Abstract
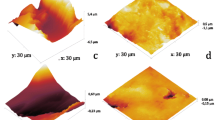
Initial bacterial adhesion on dental implant abutment is related to its surface chemical composition and physical characteristics. Selection of appropriate abutment materials resistant to bacterial adhesion is important for dental implant maintenance. The aim of present study was to evaluate the effect of different properties of abutment materials on initial bacterial adhesion in vitro. Polished zirconia (PZ group), polished titanium (PT group) and ground titanium (GT group) samples were prepared to simulate clinical dental implant abutments. Chemical compositions, morphology, roughness, hydrophilicity and surface free energy of materials were analyzed. Oral commensal bacterium Streptococcus mitis was used to evaluate initial bacterial adhesion via turbidity test and colony-forming unit counting. The results showed that GT group presented the highest roughness, hydrophilicity and surface free energy. After 6-h incubation, GT group showed the significantly highest adhered bacteria counts; while non-significant difference existed between PT and PZ groups. Within the clinically applicable range used in present study, the surface physical characteristics, instead of surface chemical composition, of dental abutment material have the pronounced influence on initial 6-h bacterial adhesion.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Doornewaard R, Christiaens V, De Bruyn H, Jacobsson M, Cosyn J, Vervaeke S, Jacquet W. Long-term effect of surface roughness and patients’ factors on crestal bone loss at dental implants. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2017;19(2):372.
Pjetursson BE, Asgeirsson AG, Zwahlen M, Sailer I. Improvements in implant dentistry over the last decade: comparison of survival and complication rates in older and newer publications. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2014;29(S):308.
Marcantonio C, Nicoli LG, Marcantonio Junior E, Zandim-Barcelos DL. Prevalence and possible risk factors of peri-implantitis: a concept review. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2015;16(9):750.
Link-Bindo EE, Soltys J, Donatelli D, Cavanaugh R. Common prosthetic implant complications in fixed restorations. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 2016;37(7):431.
Derks J, Tomasi C. Peri-implant health and disease. A systematic review of current epidemiology. J Clin Periodontol. 2015;42(S16):S158.
Rakic M, Grusovin MG, Canullo L. The microbiologic profile associated with peri-implantitis in humans: a systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2016;31(2):359.
Stokman MA, van Winkelhoff AJ, Vissink A, Spijkervet FK, Raghoebar GM. Bacterial colonization of the peri-implant sulcus in dentate patients: a prospective observational study. Clin Oral Investig. 2017;21(2):717.
Teughels W, Van Assche N, Sliepen I, Quirynen M. Effect of material characteristics and/or surface topography on biofilm development. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006;17(S2):68.
Subramani K, Jung RE, Molenberg A, Hammerle CH. Biofilm on dental implants: a review of the literature. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24(4):616.
Lee A, Wang HL. Biofilm related to dental implants. Implant Dent. 2010;19(5):387.
Elter C, Heuer W, Demling A, Hannig M, Heidenblut T, Bach FW, Stiesch-Scholz M. Supra- and subgingival biofilm formation on implant abutments with different surface characteristics. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2008;23(2):327.
Yamane K, Ayukawa Y, Takeshita T, Furuhashi A, Yamashita Y, Koyano K. Bacterial adhesion affinities of various implant abutment materials. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2013;24(12):1310.
De Bruyn H, Christiaens V, Doornewaard R, Jacobsson M, Cosyn J, Jacquet W, Vervaeke S. Implant surface roughness and patient factors on long-term peri-implant bone loss. Periodontol 2000. 2017;73(1):218.
Scarano A, Piattelli M, Caputi S, Favero GA, Piattelli A. Bacterial adhesion on commercially pure titanium and zirconium oxide disks: an in vivo human study. J Periodontol. 2004;75(2):292.
Salihoglu U, Boynuegri D, Engin D, Duman AN, Gokalp P, Balos K. Bacterial adhesion and colonization differences between zirconium oxide and titanium alloys: an in vivo human study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2011;26(1):101.
van Brakel R, Cune MS, van Winkelhoff AJ, de Putter C, Verhoeven JW, van der Reijden W. Early bacterial colonization and soft tissue health around zirconia and titanium abutments: an in vivo study in man. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2011;22(6):571.
Egawa M, Miura T, Kato T, Saito A, Yoshinari M. In vitro adherence of periodontopathic bacteria to zirconia and titanium surfaces. Dent Mater J. 2013;32(1):101.
Nascimento C, Pita MS, Fernandes FH, Pedrazzi V, de Albuquerque Junior RF, Ribeiro RF. Bacterial adhesion on the titanium and zirconia abutment surfaces. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2014;25(3):337.
Bollen CM, Lambrechts P, Quirynen M. Comparison of surface roughness of oral hard materials to the threshold surface roughness for bacterial plaque retention: a review of the literature. Dent Mater. 1997;13(4):258.
Owens DK, Wendt RC. Estimation of the surface free energy of polymers. J Appl Polym Sci. 1969;13(8):1741.
Kwok DY, Neumann AW. Contact angle measurement and contact angle interpretation. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 1999;81(3):167.
Yeo IS, Kim HY, Lim KS, Han JS. Implant surface factors and bacterial adhesion: a review of the literature. Int J Artif Organs. 2012;35(10):762.
Tanner J, Robinson C, Soderling E, Vallittu P. Early plaque formation on fibre-reinforced composites in vivo. Clin Oral Investig. 2005;9(3):154.
Al-Ahmad A, Wiedmann-Al-Ahmad M, Fackler A, Follo M, Hellwig E, Bachle M, Hannig C, Han JS, Wolkewitz M, Kohal R. In vivo study of the initial bacterial adhesion on different implant materials. Arch Oral Biol. 2013;58(9):1139.
Badihi HL, Sela MN, Steinberg D, Rosen G, Kohavi D. The adhesion of oral bacteria to modified titanium surfaces: role of plasma proteins and electrostatic forces. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2013;24(SA100):49.
Quirynen M, Bollen CM, Papaioannou W, Van Eldere J, van Steenberghe D. The influence of titanium abutment surface roughness on plaque accumulation and gingivitis: short-term observations. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1996;11(2):169.
Al-Radha AS, Dymock D, Younes C, O’Sullivan D. Surface properties of titanium and zirconia dental implant materials and their effect on bacterial adhesion. J Dent. 2012;40(2):146.
Etxeberria M, Lopez-Jimenez L, Merlos A, Escuin T, Vinas M. Bacterial adhesion efficiency on implant abutments: a comparative study. Int Microbiol. 2013;16(4):235.
Saidi W, Hfayedh N, Megriche A, Girtan M, El Maaoui M. Hydrophilic/hydrophobic and optical properties of B2O3 doped TiO2 sol–gel thin films: effect of B2O3 content, film thickness and surface roughness. Mater Chem Phys. 2018;215(15):31.
Mozammel M, Khajeh M, Ilkhechi NN. Effect of surface roughness of 316L stainless steel substrate on the morphological and super-hydrophobic property of TiO2 thin films coatings. Silicon. 2018;10(6):2603.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the National Yang-Ming University Hospital (Nos. RD 2011-009, RD 2012-021 and RD 2013-013), Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, YS., Huang, HH. Effects of clinical dental implant abutment materials and their surface characteristics on initial bacterial adhesion. Rare Met. 38, 512–519 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-019-01219-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-019-01219-0