Abstract
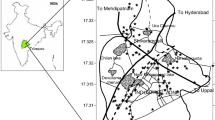
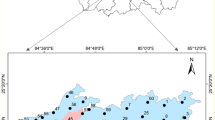
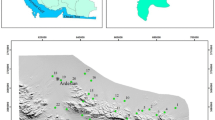
Pollution of various environmental components, such as air, water, and soil, is caused by industrialization and urbanization in urban agglomerates. This study provides information about groundwater quality and the levels of heavy metals in the surface soils of Gurugram city. The groundwater and soil samples were analyzed for various chemical parameters. Heavy metals in groundwater and soil were measured using atomic absorption spectrophotometer (AAS). Groundwater samples show higher electrical conductivity (EC), bicarbonates (HCO3−), and chlorides (Cl−). Water quality index (WQI) indicates that groundwater is not suitable for drinking purposes. Most of the groundwater samples surpassed the prescribed limits for heavy metals. While in the case of soil, Cd, Ni and Cr were found above the average background value for soils. Contamination factors (CF) and Pollution load index (PLI) for various heavy metals in soil were found to vary from 0.006 to 20.9 and 0.64 to 1.93, respectively. The 70% of samples found with PLI >1, indicate deterioration of soil quality. Three soil samples have a high ecological risk index (ERI) with values of more than 600. Average value of geo-accumulation index (Igeo) varies in the order Cd>Pb>Cu>Zn>Ni>Cr>Fe with average value 3.43, 1.73, 0.86, 0.029, −.23, −1.2 and −7.14, respectively. Principal component analysis (PCA), a multivariate statistical technique, shows that the first three principal components (PC) account for 84.99% of the variance in groundwater samples. In soil samples, the first two PCs account for 76.97% of the variance. Hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) shows three clusters for groundwater samples and two clusters for soil samples. The study area shows higher pollution levels and needs an improved environmental management plan.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (2005) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. 21st edition. American Public Health Association, Washington DC, USA.
Babiker, S.I., Mohamed, A.A., Mohamed, T.H. (2007) Assessing groundwater quality using GIS. Water Resour Manag., v.21, pp.699–715
Barakat, A., Baghdadi, M.E., Rais, J., Aghezzaf, B., Slassi, M. (2016) Assessment of spatial and seasonal water quality variation of Our Er Rbia river (Morocco) using multivariate statistical techniques. Internat. Soil Water Conserv. Res., v.4(4), pp.284–292. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2016.11.002.
BIS (2012) Indian standard specification for drinking water, IS:10500 [S]. New Delhi: Bureau of Indian Standards.
Bouteraa, O., Mebarki, A., Bouaicha, F., Nouaceur, Z., Laignel, B. (2019) Groundwater quality assessment using multivariate analysis, geostatistical modeling, and water quality index (WQI): a case of study in the Boumerzoug-El Khroub valley of Northeast Algeria. Acta Geochimica., v.38(6), pp.796–814.
CGWB (1995) Ground Water Resources of India, Gurgaon district at a glance. Central Ground Water Board, New Delhi. http://cgwb.gov.in/DistrictProfile/Haryana/Gurgaon.pdf
Chakrapany, R.A. (1981) Hydrology of Gurgaon District, Haryana. Central Ground Water Board, Ministry of Irrigation, Govt. of India.
Cook, N., Hendershot, W.H. (1996) The problem of establishing ecologically-based soil quality criteria: the case of lead. Canadian Jour. Soil Scien., v.76, pp.335–342.
Defo, C., Yerima, B.P.K., Noumsi, I.M.K., Bemmo, N. (2015) Assessment of heavy metals in soils and groundwater in an urban watershed of Yaounde (Cameroon-West Africa). Environ. Monit. Assess., v.187(3), pp.1–17.
Gao, X., Chen, C.T.A. (2012) Heavy metal pollution status in surface sediments of the coastal Bohai Bay. Water Res., v.46(6), pp.1901–1911.
Greenwood, N.N., Earnshaw, A. (2012) Chemistry of the Elements. Elsevier
Hakanson, L. (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water research., v. 14(8), pp.975–1001. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8.
Horton, R.K. (1965) An index number system for rating water quality. Jour. Water Pollut. Control. Fed., v.37(3), pp.300–306.
Howard, R.L., Schrier, R.W. (1990) A unifying hypothesis of sodium and water regulation in health and disease. Hormone Res., v.34, pp.118–123.
Islam, S., Ahmed, K., Masunaga, S. (2015) Potential ecological risk of hazardous elements in different land-use urban soils of Bangladesh. Sci. Total Environ., v.512, pp.94–102. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.12.100
Jiang, Y., Chao, S., Liu, J., Yang, Y., Chen, Y., Zhang, A., Cao, H. (2017) Source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil for a township in Jiangsu Province, China. Chemosphere., v.168. pp.1658–1668.
Kabata-Pendias, A., Pendias, H. (2001). Trace elements in soils and plants. 3rd edition. CRC press Boca Raton, Florida, USA.
Kangabam, R.D., Bhoominathan, S.D., Kanagaraj, S., Govindaraju, M. (2017) Development of a water quality index (WQI) for the Loktak Lake in India. Appl. Water Sci., v.7(6), pp.2907–2918.
Kanmani, S., Gandhimathi, R. (2013) Investigation of physicochemical characteristics and heavy metal distribution profile in groundwater system around the open dump site. Appl. Water Sci., v.3(2), pp.387–399.
Kumar, D., Malik, D.S., Kumar, N., Gupta, N., Gupta, V. (2020) Spatial changes in water and heavy metal contamination in water and sediment of river Ganga in the river belt Haridwar to Kanpur. Environ. Geochem. Health., v.42(7), pp.2059–2079.
Kumar, S., Rajesh, V., Khan, N. (2022). Evaluation of groundwater quality in Ramanathapuram district, using water quality index (WQI). Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, v.8, pp.35–45.
Liu, W.H., Zhao, J.Z., Ouyang, Z.Y., Söderlund, L., Liu, G.H. (2005) Impacts of sewage irrigation on heavy metal distribution and contamination in Beijing, China. Environ. Internat., v.31(6), pp.805–812.
Lohani, M. (2014) Impact of landuse change on hydrology: a case study of Gurgaon City. Internat. Jour. Environ. Res. Dev., v.4(3), pp.247–252.
Malik, V.K., Singh, R.K., Singh, S.K. (2010) Impact of urbanization on ground water of Gurgaon District, Haryana, India. Internat. Jour. Rural Develop. Manag. Stud., v.5(1), pp.45–57.
Martin, J.M., Meybeck, M. (1979) Elemental mass-balance of material carried by major world rivers. Marine Chemistry., v.7(3), pp.173–206. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4203(79)90039-2.
Muller, G. (1969) Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geojournal, v.2, pp.108–118.
Nasirian, M. (2007) A new water quality index for environmental contamination contributed by mineral processing: a case study of Amang (Tin Tailing) processing activity.
Oluduro, A.O., Adewoye, B.I. (2007) Efficiency of moringa Oleifer Sead extract on the microflora of surface and ground water. Jour. Plant Sci., v.6, pp.438–453.
Panghal, V., Bhateria, R. (2020) A multivariate statistical approach for monitoring of groundwater quality: a case study of Beri block, Haryana, India. Environ. Geo Health., v.43(7), pp.2615–2629.
Panghal, V., Sharma, P., Mona, S., Bhateria, R. (2021). Determining ground-water quality using indices and multivariate statistical techniques: a study of Tosham block, Haryana, India. Environ. Geochem. Health., pp.1–15.
Panghal, V., Singh, A., Kumar, R., Kumari, G., Kumar, P., Kumar, S. (2021) Soil heavy metals contamination and ecological risk assessment in Rohtak urban area, Haryana (India). Enviro Earth Sci., v.80(21), pp.1–20. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-10028-7.
Papagiannis, I., Kagalou, I., Leonardos, J., Petridis, D., Kalfakakou, V. (2004). Copper and zinc in four freshwater fish species from Lake Pamvotis (Greece). Environ. Internat., v.30(3), pp.357–362.
Patil, B., Pinto, V.B., Govindaraju, S.M., Hebbalu, T., Bhat V.V.S, Kannanur L.N. (2020) Multivariate statistics and water quality index (WQI) approach for geochemical assessment of groundwater quality—a case study of Kanavi Halla Sub-Basin, Belagavi, India. Environ. Geochem. Health., v.42(9), pp.2667–2684.
Rabinove, C.J., Long Ford, R.H., BrookHart, J.W. (1958) Saline water resource of North Dakota. USGS Water Supply Paper, v.1428, pp.72.
Rajaganapathy, V., Xavier, F., Sreekumar, D., Mandal, P.K. (2011) Heavy metal contamination in soil, water and fodder and their presence in livestock and products: a review. Jour. Environ. Sci. Tech., v.4(3), pp.234–249.
Ramakrishnaiah, C.R., Sadashivaiah, C., Ranganna, G. (2009) Assessment of water quality index for the groundwater in Tumkur Taluk, Karnataka State, India. E-Journal Chemistry, v.6(2), pp.523–530.
Rao, N.S., Rao, J.P., Devadas, D.J., Rao, K.V.S. (2002) Hydrogeochemistry and groundwater quality in a developing urban environment of a semi-arid region, Guntur, Andhra Pradesh. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.59(2), pp.159–166.
Shayler, H., McBride, M., Harrison, E. (2009) Sources and impacts of contaminants in soils. Cornell Waste Management Institute, Rice hall, Itheca. https://hdl.handle.net/1813/14282
Simoes, d.S.F., Moreira, A.B., Bisinoti, M.C., Gimenez, S.M.N., Yabe, M.J.S. (2008). Water quality index as a simple indicator of aquaculture effects on aquatic bodies. Ecological Indicators., v.8(5), pp.476–484.
Suthar, S., Bishnoi, P., Singh, S., Mutiyar, P.K., Nema, A.K., Patil, N.S. (2009) Nitrate contamination in groundwater of some rural areas of Rajasthan, India. Jour Hazard. Mate., v.171(1–3), pp.189–199.
Tomlinson, D.L., Wilson, J.G., Harris, C.R., Jeffrey, D.W. (1980) Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoländer Meeresunters., v.33(1), pp.566–575. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02414780.
Van Loon, J.C. (1985). Selected methods of trace metal analysis: biological and environmental samples. John Wiley and Sons.
Verma, A., Kumar, R., Yadav, S. (2020) Distribution, pollution levels, toxicity, and health risk assessment of metals in surface dust from Bhiwadi industrial area in North India. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Jour., v.26(8), pp.2091–2111.
Walkley, A., Black, I.A. (1934) An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci., v.37(1), pp.29–38.
Wedepohl, K.H. (1995) The composition of the continental crust. Geochim. Cosmochim Acta, v.59(7), pp.1217–1232. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(95)00038-2.
WHO (1996) Permissible limits of heavy metals in soil and plants. Geneva, Switzerland
Acknowledgment
The authors are thankful to Dean Students’ Welfare, Maharshi Dayanand University for providing a minor research project under Dr Radha Krishanan Foundation Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panghal, V., Bhateria, R., Kumar, R. et al. Assessment of Groundwater and Surface Soil using Multivariate Statistical Techniques and Contamination Indices: A Case Study of Gurugram Millennium City, Haryana, India. J Geol Soc India 99, 430–437 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-023-2327-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-023-2327-8