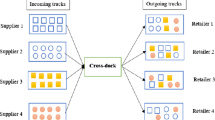
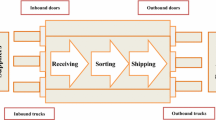
Abstract
The cross-docking policy has a significant impact on supply chain productivity. This research optimizes the rescheduling location problem for incoming and outgoing trucks in a multi-cross-docking system. Contrary to previous studies, it first considers the simultaneous effects of learning and deteriorating on loading and unloading the jobs. A mixed integer non-linear multi-objective programming model is developed. The truck rescheduling location problem in a cross-docking system is strongly considered an NP-hard problem. Thus, this study uses two meta-heuristic algorithms: multi-objective particle swarm optimization (MOPSO) and non-dominated ranking genetic algorithm (NRGA). Finally, the numerical results obtained from meta-heuristic algorithms are examined using the relative percentage deviation and comparison criteria. The findings demonstrate that MOPSO outperforms NRGA with a 91.1% degree of confidence in all metrics. Also, results show that the NRGA algorithm provides more expansive answers than the MOPSO when measured against the maximum expansion criterion.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arab, A., Sahebi, I.G., Alavi, S.A.: Assessing the key success factors of knowledge management adoption in supply chain. Int. J. Acad. Res. Bus. Soc. Sci. 7(4), 2222–6990 (2017)
Arab, A., Sahebi, I.G., Modarresi, M., Ajalli, M.: A Grey DEMATEL approach for ranking the KSFs of environmental management system implementation (ISO 14001). Calitatea 18(160), 115 (2017)
Baumol, W., Vinod, H.: An inventory theoretic model of freight transport demand. Manage. Sci. 16(7), 413–421 (1970)
Birim, Ş: Vehicle routing problem with cross docking: a simulated annealing approach. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 235, 149–158 (2016)
Bodnar, P., de Koster, R., Azadeh, K.: Scheduling trucks in a cross-dock with mixed service mode dock doors. Transp. Sci. 51(1), 112–131 (2017)
Chargui, T., Bekrar, A., Reghioui, M., Trentesaux, D.: Simulation for Pi-hub cross-docking robustness. In: Service orientation in holonic and multi-agent manufacturing (pp. 317–328). Springer (2018).
Constable, G., Whybark, D.: The interaction of transportation and inventory decisions. Decis. Sci. 9(4), 688–699 (1978)
Dondo, R., Cerdá, J.: The heterogeneous vehicle routing and truck scheduling problem in a multi-door cross-dock system. Comput. Chem. Eng. 76, 42–62 (2015)
Eberhart, R., Kennedy, J.: A new optimizer using particle swarm theory. In: MHS’95. Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium on Micro Machine and Human Science, 39–43 (1995)
Essghaier, F., Allaoui, H., Goncalves, G.: Truck to door assignment in a shared cross-dock under uncertainty. Exp. Syst. Appl. 182, 114889 (2021)
Gelareh, S., Glover, F., Guemri, O., Hanafi, S., Nduwayo, P., Todosijević, R.: A comparative study of formulations for a cross-dock door assignment problem. Omega 91, 102015 (2020)
Heidari, F., Zegordi, S.H., Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R.: Modeling truck scheduling problem at a cross-dock facility through a bi-objective bi-level optimization approach. J. Intell. Manuf. 29(5), 1155–1170 (2018)
Kusolpuchong, S., Chusap, K., Alhawari, O., Suer, G.: A genetic algorithm approach for multi objective cross dock scheduling in supply chains. Procedia Manuf. 39, 1139–1148 (2019)
Liao, T. W.: Integrated outbound vehicle routing and scheduling problem at a multi-door cross-dock terminal. In: IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems (2020)
Meidute-Kavaliauskiene, I., Davidaviciene, V., Ghorbani, S., Sahebi, I.G.: Optimal allocation of gas resources to different consumption sectors using multi-objective goal programming. Sustainability 13(10), 5663 (2021)
Meidute-Kavaliauskiene, I., Sütütemiz, N., Yıldırım, F., Ghorbani, S., Činčikaitė, R.: Optimizing multi cross-docking systems with a multi-objective green location routing problem considering carbon emission and energy consumption. Energies 15(4), 1530 (2022)
Mohtashami, A.: A novel dynamic genetic algorithm-based method for vehicle scheduling in cross docking systems with frequent unloading operation. Comput. Ind. Eng. 90, 221–240 (2015)
Mohtashami, A., Fallahian-Najafabadi, A.: Scheduling trucks transportation in supply chain regarding cross docking using meta-heuristic algorithms. Ind. Manag. Stud. 11(31), 55–84 (2014)
Mohtashami, A., Tavana, M., Santos-Arteaga, F.J., Fallahian-Najafabadi, A.: A novel multi-objective meta-heuristic model for solving cross-docking scheduling problems. Appl. Soft Comput. 31, 30–47 (2015)
Motaghedi-Larijani, A., Aminnayeri, M.: Optimizing the admission time of outbound trucks entering a cross-dock with uniform arrival time by considering a queuing model. Eng. Optim. 49(3), 466–480 (2017)
Nasiri, M.M., Ahmadi, N., Konur, D., Rahbari, A.: A predictive-reactive cross-dock rescheduling system under truck arrival uncertainty. Exp. Syst. Appl. 188, 115986 (2022)
Nasiri, M.M., Rahbari, A., Werner, F., Karimi, R.: Incorporating supplier selection and order allocation into the vehicle routing and multi-cross-dock scheduling problem. Int. J. Prod. Res. 56(19), 6527–6552 (2018)
Nassief, W.: Cross-dock door assignments: Models, algorithms and extensions. Concordia University (2017).
Ponboon, S., Qureshi, A.G., Taniguchi, E.: Evaluation of cost structure and impact of parameters in location-routing problem with time windows. Transp. Res. Procedia 12, 213–226 (2016)
Rijal, A., Bijvank, M., de Koster, R.: Integrated scheduling and assignment of trucks at unit-load cross-dock terminals with mixed service mode dock doors. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 278(3), 752–771 (2019)
Sadeghi Moghadam, M., Ghasemian Sahebi, I.: A mathematical model to improve the quality of demand responding in emergency medical centers in a humanitarian supply chain. Mod. Res. Decision Mak. 3(1), 217–242 (2018)
Sahebi, I. G., Mosayebi, A., Masoomi, B., Marandi, F.: Modeling the enablers for blockchain technology adoption in renewable energy supply chain. In: Technology in Society, 101871 (2022)
Sahebi, I. G., Toufighi, S. P., Karakaya, G., & Ghorbani, S.: An intuitive fuzzy approach for evaluating financial resiliency of supply chain. In: OPSEARCH, 1–22 (2021).
Sayed, S.I., Contreras, I., Diaz, J.A., Luna, D.E.: Integrated cross-dock door assignment and truck scheduling with handling times. TOP 28(3), 705–727 (2020)
Serrano, C., Delorme, X., Dolgui, A.: Scheduling of truck arrivals, truck departures and shop-floor operation in a cross-dock platform, based on trucks loading plans. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 194, 102–112 (2017)
Serrano, C., Delorme, X., Dolgui, A.: Cross-dock distribution and operation planning for overseas delivery consolidation: a case study in the automotive industry. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 33, 71–81 (2021)
Seyedi, I., Hamedi, M., Tavakkoli-Moghadaam, R.: Developing a mathematical model for a multi-door cross-dock scheduling problem with human factors: A modified imperialist competitive algorithm. J. Ind. Eng. Manag. Stud. 8(1), 180–201 (2021)
Tirkolaee, E.B., Goli, A., Faridnia, A., Soltani, M., Weber, G.-W.: Multi-objective optimization for the reliable pollution-routing problem with cross-dock selection using Pareto-based algorithms. J. Clean. Prod. 276, 122927 (2020)
Wang, H., Alidaee, B.: The multi-floor cross-dock door assignment problem: Rising challenges for the new trend in logistics industry. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 132, 30–47 (2019)
Wisittipanich, W., Hengmeechai, P.: Truck scheduling in multi-door cross docking terminal by modified particle swarm optimization. Comput. Ind. Eng. 113, 793–802 (2017)
Xi, X., Changchun, L., Yuan, W., Hay, L.L.: Two-stage conflict robust optimization models for cross-dock truck scheduling problem under uncertainty. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 144, 102123 (2020)
Yin, P.-Y., Chuang, Y.-L.: Adaptive memory artificial bee colony algorithm for green vehicle routing with cross-docking. Appl. Math. Model. 40(21–22), 9302–9315 (2016)
Zuluaga, J.P.S., Thiell, M., Perales, R.C.: Reverse cross-docking. Omega 66, 48–57 (2017)
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to express their gratitude to the esteemed reviewers for their valuable comments in improving the quality of this research work.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: IGS; methodology: SPT, formal analysis: IGS and SPT; investigation: MA and FZ; writing—original draft preparation: SPT; writing—review and editing: MA and FZ; supervision: IGS. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Availability of data and material
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, upon reasonable request.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sahebi, I.G., Toufighi, S.P., Azzavi, M. et al. Presenting an optimization model for multi cross-docking rescheduling location problem with metaheuristic algorithms. OPSEARCH 61, 137–162 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12597-023-00694-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12597-023-00694-5