Abstract
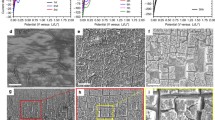
Silicon has been investigated extensively as a promising anode material for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. Understanding the failure mechanism of silicon-based anode electrodes for lithium-ion batteries is essential to solve the problem of low coulombic efficiency and capacity fading on cycling and also to further commercialize this very new energetic material in cells. To reach this goal, the structure changes of bulk silicon particles and electrode after cycling were studied using ex-situ scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) techniques. The SEM images indicated that the microstructural changes of the bulk silicon particles during cycling led to a layer rupture of the electrode and then the breakdown of the conductive network and the failure of the electrode. The result contributes to the basic understanding of the failure mechanism of a bulk silicon anode electrode for lithium-ion batteries.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sharma RA, Seefurth RN. Thermodynamic properties of the lithium–silicon system. J Electrochem Soc. 1976;123(12):1763.
Holzapfel M, Buqa H, Scheifele W, Novak P, Petrat FM. A new type of nano-sized silicon/carbon composite electrode for reversible lithium insertion. Chem Commun. 2005;28(12):1566.
Kasavajjula U, Wang C, Appleby AJ. Nano- and bulk-silicon-based insertion anodes for lithium-ion secondary cells. J Power Sources. 2007;163(2):1003.
Zhang WJ. A review of the electrochemical performance of alloy anodes for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources. 2011;196(1):13.
Li T, Yang JY, Lu SG. Effect of modified elastomeric binders on the electrochemical properties of silicon anodes for lithium-ion batteries. Int J Miner Metall Mater. 2012;19(8):752.
Chen JB, Zhao HL, He JC, Wang J. Si/MgO composite anodes for Li-ion batteries. Rare Met. 2011;30(2):166.
Li T, Qiu WH, Zhao HL, Liu JJ. Synthesis and electrochemical characterization of 5 V LiNi1/2Mn3/2O4 cathode materials by low-heating solid-state reaction. J Power Sources. 2007;174(2):515.
Gao G, Liu AF, Hu ZH, Xu YY, Liu YF. Synthesis of LiFePO4/C as cathode material by a novel optimized hydrothermal method. Rare Met. 2011;30(5):433.
Xia JH, Liu ZJ, Li DR, Lu ZC, Zhou SX. Effect of current collector on electrochemical performance of alloy anodes of lithium ion batteries. Rare Met. 2011;30(1):48.
Wang YL, Guo M, Zhang M, Wang XD. Template-free hydrothermal synthesis of single-crystalline SnO2 nanocauliflowers and their optical properties. Rare Met. 2009;28(5):449.
Zhao YJ, Wang SJ, Zhao CS, Xia DG. Synthesis and electrochemical performance of LiCoPO4 micron-rods by dispersant-aided hydrothermal method for lithium ion batteries. Rare Met. 2009;28(1):117.
Lin Y, Zeng BZ, Lin YB, Li XW, Zhao GY. Electrochemical properties of carbon-coated LiFePO4 and LiFe0.98Mn0.02PO4 cathode materials synthesized by solid-state reaction. Rare Met. 2012;31(2):145.
Ryu JH, Kim JW, Sung Y-E, Oh SM. Failure modes of silicon powder negative electrode in lithium secondary batteries. Electrochem Solid. 2004;7(10):A306.
Kalnaus S, Rhodes K, Daniel C. A study of lithium ion intercalation induced fracture of silicon particles used as anode material in Li-ion battery. J Power Sources. 2011;196(19):8116.
Obrovac MN, Krause LJ. Reversible cycling of crystalline silicon powder. J Electrochem Soc. 2007;154(2):A103.
Li J, Dahn JR. An in situ X-ray diffraction study of the reaction of Li with crystalline Si. J Electrochem Soc. 2007;154(3):A156.
Zha Q. Porous electrode. In: Shijie C, editor. Kinetics of electrode process. Beijing: Science Press; 2002;345.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51004016 and 51004017) and the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (Nos.2012AA110102 and 2011AA11A269).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, T., Yang, JY., Lu, SG. et al. Failure mechanism of bulk silicon anode electrodes for lithium-ion batteries. Rare Met. 32, 299–304 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-013-0045-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-013-0045-x