Abstract
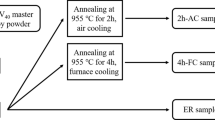
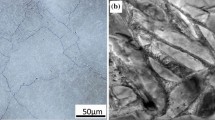
In this study, the effect of temperatures and cooling rates of heat treatment on the microstructure of a powder metallurgy (PM) Ti-46Al-2Cr-2Nb-(B,W) (at.%) alloy was studied. Depending on the cooling rate and temperature, the different structures were obtained from the initial near-γ (NG) microstructures by heat treatment in the α+γ field. The results show that the microstructures of samples after furnace cooling (FC) consist primarily of equiaxed γ and α2 grains, with a few grains containing lamellae. Duplex microstructures consist mainly of γ grains and lamellar colonies were obtained in the quenching into another furnace at 900°C (QFC) samples. However, further increasing of the cooling rate to air cooling (AC) induces the transformation of α→α2 and results in a microstructure with equiaxed γ and α2 grains, and no lamellar colonies are found.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim Y.W., Progress in the understanding of gamma titanium aluminides, JOM, 1991, 43(8): 40.
Takeyama M., Microstructural evolution and tensile properties of titanium-rich TiAl alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1992, 152(1–2): 269.
Su Y.Q., Liu X.W., Luo L.S., Zhao L., Guo J.J., and Fu H.Z., Deoxidation of Ti-Al intermetallics via hydrogen treatment, Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 2010, 35(17): 9214.
Su Y.Q., Liu C., Li X.Z., Guo J.J., Li B.S., Jia J., and Fu H.Z., Microstructure selection during the directionally peritectic solidification of Ti-Al binary system, Intermetallics, 2005, 13(3–4): 267.
Su Y.Q., Guo J.J., Jia J., Liu G.Z., and Liu Y., Composition control of a TiAl melt during the induction skull melting (ISM) process, J. Alloy. Compd., 2002, 334(1–2): 261.
Kim Y.W., Ordered intermetallic alloys, part III: gamma titanium aluminides, JOM, 1994, 46(7): 30.
Lu X., Zhu L.P., Liu C.C., Zhang L., Wu M., and QU X.H., Fabrication of micro-fine high Nb-containing TiAl alloyed powders by fluidized bed jet milling, Rare Metals, 2012, 31(1): 1.
Kim Y.W., Intermetallic alloys based on gamma titanium aluminide, JOM, 1989, 41(7): 24.
Toshimitsu T., Manufacturing technology for gamma-TiAl alloy in current and future applications, Rare Metals, 2011, 30(S1): 294.
Imayev R.M., Imayev V.M., Oehring M., and Appel F., Alloy design concepts for refined gamma titanium aluminide based alloys, Intermetallics, 2007, 15(4): 451.
Yang S.H., Kim W.Y., and Kim M.S., Fabrication of unidirectional porous TiAl-Mn intermetallic compounds by reactive sintering using extruded powder mixtures, Intermetallics, 2003, 11(8): 849.
Chu W.Y., and Thompson A.W., Effect of grain size on yield strength in TiAl, Scripta Metall., 1991, 25(3): 641.
Koeppe C., Bartels C., Seege J., and Mecking H., General aspects of the thermomechanical treatment of two-phase intermetallic TiAl compounds, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1993, 24A(8): 1795.
Arno B., Carsten K., and Heinrich M. Microstructure and properties of Ti-48Al-2Cr after thermomechanical treatment. Materials Science and Engineering A., 1995, 192–193(1): 226.
Zhang G., Blenkinsop P.A., and Wise M.L.H., Phase transformations in HIPed Ti-48Al-2Mn-2Nb powder during heat-treatments, Intermetallics, 1996, 4(6): 447.
Flower H.M., and Christodoulou J., Phase equilibria and transformations in titanium aluminides, Mater. Sci. Technol., 1999, 15(1): 45.
Denquin A., and Naka S., Phase transformation mechanism involved in two phase TiAl-II: discontinuous coarsening and massive-type transformation, Acta Metall., 1996, 44(1): 353.
Kim Y.W., Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of a forged gamma titanium aluminide alloy, Acta Metall. Mater., 1992, 40(6): 1121.
Aaronson H.I., Atomic mechanisms of diffusional nucleation and growth and comparisons with their counterparts in shear transformations, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1993, 24(2): 241.
Mishin Y., and Herzig C., Dision in the Ti-Al system, Acta Metall., 2000, 48(2): 589.
Denquin A., and Naka S., Phase transformation mechanism involved in two phase TiAl-I: lamellar structure formation, Acta Metall., 1996, 44(1): 343.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, M., Zheng, L., Lang, Z. et al. Microstructural evolution of a PM TiAl alloy during heat treatment in α+γ phase field. Rare Metals 31, 424–429 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-012-0532-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-012-0532-5