Abstract
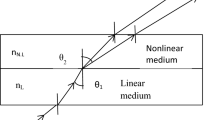
An innovative all-optical device is proposed to effectively express the trigonometric ratios of compound angles based on the fascinating intensity dependent changes of refractive index of a nonlinear material. The device has profound applications in numerous domains of research, such as astronomy, oceanography, seismology, civil engineering, electronics, phonetics, medical imaging, and the development of computer music. Optical switch and optical Ternary Encoder play major role in this proposed device. To effectively execute this process, a single constant light source with a standardized intensity level ‘I’ has been strategically utilized, alongside multiple constant light sources, a beam combiner, and a beam splitter. In this scheme, different value of angles is represented by the different value of standard intensity level to express the trigonometric ratios of compound angles. Furthermore, in the proposed design, the output expression of the trigonometric ratios of compound angles are illustrated as the sum or subtraction of two outputs (2-bit ternary form) of two number of optical Ternary Encoders. As the proposed scheme is fully optical in nature, so this device can be employed in optical computation as well as photonic application.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Garmire, Nonlinear optics in daily life. Opt. Express 21(25), 30532–30544 (2013)
R. Bano, M. Asghar, K. Ayub, T. Mahmood, J. Iqbal, S. Tabassum, R. Zakaria, M.A. Gilani, A theoretical perspective on strategies for modelling high performance nonlinear optical materials. Front. Mater. 8, 532 (2021)
A. Chatterjee, S. Biswas, S. Mukhopadhyay, Method of frequency conversion of Manchester encoded data from a Kerr type of nonlinear medium. J. Opt. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-017-0393-2
S.K. Chandra, S. Biswas, S. Mukhopadhyay, Phase-encoded all-optical reconfigurable integrated multilogic unit using phase information processing of four-wave mixing in semiconductor optical amplifier. IET Optoelectron 10(1), 1–6 (2016)
S. Saha, de Paromita, S. Mukhopadhyay, All optical frequency encoded quaternary memory unit using symmetric configuration of MZI-SOA. Opt. Laser Technol. 131, 106386 (2020)
S. Biswas, S. Mukhopadhyay, All-optical approach for conversion of a binary number having a fractional part to its decimal equivalent to three places of decimal using single system optical tree architecture. J Opt 43(2), 122–129 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-014-0187-8
R.W. Boyd, Nonlinear optics (Academic press, Massachusetts, 2020)
S.D. Smith, Optical bistability, photonic logic and optical computation. Appl. Opt. 25, 1550–1564 (1986)
G. Li, L. Lin, L. Shao, Y. Yin, J. Hua, Parallel optical negabinary arithmetic based on logic operations. Appl. Opt. 36, 1011–1016 (1997)
H.J. Caulfield, Perspectives in optical computing. Computer 31(2), 22–25 (1998)
M.A. Karim, A.A.S. Awwal, Optical computing: an Intro-duction (Wiley, New York) Chap. 3 pp. 35–56 (2003)
L.K. Cotter, T.J. Drabik, R.J. Dillon, M.A. Handaschy, Ferro- electric-liquid-crystal/silicon-integrated circuit spatial light modulator. Opt. Lett. 15(5), 291–293 (1990)
S.D. Smith, H.A. Mackenzie, J.G.H. Mathew, J.J.E. Reid, M.R. Taghizadeh, F.A.P. Tooley, A.C. Walker, Nonlinear optical circuit elements, logic gates for optical computers: the first digital circuits. Opt. Eng. 24(4), 569–574 (1985)
N. Pahari, D.N. Das, S. Mukhopadhyay, All-optical method for the addition of binary data nonlinear materials. Appl. Opt. 43(33), 6147–6150 (2004)
D. Psaltis, D. Brady, K. Wagner, Adaptive optical networks using photorefractive crystals. Appl. Opt. 27(9), 1752–1759 (1998)
N. Pahari, A. Guchhait, All-optical serial data transfer between registers using optical mom-linear materials. Optik 123(5), 462–466 (2012)
N. Pahari, A. Guchhait, A.D. Jana, Image edge detection scheme by the use of Kerr-type non-linear material and the verification of the scheme by computer simulation. Opt. Soc. India (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-012-0082-0
A. Guchhait, N. Pahari, N.B. Manik, Optical Kerr nonlinear material for calculating the coefficient of binomial expansion under any positive integral index. J. Opt. 51, 851–865 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-021-00823-7
S. Biswas, S. Mukhopadhyay, An all optical scheme of secured cryptographic communication encoded with decimal data. Optik 124, 2376–2378 (2013)
S. Biswas, S. Mukhopadhyay, An all optical approach for developing a system involving Kerr-material based switches for cryptographic encoding of binary data depending on the input parity. Optik 125, 1954–1956 (2014)
S.P. Medhekar, P. Paltani, Proposal for optical switch using non- linear refraction. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 18(15), 1579–1581 (2006)
N. Mitra, S. Mukhopadhyay, Method of developing an all-optical synchronous counter by exploiting the Kerr non-linearity of the medium. Opt. Photonics Lett. 3(1), 23–30 (2010)
Y. Fainman, C.C. Guest, S.H. Lee, Optical digital logic operations by two beams coupling in photorefractive material. Appl. Opt. 25(10), 1598–1603 (1986)
N. Pahari, S. Mukhopadhyay, An all-optical R-S flip-flop by optical non-linear material. J. Opt. 34(3), 108–114 (2005)
J.N. Roy, A.K. Maiti, D. Samanta, S. Mukhopadhyay, Tree-net architecture for integrated all-optical arithmetic operations and data comparison scheme with optical nonlinear material. Opt. Switch. Netw. 4(231), 237 (2007)
S.D. Smith, Lasers, nonlinear optics and optical computers. Nature 316(6026), 319–324 (1985)
W. Nie, Optical nonlinearity: phenomena, applications, and materials. Adv. Mater. 5(7–8), 520–545 (1993)
N.L. Kazanskiy, M.A. Butt, S.N. Khonina, Optical computing: status and perspectives. Nanomaterials 12(13), 2171 (2022)
Z. Chai, X. Hu, F. Wang, X. Niu, J. Xie, Q. Gong, Ultrafast all-optical switching. Adv. Opt. Mater. 5(7), 1600665 (2017)
S. Sahu, S. Dhar, Implementation of J-K and J–K master–slave flip-flops with nonlinear material in all-optical domain. Opt. Eng. 48(7), 075401–075401 (2009)
S. Sahu, S. Dhar, All-optical implementation of arithmetic operation scheme using optical nonlinear material-based switching technique. Photonics Optoelectron 3, 37–50 (2014)
X. Yang, X. Hu, H. Yang, Q. Gong, Ultracompact all-optical logic gates based on nonlinear plasmonic nanocavities. Nano Photonics 6(1), 365–376 (2017)
Y.-D. Wu, T.-T. Shih, M.-H. Chen, New all-optical logic gates based on the local nonlinear Mach-Zehnder interferometer. Opt. Express 16(1), 248–257 (2008)
M. Moradi, M. Danaie, A.A. Orouji, Design of all-optical XOR and XNOR logic gates based on Fano resonance in plasmonic ring resonators. Opt. Quantum Electron. 51, 1–18 (2019)
D. Samanta, S. Mukhopadhyay, All-optical method for maintaining a fixed intensity level of a light signal in optical computation. Opt. Commun. 281, 4851–4853 (2008)
A. Guchhait, N. Pahari, N.B. Manik, All-optical decimal to ternary converter with the proper use of optical non-linear material. J. Opt. 49, 59–68 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-019-00579-1
B. Sarkar, S. Mukhopadhyay, An optical system for sharp increase of light frequency by the use of multiple numbers of LiNbO3 crystals biased by sawtooth electronic pulse. Indian J. Phys. 95, 1865 (2021)
S. Mukhopadhyay, Role of optics in super-fast information processing. Indian J. Phys. 84, 1069 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest related to this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Guchhait, A., Pahari, N. & Manik, N.b. Optical Kerr nonlinear material for expressing the trigonometric ratios of compound angles. J Opt 53, 892–905 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-023-01245-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-023-01245-3