Abstract
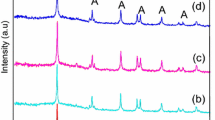
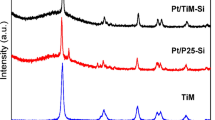
Three different photocatalysts including TiO2, TiO2/SiO2 and TiO2/SiO2/Ag were synthesized via sol–gel growth method, in which colloidal silica was used as Si source, titanium tetra iso-propoxide (TTiP) as titanium source, Ag+ as dopant ion and hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) as dispersant. The purpose was to study the enhancement of photocatalytic activity of TiO2 by deposition on SiO2 colloids and also doping with Ag ion. The catalysts were characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray fluorescence (XRF), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) methods. It is confirmed that the major phase in all catalysts is anatase. Photocatalytic activity was studied in various conditions for degradation of methylorange (as a model pollutant) to evaluate the effect of some parameters on degradation efficiency. Studying the degradation process in various pH values reveals that the degradation is more efficient in acidic solution than alkaline condition. Coupling the photocatalytic process with some fields called electro-photochemical (EP), magnetic-photochemical (MP) and ultrasonic-photochemical (UP) was studied at two pH values which were compared with photochemical (P) alone. It is concluded that in most cases, the EP is the best coupled system and has the maximum efficiency. Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC–MS) analysis was used to check the complete decomposition of methylorange at the end of process.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sakthivel S, Neppolian B, Shankar MV, Arabindoo B, Palanichamy M, Murugesan V. Solar photocatalytic degradation of azo dye: comparison of photocatalytic efficiency of ZnO and TiO2. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells. 2003;77(1):65.
Mrowetz M, Selli E. Photocatalytic degradation of formic and benzoic acids and hydrogen peroxide evolution in TiO2 and ZnO water suspensions. J Photochem Photobiol A. 2006;180(1–2):15.
Height MJ, Pratsinis SE, Mekasuwandumrong O, Praserthdam P. Ag–ZnO catalysts for UV-photodegradation of methylene blue. Appl Catal B. 2006;63(3–4):305.
Wang SZ. Titania deposited on soft magnetic activated carbon as a magnetically separable photocatalyst with enhanced activity. Appl Surf Sci. 2010;256(21):6191.
Akpan UG, Hameed BH. Parameters affecting the photocatalytic degradation of dyes using TiO2-based photocatalysts: a review. J Hazard Mater. 2009;170(2–3):520.
Bellardita M, Addamo M, Paola AD, Marci G, Palmisano L, Cassar L, Borsac M. Photocatalytic activity of TiO2/SiO2 systems. J Hazard Mater. 2010;174(1–3):707.
Hu C, Tang Y, Yu JC, Wong PK. Photocatalytic degradation of cationic blue XGRL adsorbed on TiO2/SiO2 photocatalyst. Appl Catal B. 2003;40(2):131.
Patrick W, Dietmar S. Photodegradation of rhodamine B in aqueous solution via SiO2–TiO2 nano-spheres. J Photochem Photobiol A. 2007;185(1):19.
Marugán J, Lopez-Munoz MJ, Aguado J, van Grieken R. On the comparison of photocatalysts activity: a novel procedure for the measurement of titania surface in TiO2/SiO2 materials. Catal Today. 2007;124(3–4):103.
Zhang M, An T, Fu J, Sheng G, Wang X, Hu X, Ding X. Photocatalytic degradation of mixed gaseous carbonyl compounds at low level on adsorptive TiO2/SiO2 photocatalyst using a fluidized bed reactor. Chemosphere. 2006;64(3):421.
Aguado J, van Grieken R, Lopez-Munoz MJ, Marugan JA. Comprehensive study of the synthesis, characterization and activity of TiO2 and mixed TiO2/SiO2 photocatalysts. Appl Catal A. 2006;312(1):202.
Beril E, Ufuk B, Gurkan K. Photocatalytic antibacterial activity of TiO2–SiO2 thin films: the effect of composition on cell adhesion and antibacterial activity. J Photochem Photobiol A. 2014;283(1):819.
Chen Y, Wang K, Lou L. Photodegradation of dye pollutants on silica gel supported TiO2 particles under visible light irradiation. J Photochem Photobiol A. 2004;163(1–2):281.
Anderson C, Bard AJ. Improved photocatalytic activity and characterization of mixed TiO2/SiO2 and TiO2/Al2O3 materials. J Phys Chem. 1997;101(14):26.
Xu Y, Zheng W, Liu W. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of supported TiO2: dispersing effect of SiO2. J Photochem Photobiol A. 1999;122(1):57.
Ding Z, Lu GQ, Greenfield PF. Kinetic study on photocatalytic oxidation of phenol in water by silica-dispersed titania nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000;232(1):1.
Bouras P, Stathatos E, Lianos P. Pure versus metal-ion-doped nanocrystalline titania for photocatalysis. Appl Catal B. 2007;73(1–2):51.
Ding X, An T, Li G, Zhang S, Chen J, Yuan J, Zhao H, Chen H, Sheng G, Fu J. Preparation and characterization of hydrophobic TiO2 pillared clay: the effect of acid hydrolysis catalyst and doped Pt amount on photocatalytic activity. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2008;320(2):501.
Cheng JR, Guang PW, Yu ChCh, Yao QCh. Degradation of benzene on Zr-doped TiO2 photocatalysts with a bimodal pore size distribution. Rare Metals. 2014;33(6):714.
Liao DL, Badour CA, Liao BQ. Preparation of nanosized TiO2/ZnO composite catalyst and its photocatalytic activity for degradation of methylorange. J Photochem Photobiol A. 2008;194(1):11.
Rengaraj S, Li XZ. Photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol A as an endocrine disruptor in aqueous suspension using Ag–TiO2 catalysts. J Environ Pollut. 2006;27(1/2/3):20.
Xu AW, Gao Y, Liu HQ. The preparation, characterization, and their photocatalytic activities of rare-earth-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. J Catal. 2002;207(2):151.
Naveen CS, Raghu P, Mahesh HM, Narasimha RK, Rakesh KR, Phani AR. Optical and structural properties of highly porous shell structured Fe doped TiO2 thin films. Rare Metals. 2014;33(5):578.
Ranjit KT, Willner I, Bossmann SH, Braun AM. Lanthanide oxidedoped titanium dioxide photocatalysts: novel photocatalysts for the enhanced degradation of p-chlorophenoxyacetic acid. Environ Sci Technol. 2001;35(7):1544.
Ranjit KT, Willner I, Bossmann SH, Braun AM. Lanthanide oxide doped titanium dioxide photocatalysts: effective photocatalysts for the enhanced degradation of salicylic acid and t-Cinnamic acid. J Catal. 2001;204(2):305.
Aberoomand AP, Moradi DSH, Samadi S, Tehrani MS, Givianrad MH, Kamyar S. Effect comparison of Nd3+, pectin and poly(ethylene glycol) on the photocatalytic activity of TiO2/SiO2 film. Asian J Chem. 2010;22(10):1619.
Yu JG, Yu HG, Cheng B, Zhao XJ, Yu JC, Ho WK. The effect of calcination temperature on the surface microstructure and photocatalytic activity of TiO2 thin films prepared by liquid phase deposition. J Phys Chem B. 2003;107(50):13871.
Meltem A, Funda S, Ertugrul A. Effect of Fe3+ ion doping to TiO2 on the photocatalytic degradation of malachite green dye under UV and Vis-irradiation. J Photochem Photobiol A. 2009;203(1):64.
Lopez T, Sanchez E, Bosch P, Meas Y, Gomez R. FTIR and UV–Vis (diffuse reflectance) spectroscopic characterization of TiO2. Mater Chem Phys. 1992;32(2):141.
Suwarnkar MB, Dhabbe RS, Kadam AN, Garadkarn KM. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of Ag doped TiO2 nanoparticles synthesized by a microwave assisted method. Ceram Int. 2014;40(4):5489.
Ioannis KK, Triantafyllos AA. TiO2-assisted photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes in aqueous solution: kinetic and mechanistic investigations: a review. Appl Catal B. 2004;49(1):1.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Nuclear Science and Technology Research Institute of Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghasemi Mobtaker, H., Ahmadi, S.J., Moradi Dehaghi, S. et al. Coupling system application in photocatalytic degradation of methylorange by TiO2, TiO2/SiO2 and TiO2/SiO2/Ag. Rare Met. 34, 851–858 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-015-0455-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-015-0455-z