW, Sherwood P, Walsh A, Sokol AA. Band alignment of rutile and anatase TiO2. Nat Mater. 2013;12(9):798.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51408528) and the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province, China (No. E2014203089).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, ZX., Wang, AQ. & Zhu, YF. Controllable synthesis and tunable photocatalytic activity of TiO2 nanowires via alcohol-thermal method. Rare Met. 38, 390–396 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-019-01243-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-019-01243-0