Abstract
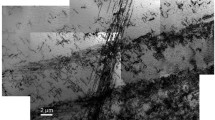
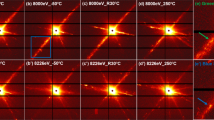
An abnormal phenomenon was investigated in Ti44Ni51Nb5 alloy which exhibits an absence of martensite transformation and a negative temperature dependence of electrical resistivity with the temperature decreasing. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis shows the matrix phase keeps a B2 structure during cooling without a martensite transformation, and dynamic mechanical analysis displays a frequency-dependent AC modulus/loss anomaly at T g according to Vogel-Fulcher relation. Simultaneously, transmission electronic microscope (TEM) analysis manifests the superlattice spots at near 1/3 commensurate position, implying an existence of strain nanodomains with an R-like structure. And above experiment results provide evidence for the “strain glass” transition in defect-containing ferroelastic Ti44Ni51Nb5 alloy.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Otsuka K, Ren X. Physical metallurgy of Ti–Ni-based shape memory alloys. Prog Mater Sci. 2005;50(5):511.
Sarkar S, Ren X, Otsuka K. Evidence for strain glass in the ferroelastic-martensitic system Ti(50−x)Ni(50+x). Phys Rev Lett. 2005;95(20):205702.
Otsuka K, Wayman CM. Shape Memory Materials. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 1998. 45.
Otsuka K, Kakeshita. Science and technology of shape-memory alloys: new developments T. MRS Bull. 2002;27(02):91.
Khachaturyan AG. Theory of Structural Transition in Solids. New York: Wiley; 1983. 102.
Lashley JC, Shapiro SM, Winn BL, Opeil CP, Manley ME, Alatas A, Ratcliff W, Park T, Fisher RA, Mihaila B, Riseborough P, Salje EK, Smith JL. Observation of a continuous phase transition in a shape-memory alloy. Phys Rev Lett. 2008;101(13):135703.
Murakami Y, Shindo D. Precursor effects of martensitic transformations in Ti-based alloys studied by electron microscopy with energy filtering. Philos Mag Lett. 2001;203(1):22.
Ren XB, Wang Y, Otsuka K. Ferroelastic nanostructures and nanoscale transitions: ferroics with point defects. MRS Bull. 2009;34(11):838.
Wang SM, Ma TD, Yin XQ, Li YF. Texture evolvement of thermal and stress induced martensite phase transformation in Ti50Ni49.5Fe0.5 alloy. Chin J Rare Metals. 2013;37(3):341.
Liu GQ, Kou SZ. Effect of Nb on thermal stability and mechanical properties of Zr55Cu30Ni5Al10 bulk metallic glass. Chin J Rare Metals. 2013;37(4):576.
Zhou YM, Xue DZ, Ding XD, Wang Y, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Wang S, Otsuka K, Sun J, Ren XB. Strain glass in doped Ti50(Ni50−x D x ) (D=Co, Cr, Mn) alloys: implication for the generality of strain glass in defect-containing ferroelastic systems. Acta Mater. 2010;58(16):5433.
Zhou YM, Xue DZ, Ding XD, Otsuka K, Sun J, Ren XB. High temperature strain glass in Ti50(Pd50−x Cr x ) alloy and the associated shape memory effect and superelasticity. Appl Phys Lett. 2009;95(15):151906.
Wang D, Zhang Z, Zhang J, Zhou YM, Wang Y, Ding XD, Wang YZ, Ren XB. Strain glass in Fe-doped Ti–Ni. Acta Mater. 2010;58(18):6206.
Ren XB. Disorder and Strain-Induced Complexity in Functional Materials. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag; 2011. 21.
Ren XB, Wang Y, Zhou YM, Zhang Z, Wang D, Fan GL, Otsuka K, Suzuki T, Ji YC, Zhang J, Tian Y, Hou S, Ding XD. Strain glass in ferroelastic systems: premartensitic tweed versus strain glass. Philos Mag. 2010;90(1–4):141.
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51271010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, GY., Chen, B., Meng, QK. et al. Strain glass in defect-containing ferroelastic Ti44Ni51Nb5 alloy. Rare Met. 34, 829–832 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-014-0229-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-014-0229-z