Abstract
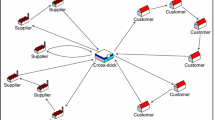
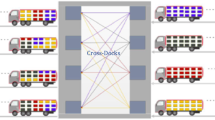
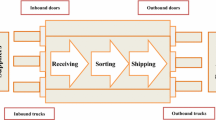
This paper addresses an integrated material flow optimization problem of cross-docking satellites, in which the transportation problem, the truck-door assignment problem with material placement plans, and the two-dimensional truck loading problem are taken into account. The study aims to find the best distribution and operational plans for the cross-docking satellites to minimize the total transportation cost of the materials. To solve the considered problem, a hybrid genetic algorithm (HGA) is developed, which integrates simulated annealing (SA) algorithm within a genetic algorithm (GA). In this way, a new individual with a low solution quality is rejected by using the stochastic solution acceptance feature of the SA. Moreover, the HGA is enhanced with an advanced two-dimensional loading-check procedure and a rule-based material placement procedure to obtain efficient solutions. The proposed loading-check procedure reduces the processing time of the HGA by avoiding duplicate examinations for the truck loading plans. Likewise, the rule-based material placement procedure prevents unnecessary searches for the assignment plans of the products in a temporary storage area. In computational studies, the performance of the HGA is tested on two different problem sets by comparing HGA with the SA and GA. Furthermore, the HGA is applied to a problem set that is formed by using real-life data of a logistics company. The computational results show that the HGA introduces effective solutions and outperforms both the SA and GA. In addition, the results of the real-life application denote that the HGA can be employed to find effective material flow plans in real situations of cross-docking operations.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abouee-Mehrizi H, Berman O, Baharnemati MR (2013) Designing production-inventory-transportation systems with capacitated cross-docks. Transp Sci 48(1):121–135
Agustina D, Lee CKM, Piplani R (2014) Vehicle scheduling and routing at a cross docking center for food supply chains. Int J Prod Econ 152(1):29–41
Boysen N, Fliedner M (2010) Cross dock scheduling: classification, literature review and research agenda. Omega Int J Manag Sci 38(6):413–422
Bozer YA, Carlo HJ (2008) Optimizing inbound and outbound door assignments in less-than-truckload crossdocks. IIE Trans 40(11):1007–1018
Charkhgard H, Tabar AAY (2011) Transportation problem of cross-docking network with three-dimensional trucks. Afr J Bus Manag 5(22):9297–9303
Chen P, Guo YS, Lim A, Rodrigues B (2006) Multiple crossdocks with inventory and time windows. Comput Oper Res 33(1):43–63
Chen M-C, Hsiao Y-H, Reddy RH, Tiwari MK (2016) The self-learning particle swarm optimization approach for routing pickup and delivery of multiple products with material handling in multiple cross-docks. Transp Res Part E Logist Transp Rev 91:208–226
Cohen Y, Keren B (2008) A simple heuristic for assigning doors to trailers in cross-docks. In: International conference on industrial logistics (ICIL 2008), Tel Aviv, Israel, pp 1–14
Deep K, Mebrahtu H (2011) New variations of order crossover for travelling salesman problem. Int J Comb Optim Probl Inform 2(1):2–13
Donaldson H, Johnson EL, Ratliff HD, Zhang M (1998) Schedule-driven cross-docking networks. The Logistics Institute, Georgia Tech, Atlanta
Enderer F, Contardo C, Contreras I (2017) Integrating dock-door assignment and vehicle routing with cross-docking. Comput Oper Res 88:30–43
Fathi Y, Karimi B, Al-e-Hashem SM (2016) A quadratic programming for truck-to-door assignment problem. World Acad Sci Eng Technol Int J Mech Aerosp Ind Mechatron Manuf Eng 10(8):1550–1553
Gelareh S, Monemi RN, Semet F, Goncalves G (2016) A branch-and-cut algorithm for the truck dock assignment problem with operational time constraints. Eur J Oper Res 249(3):1144–1152
Gen M, Altiparmak F, Lin L (2006) A genetic algorithm for two-stage transportation problem using priority-based encoding. Or Spectrum 28(3):337–354
Goldberg DE (1989) Genetic algorithms in search, optimization, and machine learning. Addion-Wesley, Boston
Holland JH (1992) Genetic algorithms. Sci Am 267(1):66–72
Hosseini SD, Shirazi MA, Karimi B (2014) Cross-docking and milk run logistics in a consolidation network: a hybrid of harmony search and simulated annealing approach. J Manuf Syst 33(4):567–577
Javanmard S, Vahdani B, Tavakkoli-Moghaddam R (2014) Solving a multi-product distribution planning problem in cross docking networks: an imperialist competitive algorithm. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 70(9–12):1709–1720
Jayaraman V, Ross A (2003) A simulated annealing methodology to distribution network design and management. Eur J Oper Res 144(3):629–645
Jebari K, Madiafi M (2013) Selection methods for genetic algorithms. Int J Emerg Sci 3(4):333–344
Kheirkhah A, Rezaei S (2015) Using cross-docking operations in a reverse logistics network design: a new approach. Prod Eng Res Devel 10(2):175–184
Kirkpatrick S, Gelatt CD, Vecchi MP (1983) Optimization by simulated annealing. Science 220(4598):671–680
Küçükoğlu I, Öztürk N (2014) Simulated annealing approach for transportation problem of cross-docking network design. In: 2nd World conference on business, economics and management vol 109, no 1, pp 1180–1184
Küçükoğlu I, Öztürk N (2017) Two-stage optimisation method for material flow and allocation management in cross-docking networks. Int J Prod Res 55(2):410–429
Ladier AL, Alpan G (2016) Cross-docking operations: current research versus industry practice. Omega Int J Manag Sci 62:145–162
Liao TW, Egbelu PJ, Chang PC (2013) Simultaneous dock assignment and sequencing of inbound trucks under a fixed outbound truck schedule in multi-door cross docking operations. Int J Prod Econ 141(1):212–229
Lim A, Miao ZW, Rodrigues B, Xu Z (2005) Transshipment through crossdocks with inventory and time windows. Nav Res Logist 52(8):724–733
Lim A, Ma H, Miao Z (2006) Truck dock assignment problem with operational time constraint within crossdocks. In: International conference on industrial, engineering and other applications of applied intelligent systems. Springer, pp 262–271
Luo GH, Noble JS (2012) An integrated model for crossdock operations including staging. Int J Prod Res 50(9):2451–2464
Ma H, Miao ZW, Lim A, Rodrigues B (2011) Crossdocking distribution networks with setup cost and time window constraint. Omega Int J Manag Sci 39(1):64–72
Maknoon M, Soumis F, Baptiste P (2016) Optimizing transshipment workloads in less-than-truckload cross-docks. Int J Prod Econ 179:90–100
Marjani MR, Husseini SMM, Karimi B (2012) Bi-objective heuristics for multi-item freights distribution planning problem in crossdocking networks. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 58(9–12):1201–1216
Marmolejo J, Soria I, Perez H (2015) A decomposition strategy for optimal design of a soda company distribution system. Math Probl Eng 2015:1–7
Miao ZW, Lim A, Ma H (2009) Truck dock assignment problem with operational time constraint within crossdocks. Eur J Oper Res 192(1):105–115
Miao ZW, Yang F, Fu K, Xu DS (2012) Transshipment service through crossdocks with both soft and hard time windows. Ann Oper Res 192(1):21–47
Miao Z, Cai S, Xu D (2014) Applying an adaptive tabu search algorithm to optimize truck-dock assignment in the crossdock management system. Expert Syst Appl 41(1):16–22
Mitchell M (1998) An introduction to genetic algorithms, 5th edn. MIT Press, London
Musa R, Arnaout JP, Jung H (2010) Ant colony optimization algorithm to solve for the transportation problem of cross-docking network. Comput Ind Eng 59(1):85–92
Nassief W, Contreras I, As’ad R (2016) A mixed-integer programming formulation and Lagrangean relaxation for the cross-dock door assignment problem. Int J Prod Res 54(2):494–508
Oh Y, Hwang H, Cha CN, Lee S (2006) A dock-door assignment problem for the Korean mail distribution center. Comput Ind Eng 51(2):288–296
Otten RHJM, Van Ginneken LPPP (1988) Stop criteria in simulated annealing. In: IEEE international conference on computer design: VLSI in computers and processors, pp 549–552
Qiu Y, Zhou D, Du Y, Liu J, Pardalos PM, Qiao J (2021) The two-echelon production routing problem with cross-docking satellites. Transp Res Part E Logist Transp Rev 147:102210
Serrano C, Delorme X, Dolgui A (2017) Scheduling of truck arrivals, truck departures and shop-floor operation in a cross-dock platform, based on trucks loading plans. Int J Prod Econ 194:102–112
Shuib A, Fatthi WNAWA (2012) A review on quantitative approaches for dock door assignment in cross-docking. Int J Adv Sci Eng Inf Technol 2(5):30–34
Sivanandam SN, Deepa SN (2007) Introduction to genetic algorithms. Springer Science & Business Media, New York
Staudt FH, Alpan G, Di Mascolo M, Rodriguez CMT (2015) Warehouse performance measurement: a literature review. Int J Prod Res 53(18):5524–5544
Stephan K, Boysen N (2011) Vis-a-vis vs. mixed dock door assignment: a comparison of different cross dock layouts. Oper Manag Res 4(3–4):150–163
Sun L, Wang HM, Hou J (2015) Optimization of postal distribution network based on rendezvous with heterogeneous vehicles and capacity constraints. In: Knowledge-based and intelligent information & engineering systems 19th annual conference, KES-2015, vol 60, pp 1347–1356
Sung CS, Song SH (2003) Integrated service network design for a cross-docking supply chain network. J Oper Res Soc 54(12):1283–1295
Tootkaleh RS, Shirazi AM, Ghomi FSMT, Hosseini SD (2014) Truck capacity analysis in a cross-dock transportation network considering direct shipment. J Adv Transp 48(7):891–901
Tsui LY, Chang CH (1990) A microcomputer based decision support tool for assigning dock doors in freight yards. Comput Ind Eng 19(1–4):309–312
Tsui LY, Chang CH (1992) An optimal solution to a dock door assignment problem. Comput Ind Eng 23(1–4):283–286
Van Belle J, Valckenaers P, Cattrysse D (2012) Cross-docking: state of the art. Omega 40(6):827–846
Wang H, Alidaee B (2019) The multi-floor cross-dock door assignment problem: rising challenges for the new trend in logistics industry. Transp Res Part E Logist Transp Rev 132:30–47
Yan H, Tang S-l (2009) Pre-distribution and post-distribution cross-docking operations. Transp Res Part E Logist Transp Rev 45(6):843–859
Yazdani M, Naderi B, Mousakhani M (2015) A model and metaheuristic for truck scheduling in multi-door cross-dock problems. Intell Autom Soft Comput 21(4):633–644
Yu VF, Sharma D, Murty KG (2008) Door allocations to origins and destinations at less-than-truckload trucking terminals. J Ind Syst Eng 2(1):1–15
Yu VF, Jewpanya P, Kachitvichyanukul V (2016) Particle swarm optimization for the multi-period cross-docking distribution problem with time windows. Int J Prod Res 54(2):509–525
Zachariadis EE, Tarantilis CD, Kiranoudis CT (2009) A guided Tabu search for the vehicle routing problem with two-dimensional loading constraints. Eur J Oper Res 195(3):729–743
Zhang Y-H, Gong Y-J, Chen W-N, Gu T-L, Yuan H-Q, Zhang J (2018) A dual-colony ant algorithm for the receiving and shipping door assignments in cross-docks. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 20:2523–2539
Zhao H, Chen L (2015) Hybrid particle swarm optimization for two-stage cross docking scheduling. Int J Hybrid Inf Technol 8(11):249–266
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception, design, analyses, and writing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kucukoglu, I., Öztürk, N. A new hybrid genetic algorithm to optimize distribution and operational plans for cross-docking satellites. Soft Comput 27, 18723–18738 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-09137-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-09137-1