Abstract
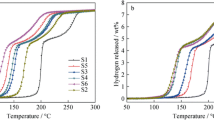
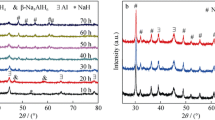
Catalytic effects of NiCl2, TiC and TiN on the dehydrogenation/rehydrogenation characteristics of LiAlH4 were investigated by pressure-content-temperature (PCT), X-ray diffraction (XRD), differential scanning calorimatory (DSC), and field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM). The doped samples exhibit dehydrogenation at much lower temperatures. Doping with NiCl2, TiC and TiN induce a decrease in the decomposition of first step by about 50–65 °C compared to that of as received LiAlH4. Also, amount of hydrogen release is significantly higher for TiC additions than that of samples doped with TiN and NiCl2. Isothermal desorption results at 125 °C reveal that dehydrating rate of doped alanate is much faster than that of pure LiAlH4. TiC, TiN and NiCl2 dopants show the reabsorption of about 1.9 wt.%, 1.3 wt.%, and 1.1 wt.%, respectively. XRD and FESEM analyses suggest that both TiC and TiN are stable during the ball milling as well as the dehydrogenation processes. On the contrary, NiCl2 reacts and causes the partial decomposition of Li alanate during the ball milling process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hashimoto K., Habazaki H., Yamasaki M., Meguro S., Sasaki T., Katagiri H., Matsui T., Fujimura K., Izumiya K., Kumagai N., and Akiyama E., Advanced materials for global carbon dioxide recycling, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2001, 304–306: 88.
Varin R.A., Czujko T., and Wronski Z.S., Nanomaterials for solid state hydrogen storage, Springer Science + Business Media, New York, NY, 2009.
Yang J., Sudik A., Wolverton C., and Siegel D. J., High capacity hydrogen storage materials: attributes for automotive applications and techniques for materials discovery. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2010, 39: 656.
Yang J., and Hirano S., Improving the hydrogen desorption kinetics of complex hydrides, Advanced Materials, 2009, 21: 3023.
Grochala W., and Edwards P.P., Hydrides of the chemical elements for the storage and production of hydrogen. Chem. Rev., 2004, 104(3): 1283.
Maelan A. J., Approaches to increasing gravimetric hydrogen storage capacities of solid hydrogen storage materials. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2003, 28(8): 821.
U.S. Department of Energy, Basic research needs for the hydrogen economy, Second Printing, Washington, DC, 2004. 31.
Schlapbach L., and Zuttel L.A., Hydrogen-storage materials for mobile applications, Nature, 2001, 414: 353.
Iosub V., Matsunaga T., Tange K., and Ishikiriyama M., Direct synthesis of Mg (AlH4)2 and CaAlH5 crystalline compounds by ball milling and their potential as hydrogen storage materials, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2009, 34(2): 906.
Bogdanovic B., and Schwickardi M., Ti-doped alkali metal aluminum hydrides as potential novel reversible hydrogen storage materials. J Alloys Compd., 1997, 253–254: 1.
Varin R.A., and Zbroniec L., Decomposition behavior of unmilled and ball milled lithium alanate (LiAlH4) including long-term storage and moisture effects, J. Alloys Compd., 2010, 504(1): 89.
Fernandez J.R.A., Aguey-Zinsou F., Sykes J.M., Dornheim M., Klassen T., and Bormann R., Thermal and mechanically activated decomposition of LiAlH4, Materials Research Bulletin, 2008, 43: 1263.
Sartori S., Qi X., Eigen N., Muller J., Klassen T., Dornheim M., and Hauback B. C., A search for new Mg-and K-containing alanates for hydrogen storage, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2009, 34: 4582
Kojima Y., Kawai Y., Matsumoto M., and Haga T., Hydrogen release of catalyzed lithium aluminum hydride by a mechanochemical reaction, J. Alloys Compd., 2008, 462: 275.
Resan M., Hampton M.D., Lomness J.K., and Slattery D.K., Effect of TixAly catalysts on hydrogen storage properties of LiAlH4 and NaAlH4, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2005, 30: 1417.
Garner W.E., and Haycock E.W., The thermal decomposition of lithium aluminium hydride, Proc. Roy. Soc. A, 1952, 211: 335.
Graetz J., and Reilly J.J., Kinetically stabilized hydrogen storage materials, Scripta Materialia, 2007, 56: 835.
Liu S.S., Sun L.X., Zhang Y., Xu F., Zhang J., Chu H.L., Fan M.Q., Zhang T., Song X.Y., and Grolier J. P., Effect of ball milling time on the hydrogen storage properties of TiF3-doped LiAlH4, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2009, 34: 8079.
Xueping Z., Ping L., Qu X., Humail I.S., Zhang Y., and Guoqing W., Effect of different additives on the properties of lithium alanate. J. Univ. Sci. Technog. Beijing, 2008, 15(6): 786.
Xueping Z., and Shenglin L., Study on hydrogen storage properties of LiAlH4, J. Alloys Compd., 2009, 481: 761.
Blanchard D., Brinks H.W., Hauback B.C., Norby P., and Muller J., Isothermal decomposition of LiAlD4 with and without additives. J. Alloys Compd., 2005, 404–406: 743.
Chen. J., Kuriyama N., Qu. X, H. Takeshita T., and Sakai T., Reversible hydrogen storage via titanium-catalyzed LiAlH4 and Li3AlH6, J. Phys Chem. B, 2001, 105(45): 11214.
Xueping Z., Ping L., Humail I.S., Fuqiang A., Guoqing W., and Qu. X., Effect of catalyst LaCl3 on hydrogen storage properties of lithium alanate (LiAlH4), Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2007, 32: 4957.
Fernandez J.R.A., Aguey-Zinsou F., Elsaesser M., Ma X. Z., Dornheim M., Klassen T., and Bormann R., Mechanical and thermal decomposition of LiAlH4 with metal halides, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2007, 32: 1033.
Xueping Z., Ping L., Fuqiang A., Guoqing W., and Qu. X., Effects of Ti and Fe additives on hydrogen release, Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2008, 37(3): 400.
Naik M., Rather S., So C.S., Hwang S.W., Kim A.R., and Nahm K.S., Thermal decomposition of LiAlH4 chemically mixed with Lithium amide and transition metal chlorides. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2009, 34: 8937.
Sun T., Huang C.K., Wang H., Sun L.X., and Zhu M., The effect of doping NiCl2 on the dehydrogenation properties of LiAlH4, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2008, 33: 6216.
Ismail M., Zhao Y., Yu X.B., and Dou S.X., Effects of NbF5 addition on the hydrogen storage properties of LiAlH4, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2010, 35: 2361.
Kumar L.H., Viswanathan B., and Murthy S. S., Dehydriding behavior of LiAlH4—the catalytic role of carbon nanofibers, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2008, 33: 366.
Alonso F., and Yus M., Hydrogenation of olefins with hydrated nickel chloride, lithium and a catalytic amount of naphthalene, Tetrahedron Letters, 1996, 37(38): 6925.
Xuezhang X, Xiulin F, Kairong Y., Shouquan L., Changpin C., Qidong W., and Lixin C., Catalytic mechanism of new TiC-doped sodium alanate for hydrogen storage, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113: 20745.
Ji K.W., Shim J.H., Kim S.C., Remhof A., Borgschulte A., Friedrichs O., Gremaud R., Pendoline F., Zuttel A., Cho W.Y., and Oh K.H., Catalytic effect of titanium nitride nanopowder on hydrogen desorption properties of NaAlH4 and its stability in NaAlH4, Journal of Power Sources, 2009, 192: 582.
Mashkoor A., Rafi-ud-Din, Caofeng P., and Jing Z., Investigation of hydrogen storage capabilities of ZnO-based nanostructures, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010, 114: 2560.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rafi-ud-din, Qu, X., Li, P. et al. Comparative catalytic effects of NiCl2, TiC and TiN on hydrogen storage properties of LiAlH4 . Rare Metals 30 (Suppl 1), 27–34 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-011-0231-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-011-0231-7