Abstract
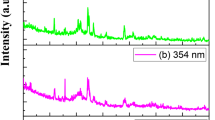
As a novel structure, inverse opal, with three-dimensional periodic macropore and mesopore and huge specific surface area, has great promising applications. In this paper, tin dioxide (SnO2) inverse opal films were prepared with sol–gel method by cooperative opal template. The surface morphologies of SnO2 inverse opal films were examined by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), the inner structure of SnO2 inverse opal films was examined by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), the optical properties of SnO2 inverse opal films were studied and discussed in detail. Optical reflectance spectra reveal that, for the opal films, the wavelengths of the reflectance peak confirmed by the experimental reflectance spectra are consistent with the theoretical values; for the SnO2 inverse opal films, the wavelengths of the reflectance peak confirmed by the experimental reflectance spectra deviate from theoretical values largely.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sözüer H, Haus J, Inguva R. Photonic bands: convergence problems with the plane-wave method. Phys Rev B. 1992;45(24):13962.
Yan CH, Xie ZY, Wang ZF, Zhang ZJ, Wu YY, Zhang M. Preparation and ER performance of hard-shell composite TiO2/PS microspheres. Chin J Rare Met. 2013;37(4):650.
Liu Y, Hu X, Zhang D, Cheng B, Zhang D, Meng Q. Subpicosecond optical switching in polystyrene opal. Appl Phys Lett. 2005;86(15):151102.
Scalora M, Dowling JP, Bowden CM, Bloemer MJ. Optical limiting and switching of ultrashort pulses in nonlinear photonic band gap materials. Phys Rev Lett. 1994;73(10):1368.
Shin JH, Moon JH. Bilayer inverse opal TiO2 electrodes for dye-sensitized solar cells via post-treatment. Langmuir. 2011;27(10):6311.
Scott RWJ, Yang S, Chabanis G, Coombs N, Williams D, Ozin G. Tin dioxide opals and inverted opals: near–ideal microstructures for gas sensors. Adv Mater. 2001;13(19):1468.
Stein A, Schroden RC. Colloidal crystal templating of three-dimensionally ordered macroporous solids: materials for photonics and beyond. Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci. 2001;5(6):553.
Holland BT, Blanford CF, Stein A. Synthesis of macroporous minerals with highly ordered three-dimensional arrays of spheroidal voids. Science. 1998;281(5376):538.
Norris DJ, Vlasov YA. Chemical approaches to three-dimensional semiconductor photonic crystals. Adv Mater. 2001;13(6):371.
Holland BT, Blanford CF, Do T, Stein A. Synthesis of highly ordered, three-dimensional, macroporous structures of amorphous or crystalline inorganic oxides, phosphates, and hybrid composites. Chem Mater. 1999;11(3):795.
Miguez H, Meseguer F, Lopez C, Holgado M, Andreasen G, Mifsud A, Fornés V. Germanium FCC structure from a colloidal crystal template. Langmuir. 2000;16(10):4405.
Chung Y-W, Leu I-C, Lee J-H, Hon M-H. Filling behavior of ZnO nanoparticles into opal template via electrophoretic deposition and the fabrication of inverse opal (Discussion). Electrochim Acta. 2009;54(13):3677.
Hatton B, Mishchenko L, Davis S, Sandhage KH, Aizenberg J. Assembly of large-area, highly ordered, crack-free inverse opal films. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2010;107(23):10354.
Zheng Z, Gao K, Luo Y, Li D, Meng Q, Wang Y, Zhang DZ. Rapidly infrared-assisted cooperatively self-assembled highly ordered multiscale porous materials. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130(30):9785.
Scharrer M, Wu X, Yamilov A, Cao H, Chang RPH. Fabrication of inverted opal ZnO photonic crystals by atomic layer deposition. Appl Phys Lett. 2005;86(15):151113.
Fu M, Zhou J, Xiao Q, Li B, Bai Y, Li L. Preparation and characterization of nanocrystalline ZnS/ZnO doped silica inverse opals. J Electroceram. 2008;21(14):374.
Nagasawa M, Shionoya S, Makishima S. Vapor reaction growth of SnO2 single crystals and their properties. Jpn J Appl Phys. 1965;4(3):195.
Scott RWJ, Yang SM, Chabanis G, Coombs N, Williams DE, Ozin GA. Tin dioxide opals and inverted opals: near-ideal microstructures for gas sensors. Adv Mater. 2001;13(19):1468.
Scott RWJ, Yang SM, Coombs N, Ozin GA, Williams DE. Engineered sensitivity of structured tin dioxide chemical sensors: opaline architectures with controlled necking. Adv Funct Mater. 2003;13(3):225.
Sutti A, Baratto C, Calestani G, Dionigi C, Ferroni M, Faglia G, Sberveglieri G. Inverse opal gas sensors: Zn(II)-doped tin dioxide systems for low temperature detection of pollutant gases. Sens Actuators B. 2008;130(1):567.
Arsenault E, Soheilnia N, Ozin GA. Periodic macroporous nanocrystalline antimony-doped tin oxide electrode. ACS Nano. 2011;5(4):2984.
Reese CE, Guerrero CD, Weissman JM, Lee K, Asher SA. Synthesis of highly charged, monodisperse polystyrene colloidal particles for the fabrication of photonic crystals. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2000;232(1):76.
Pang CX, Zhang LX, Tan J, Ye ZM, Chen JH. The study of preparing nanocrystalline SnO2 by sol–gel method. J Guangxi Teach Educ Univ (Nat Sci Ed). 2006;23(9):26.
Meng Q-B, Gu Z-Z, Sato O, Fujishima A. Fabrication of highly ordered porous structures. Appl Phys Lett. 2000;77(26):4313.
Yan G, Zhang X, Huang P, Wang L, Qi F, Feng B. Influence of deposition time on the morphology and optical properties of SiO2–ZnO composite photonic crystals. Chin Sci Bull. 2011;56(6):562.
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51072177), Jiangsu Province Environmental Material Key Laboratory Project (No. 017375003), and Jiangsu Ordinary University Graduate Students Scientific Research Innovation Project (No. CXZZ12_0896). The authors would like to thank Zhi-Feng Wang professor for many useful discussions concerning the SEM image.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, JQ., Wu, YY., Yuan, SS. et al. Preparation and optical properties of tin dioxide inverse opal film. Rare Met. 41, 1032–1036 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-014-0427-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-014-0427-8