Abstract
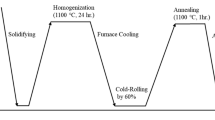
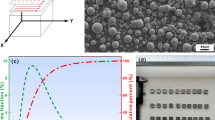
The effect of heat treatment on microstructure and tensile properties of as-cast Al0.5CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy was investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) equipped with energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), and tensile tests. The results show that heat treatment strongly affects the microstructure, particularly the morphology of bcc phases, and improves tensile properties. Microstructure analysis reveals that rod-shaped and elliptoid phases appear in the matrix after heat treatment at 1150 °C. Besides, under 850 °C heat-treated condition, ultimate tensile strength increases by about 60% without sacrificing much plasticity, which can be attributed to the content of bcc phases and fine precipitates dispersed in the dendrites. For other heat-treated conditions, tensile ductility increases by at least 30%, especially 60% for heat treatment at 450 °C, and strength also improves. Fracture analysis indicates that the fracture mode of heat treatment at 850 °C is a mixture of quasi-cleavage and ductile fracture, while the other heat-treated conditions show the mode of ductile fracture.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang Y, Zuo TT, Tang Z, Gao MC, Dahmen KA, Liaw PK, Lu ZP. Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys. Prog Mater Sci. 2014;61(8):1.
Murty BS, Yeh JW, Ranganathan S. High Entropy Alloys. Murty BS, Yeh JW, Ranganathan S, Boston, editors. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2014. 7.
Tsai MH, Yeh JW. High-entropy alloys: a critical review. Mater Res Lett. 2014;2(3):107.
He JY, Liu WH, Wang H, Wu Y, Liu XJ, Nieh TG, Lu ZP. Effects of Al addition on structural evolution and tensile properties of the FeCoNiCrMn high-entropy alloy system. Acta Mater. 2014;62(5):105.
Otto F, Dlouhý A, Somsen C, Bei H, Eggeler G, George EP. The influences of temperature and microstructure on the tensile properties of a CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 2013;61(15):5743.
Lu YP, Dong Y, Guo S, Jiang L, Kang HJ, Wang TM, Wen B, Wang ZJ, Jie JC, Cao ZQ, Ruan HH, Li TJ. A Promising new class of high-temperature alloys: eutectic high-entropy alloys. Sci Rep. 2014;4(6200):1.
Pan M, Zhao YQ, Zeng WD. Phase transformation kinetics of Ti-1300 alloy during continuous heating. Rare Met. 2015;34(4):233.
Zhu JM, Meng JL, Liang JL. Microstructure and mechanical properties of multi-principal component AlCoCrFeNiCux alloy. Rare Met. 2014;33(1):1.
He JY, Wang H, Huang H, Xu XD, Chen MW, Wu Y, Liu XJ, Nieh TG, An K, Lu ZP. A precipitation-hardened high-entropy alloy with outstanding tensile properties. Acta Mater. 2016;102:187.
Kao YF, Chen TJ, Chen SK, Yeh JW. Microstructure and mechanical property of as-cast, -homogenized, and -deformed AlxCoCrFeNi (0 ≤ x≤2) high-entropy alloys. J Alloys Compd. 2009;488(1):57.
Lin CM, Tsai HL. Evolution of microstructure, hardness, and corrosion properties of high-entropy Al0.5CoCrFeNi alloy. Intermetallics. 2011;19(3):288.
Chou HP, Chang YS, Chen SK, Yeh JW. Microstructure, thermophysical and electrical properties in AlxCoCrFeNi (0 ≤ x≤2) high-entropy alloys. Mater Sci Eng B. 2009;163(3):184.
Wang WR, Wang WL, Yeh JW. Phases, microstructure and mechanical properties of AlxCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys at elevated temperatures. J Alloys Compd. 2014;589(9):143.
Wang YP, Li BS, Ren MX, Yang C, Fu HZ. Microstructure and compressive properties of AlCrFeCoNi high entropy alloy. Mater Sci Eng A. 2008;491(1–2):154.
Li C, Li JC, Zhao M, Jiang Q. Effect of aluminum contents on microstructure and properties of AlxCoCrFeNi alloys. J Alloys Compd. 2010;504(4):S515.
Kuznetsov AV, Shaysultnov DG, Stepanov ND, Salishchev GA, Senkov ON. Tensile properties of an AlCrCuNiFeCo high-entropy alloy in as-cast and wrought conditions. Mater Sci Eng A. 2012;533(1):107.
Klement W, Willens RH, Duwez P. Non-crystalline structure in solidified gold–silicon alloys. Nature. 1960;187(4740):869.
Gschneidner KA, Calderwood J, Calderwood FW. ASM Handbook, Volume 3. Alloy Phase Diagrams. In: ASM International, editor. Alloy Phase Diagram and the Handbook Committees. Detroit: ASM International; 1992. 7.
Zhang F, Zhang C, Chen SL, Zhu J, Cao WS, Kattner UR. An understanding of high entropy alloys from phase diagram calculations. Calphad. 2014;45(24):1.
Ng C, Guo S, Luan J, Wang Q, Lu J, Shi SQ, Liu CT. Phase stability and tensile properties of Co-free Al0.5CrCuFeNi2 high-entropy alloys. J Alloys Compd. 2014;584(3):530.
Gali A, George EP. Tensile properties of high- and medium-entropy alloys. Intermetallics. 2013;39(4):74.
Li DY, Zhang Y. The ultrahigh charpy impact toughness of forged AlxCoCrFeNi high entropy alloys at room and cryogenic temperatures. Intermetallics. 2016;70:24.
Chen C, Pang SJ, Cheng YY, Zhang T. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Al20−xCr20+0.5xFe20Co20Ni20+0.5x high entropy alloys. J Alloys Compd. 2016;659:279.
Tsai SW, Massard TN. Composites Design. Tsai SW, Massard TN, editors. Dayton: Think Composites Press; 1984. 11.
Li YJ, Arnberg L. Quantitative study on the precipitation behavior of dispersoids inDC-cast AA3003 alloy during heating and homogenization. Acta Mater. 2003;51(12):3415.
Li YJ, Muggerud AMF, Olsen A, Furu T. Precipitation of partially coherent α-Al(Mn, Fe)Si dispersoids and their strengthening effect in AA 3003 alloy. Acta Mater. 2012;60(3):1004.
Funakawa Y, Shiozaki T, Tomita K, Yamamoto T, Maeda E. Development of high strength hot-rolled sheet steel consisting of ferrite and nanometer-sized carbides. ISIJ Int. 2004;44(11):1945.
Li J, Hui J, Lu YP, Wang TM, Cao ZQ, Li TJ. Mechanical properties improvement of AlCrFeNi2Ti0.5 high entropy alloy through annealing design and its relationship with its particle-reinforced microstructures. J Mater Sci Technol. 2014;31(04):397.
Shun TT, Du YC. Microstructure and tensile behaviors of fcc Al0.3CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. J Alloys Compd. 2009;479(s 1–2):157.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51571161 and 51271151) and the Program of Introducing Talents of Discipline to Universities (No. B08040).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niu, SZ., Kou, HC., Wang, J. et al. Improved tensile properties of Al0.5CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy by tailoring microstructures. Rare Met. 40, 1–6 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-016-0860-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-016-0860-y