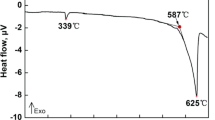
Abstract
Ultrasonic effect on microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of Mg–6Zn–0.5Y magnesium alloy was investigated. The results show that ultrasonic treatment can significantly modify the as-cast microstructure of Mg–6Zn–0.5Y alloy. With the application of ultrasonic treatment, the primary α-Mg phase transforms from coarse dendrites to nearly fine equiaxed grains, and the continuous I-phase at α-Mg boundaries is modified into discontinuous one. Interestingly, the area fraction of I-phase decreases after ultrasonic treatment. Besides, the tensile properties of Mg–6Zn–0.5Y alloy are apparently improved after ultrasonic treatment. Compared to those of the untreated alloy, the ultimate tensile strength and elongation of Mg–6Zn–0.5Y alloy are improved by 67 % and 56 %, respectively.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang J, Ma Q, Pan F. Effects of trace Er addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg–Zn–Zr alloy. Mater Des. 2010;31(9):4043.
Yan X, Lian XH, Yu S. Hot deformation behavior and microstructure evolution of as-cast AZ91D magnesium alloy without pre-homogenization treatment. Rare Met. 2013;32(4):338.
He XL, Wei YH, Hou LF, Yan ZF, Guo CL, Han PJ. Corrosion fatigue behavior of epoxy-coated Mg–3Al–1Zn alloy in NaCl solution. Rare Met. 2014;33(3):276.
Lou Y, Li LX, Zhou J, Na L. Deformation behavior of Mg–8Al magnesium alloy compressed at medium and high temperatures. Mater Charact. 2011;62(3):346.
Zhang Y, Zeng XQ, Liu LF, Lu C, Zhou HT, Li Q, Zhu YP. Effects of yttrium on microstructure and mechanical properties of hot-extruded Mg–Zn–Y–Zr alloys. Mater Sci Eng A. 2004;373(1–2):320.
Singh A, Watanabe M, Kato A, Tsai AP. Crystallographic orientations quasicrystalline phase growing on and interfaces of icosahedral cubic W phase in Mg–Zn–Y alloys. Mater Sci Eng A. 2005;397(1–2):22.
Singh A, Tsai AP. A new orientation relationship OR4 of icosahedral phase with magnesium matrix in Mg–Zn–Y alloys. Scr Mater. 2005;53(9):1083.
Asgharzadeh H, Yoon EY, Chae HJ, Kim TS, Lee JW, Kim HS. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a Mg–Zn–Y alloy produced by a powder metallurgy route. J Alloys Compd. 2014;586(S1):S95.
Li D, Zhang JS, Que ZP, Xu CX, Niu XF. Effects of Mn on the microstructure and mechanical properties of long period stacking ordered Mg95Zn2.5Y2.5 alloy. Mater Lett. 2013;109:46.
Kim DH, Lee JY, Lim HK, Kim WT, Kim DH. Effect of Al addition on the elevated temperature deformation behavior of Mg–Zn–Y alloy. Mater Sci Eng A. 2008;487(1–2):481.
Chen B, Lu C, Lin DL, Zeng XQ. Effect of zirconium addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg97Y2Zn1 alloy. Trans Nonferr Met Soc China. 2012;22(4):773.
Kim J, Kawamura Y. Influence of rare earth elements on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg97Zn1Y1RE1 alloys. Mater Sci Eng A. 2013;573:62.
Liu XB, Osawa Y, Takamori S, Mukai T. Microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ91 alloy produced with ultrasonic vibration. Mater Sci Eng A. 2008;487(1–2):120.
Puga H, Costa S, Barbosa J, Ribeiro S, Prokic M. Influence of ultrasonic melt treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of AlSi9Cu3 alloy. Mater Process Technol. 2011;211(11):1729.
Zhang SL, Zhao YT, Cheng XN, Chen G, Dai QX. High-energy ultrasonic field effects on the microstructure and mechanical behaviors of A356 alloy. J Alloys Compd. 2009;470(1–2):168.
Patel B, Chaudhari GP, Bhingole PP. Microstructural evolution in ultrasonicated AS41 magnesium alloy. Mater Lett. 2012;66(1):335.
Qian M, Ramirez A, Das A. Ultrasonic refinement of magnesium by cavitation: clarifying the role of wall crystals. J Cryst Growth. 2009;311(14):3708.
Pan J, Yoshida M, Sasaki G, Fukunaga H. Metal pipe joining with aluminum alloy by ultrasonic insert casting. Mater Manuf Process. 2000;15(6):867.
Zhang ZQ, Le QC, Cui JZ. Microstructures of Mg–Al binary magnesium alloy solidified with ultrasonic treatment. Mater Sci Technol. 2009;25(7):931.
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the National Great Theoretic Research Project of China (No. 2013CB632200) and the Sharing Fund of Chongqing University’s Large-Scale Equipment (No. 2013063009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, D., Xue, HS., Yang, G. et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg–6Zn–0.5Y magnesium alloy prepared with ultrasonic treatment. Rare Met. 36, 622–626 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-015-0553-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-015-0553-y