Abstract
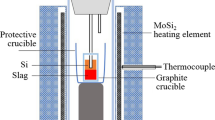
In order to investigate the boron removal effect in slag refining process, intermediate frequency furnace was used to purify boron in SiO2-CaO-Na3AlF6-CaSiO3 slag system at 1,550 °C, and back propagation (BP) neural network was used to model the relationship between slag compositions and boron content in SiO2-CaO-Na3AlF6-CaSiO3 slag system. The BP neural network predicted error is below 2.38 %. The prediction results show that the slag composition has a significant influence on boron removal. Increasing the basicity of slag by adding CaO or Na3AlF6 to CaSiO3-based slag could contribute to the boron removal, and the addition of Na3AlF6 has a better removal effect in comparison with the addition of CaO. The oxidizing characteristic of CaSiO3 results in the ineffective removal with the addition of SiO2. The increase of oxygen potential (\(p_{{{\text{O}}_{2} }}\)) in the CaO-Na3AlF6-CaSiO3 slag system by varying the SiO2 proportion can also contribute to the boron removal in silicon ingot. The best slag composition to remove boron was predicted by BP neural network using genetic algorithm (GA). The predicted results show that the mass fraction of boron in silicon reduces from 14.0000 × 10−6 to 0.4366 × 10−6 after slag melting using 23.12 % SiO2-10.44 % CaO-16.83 % Na3AlF6-49.61 % CaSiO3 slag system, close to the experimental boron content in silicon which is below 0.5 × 10−6.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zheng SS, Thorvald E, Merete T, Lue XT. Separation of phosphorus from silicon by induction vacuum refining. Sep Purif Technol. 2011;82:128.
Reimann C, Trempa M, Jung T, Friedrich J, Muller G. Modeling of incorporation of O, N, C and formation of related precipitates during directional solidification of silicon under consideration of avariable processing parameters. J Cryst Growth. 2010;312(7):878.
Martorano MA, Ferreira Neto JB, Oliveira TS, Tsubaki TO. Refining of metallurgical silicon by directional solidification. Mater Sci Eng B. 2011;176(3):217.
Yves D. Purification of silicon for photovoltaic applications. J Cryst Growth. 2012;360:61.
Yu ZL, Chen Jh, Xie G, Ma WH, Xie KQ. Aluminum removal from metallurgical grade silicon with pressure leaching. Chin J Rare Met. 2013;37(3):453.
Leandro AVT, Yomei T, Toshinobu Y, Kazuki M. Behavior and state of boron in CaO-SiO2 slags during refining of solar grade silicon. ISIJ Int. 2009;49(6):777.
Johnston MD, Barati M. Distribution of impurity elements in slag-silicon equilibria for oxidative refining of metallurgical silicon for solar cell applications. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cell. 2010;94(12):2085.
Wu JJ, Ma WH, Jia BJ, Yang B, Liu DC, Dai YN. Boron removal from metallurgical grade silicon using a CaO-Li2O-SiO2 molten slag refining technique. J Non-Cryst Solids. 2012;358(23):3079.
Cai J, Li JT, Chen WH, Chen C, Luo XT. Boron removal from metallurgical silicon using CaO-SiO2-CaF2 slags. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China. 2011;21(6):1402.
Luo DW, Liu N, Lu YP, Zhang GL, Li TJ. Removal of boron from metallurgical grade silicon by electromagnetic induction slag melting. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China. 2011;21(5):1178.
Ding Z, Ma WH, Wei KX, Wu JJ, Zhou Y, Xie KQ. Boron removal from metallurgical-grade silicon using lithium containing slag. J Non-Cryst Solid. 2012;358(18):2708.
Liu K, Guo WY, Shen XL, Tan ZF. Research on the forecast model of electricity power industry loan based on GA-BP neural network. Energy Procedia. 2014;14:1918.
Yu SW, Zhu KJ, Diao FQ. A dynamic all parameters adaptive BP neural networks model and its application on oil reservoir prediction. Appl Math Comput. 2008;195(1):66.
Zhang L, Sun S, Jahanshahi S. An approach to modeling Al2O3 containing slags with the cell model. J Phase Equilib Diffus. 2007;28(1):121.
Zhang L, Tan Y, Li JY, Liu Y, Wang DK. Study of boron removal from molten silicon by slag refining under atmosphere. Mater Sci Semicond Process. 2013;16(6):1645.
Johnston MD, Barati M. Effect of slag basicity and oxygen potential on the distribution of boron and phosphorus between slag and silicon. J Non-Cryst Solid. 2011;357(3):970.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (No. 2012AA062302).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, SL., Lu, HM., Wang, PP. et al. Boron removal from metallurgical grade silicon by slag refining based on GA-BP neural network. Rare Met. 40, 237–242 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-014-0373-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-014-0373-5