Abstract
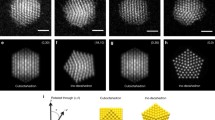
Nanometre-size gold displays exceptional physical and chemical properties that depend not only on their sizes but also on their shapes. Here we investigate the growth of size-selected gold nanoclusters and their shapes characterized using both TEM and STEM. It is found that the cluster-substrate interaction influences the height of small nanoclusters Au80, as indicated by comparison between MgO and amorphous carbon substrate, but this effect is overcome by the dynamical landing process at high deposition energy. Moreover, large gold nanoclusters, Au8860 have asymmetric structures with aspect ratio between 1 and 2. The simulation shows that the icosahedral shape observed is significantly lower in energy than the alternatives and is expected to be stable.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim W.B., Voitl T., Rodriguez-Rivera G.J., and Dumesic J.A., Powering fuel cells with CO via aqueous polyoxometalates and gold catalysts, Science, 2004, 305: 1280.
Yoon B., Hakkinen H., Landman U., Worz A.S., Antonietti J.-M., Abbet S., Judai K., and Heiz U., Charging effects on bonding and catalyzed oxidation of CO on Au-8 clusters on MgO, Science, 2005, 307: 403.
Gluhoi A.C., Lin S.D., and Nieuwenhuys B.E., The beneficial effect of the addition of base metal oxides to gold catalysts on reactions relevant to air pollution abatement, Cata. Today, 2004, 90: 175.
Liu Z.P., Jenkins S.J., and King D.A., Origin and activity of oxidized gold in water-gas-shift catalysis, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2005, 94: 196102.
Hughes M.D., Xu Y-J., Jenkins P., Mcmorn P., Landon P., Enache D.L., Carley A. F., Attard G.A., Hutchings G.J, King F., Stitt E.H., Johnston P., Griffin K., and Kiely C.J., Tunable gold catalysts for selective hydrocarbon oxidation under mild conditions, Nature, 2005, 437: 1132.
Kowalska E., Mahaney O.O.P., Abe R., and Ohtani B., Visible-light-induced photocatalysis through surface plasmon excitation of gold on titania surfaces, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2010, 12: 2344.
Chen M.S., and Goodman D.W., The structure of catalytically active gold on titania, Science, 2004, 306: 252.
Molina L.M., and Hammer B., Active role of oxide support during CO oxidation at Au/MgO, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2003, 90: 206102.
Pratontep S., Carroll S.J., Xirouchaki C., Streun M., and Palmer R.E. Size-selected cluster beam source based on radio frequency magnetron plasma sputtering and gas condensation, Rev. Sci. Instrum., 2005, 76: 045103.
Di Vece M., Young N.P., Li Z., Chen Y., and Palmer R.E., Co-deposition of atomic clusters of different size and composition, Small, 2006, 2: 1270.
Hacquart R., and Jupille J., Hydrated MgO smoke crystals from cubes to octahedra. Chem. Phys. Lett., 2007, 429: 91.
Chen Y., Palmer R.E., and Wilcoxon J.P., Sintering of passivated gold nanoparticles under the electron beam, Langmuir, 2006, 22: 2851.
Li Z.Y., Yuan J., Chen Y., Palmer R.E., and Wilcoxon J.P., Local three-dimensional visualization of nanoparticle assemblies, Adv. Mater. 2005, 17: 2885.
Li Z.Y., Yuan J., Chen Y., Palmer R.E., and Wilcoxon J.P., Direct imaging of core-shell structure in silver-gold bimetallic nanoparticles Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87: 243103.
Li Z.Y., Wilcoxon J.P., Yin F., Chen Y., and Palmer R. E., Structures and optical properties of 4-5 nm bimetallic AgAu nanoparticles, Faraday Discuss, 2008, 138: 363.
Young N.P., Li Z.Y., Chen Y., Palomba S., Di. Vece M., and Palmer R.E., Weighing supported nanoparticles: Size-selected clusters as mass standards in nanometrology, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2008, 101: 246103.
Curley B.C., Johnston R.L., Young N.P., Li Z.Y., Di Vece M., Palmer R.E., and Bleloch A.L., Combining theory and experiment to characterize the atomic structures of surface-deposited AU(309) clusters, J. Phys Chem., 2007, 111: 17846.
Miyamoto A., Hattori T., and Inui T., Moleular-dynamcs simulation of deposition process of ultrafine metal particles on MgO(100) surface, Appl. Surf. Sci., 1992, 60/61: 660.
Barnard A.S., Young N., Kirkland A.I., van Huis M.A., and Xu H., Nanogold: a quantitative phase map, ACS Nano, 2009, 3: 1431.
Barnard A.S., and Curtiss LA., Modeling the preferred shape, orientation and aspect ratio of gold nanorods J. Mater. Chem., 2007, 17: 3315.
Barnard A.S., Shape, orientation, and stability of twinned gold nanorods, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112: 1385.
Barnard A.S., A thermodynamic model for the shape and stability of twinned nanostructures, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110: 24498.
Barnard A.S., Lin X.M., and Curtiss L.A., Equilibrium morphology of face-centered cubic gold nanoparticles > 3 nm and the shape changes induced by temperature, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2005, 109: 24465.
Hofmeister H., Shape variations and anisotropic growth of multiply twinned nanoparticles, Z. Kristallogr, 2009, 224: 528.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y. Gold nanoparticles for applications in energy and environment: synthesis and characterization. Rare Metals 30 (Suppl 1), 116–120 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-011-0251-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-011-0251-3