Abstract
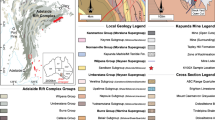
Gold mineralization associated with quartz veins and sulfide minerals has been reported in Banded Iron Formation (BIF) at Girar, Bundelkhand Craton, India. The BIF is deformed with the development of tight- isoclinal folds in high strain zones and hosts four types of quartz veins viz., (i) folded veins, (ii) band parallel veins, (iii) low angle cross-cutting veins, and (iv) high angle cross-cutting veins. Folded and band parallel veins are continuous with each other and spatially restricted to zones of tight-isoclinal folds in BIF. Shape of quartz aggregates in the folded and band parallel veins is interlobate, and these veins contain pyrite and chalcopyrite as dominant sulfide minerals along with gold. Microstructure of quartz grains and presence of fragments of BIF in sulfide mineralgold bearing folded and band parallel veins indicate that the formations of these veins were related to a single deformation episode. Spatial association of folded and band parallel veins to intensely folded zones in BIF is attributed to epigenetic nature of sulfide and gold mineralization.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adomako-Ansah, K., Mizuta, T., Ishiyama, D. and Hammond, N.Q. (2017) Nature of ore-forming fluid and formation conditions of BIF-hosted gold mineralization in the Archean Amalia Greenstone Belt, South Africa: Constraints from fluid inclusion and stable isotope studies. Ore Geol. Rev., v.89, pp.609–626.
Bhattacharya, A.R. and Singh, S.P. (2013) Proterozoic crustal scale shearing in the Bundelkhand massif with special reference to quartz reefs. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.82(5), pp.474–484.
de Souza Martins, B., Lobato, L.M., Rosière, C.A., Hagemann, S.G., Santos, J.O.S., Villanova, F.L.D.S.P. and de Ávila Lemos, L.H. (2016) The Archean BIF-hosted Lamego gold deposit, Rio das Velhas greenstone belt, Quadrilátero Ferrífero: Evidence for Cambrian structural modification of an Archean orogenic gold deposit. Ore Geol. Rev., v.72, pp.963–988.
Dinkar, G.K., Farooqui, S.A., Tantua, R.K., Prabhat., P and Verma, A.K. (2019) Greenstone belt of Girar-Mandwara area, district Lalitpur, Uttar Pradesh: Suitable for gold associated poly-metallic deposits. Gold Mining in India: The way forward, Oorgaum, pp. 84.
Dowling, K. and Morrison, G. (1989) Application of quartz textures to the classification of gold deposits using North Queensland examples. Econ. Geol. Monog., v.6, pp.342–355.
Farooqui, S.A., Dinkar, G.K. and Tantua, R.K. (2010) Shear controlled gold mineralization in precambrian iron formation around Girar, Lalitpur District, U.P. Abstract Volume, National Symposium on Geology and Mineral Resources of Bundelkhand Craton (GMRB-2010), pp.65∣66.
Fripp, R.E.P. (1976) Stratabound gold deposits in Archean banded iron-formation, Rhodesia. Econ. Geol., v.71(1), pp.58–75.
Gourcerol, B., Kontak, D.J., Thurston, P.C. and Petrus, J.A. (2018) Results of LA-ICP-MS sulfide mapping from Algoma-type BIF gold systems with implications for the nature of mineralizing fluids, metal sources, and deposit models. Miner. Depos., v.53(6), pp.871–894.
Hammond, N.Q. and Moore, J.M. (2006) Archaean lode gold mineralisation in banded iron formation at the Kalahari Goldridge deposit, Kraaipan Greenstone Belt, South Africa. Miner. Depos., v.41(5), pp.483–503.
Hiloidari, S., Satyanarayanan, M., Singh, S.P., Bhutani, R., Subramanyam, K.S.V. and Sarma, D.S. (2021) Evidence for Mesoarchean subduction in Southern Bundelkhand Craton, India: Geochemical fingerprints from metavolcanics of Kurrat-Girar-Badwar Greenstone Belt. Geochemistry, v.81(3), pp.125787.
Kaur, P., Zeh, A. and Chaudhri, N. (2014) Characterisation and U-Pb-Hf isotope record of the 3.55 Ga felsic crust from the Bundelkhand Craton, northern India. Precambrian Res., v.255, pp.236–244.
Kaur, P., Zeh, A., Chaudhri, N. and Eliyas, N. (2016) Unravelling the record of Archaean crustal evolution of the Bundelkhand Craton, northern India using U-Pb zircon-monazite ages, Lu-Hf isotope systematics, and whole-rock geochemistry of granitoids. Precambrian Res., v.281, pp.384–413.
Kerrich, R. and Fryer, B.J. (1979) Archaean precious-metal hydrothermal systems, Dome Mine, Abitibi Greenstone Belt. II. REE and oxygen isotope relations. Can. Jour. Earth Sci., v. 16(3), pp.440–458.
Kerswill, J.A., Henderson, J.R. and Henderson, M.N. (1996) Distribution of gold and sulfides at Lupin, Northwest Territories; discussion. Econ. Geol., v.91(5), pp.957–964.
Klein, C. (2005) Some Precambrian banded iron-formations (BIFs) from around the world: Their age, geologic setting, mineralogy, metamorphism, geochemistry, and origins. Amer. Mineral., v.90(10), pp.1473–1499.
Kolb, J., Hellmann, A., Rogers, A., Sindern, S., Vennemann, T., Bottcher, M.E. and Meyer, F.M. (2004) The role of a transcrustal shear zone in orogenic gold mineralization at the Ajjanahalli Mine, Dharwar Craton, South India. Econ. Geol., v.99(4), pp.743–759.
Kresse, C., Lobato, L.M., Figueiredo e Silva, R.C., Hagemann, S.G., Banks, D. and Vitorino, A.L. (2020) Fluid signature of the shear zone-controlled Veio de Quartzo ore body in the world-class BIF-hosted Cuiabá gold deposit, Archaean Rio das Velhas greenstone belt, Brazil: a fluid inclusion study. Miner. Depos., v.55(7), pp.1441–1466.
Kumar, G., Kumar, S. and Yi, K. (2021) Three distinct Archean crustal growth events as recorded from 3.48 Ga migmatite, 2.70 Ga leucogranite, and 2.54 Ga alkali granite in the Bundelkhand Craton, Central India. Jour. Asian Earth Sci., v.219, pp.104886.
Lawley, C.J., Dubé, B., Mercier-Langevin, P., Kjarsgaard, B., Knight, R. and Vaillancourt, D. (2015) Defining and mapping hydrothermal footprints at the BIF-hosted Meliadine gold district, Nunavut, Canada. Jour. Geochem. Explor., v.155, pp.33–55.
Liu, L., Ireland, T.R., Holden, P., Ávila, J., Vasconcelos, P. and Mavrogenes, J. (2021) Sources of auriferous fluids associated with a Neoarchean BIF-hosted orogenic gold deposit revealed by the multiple sulfur isotopic compositions of zoned pyrites. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., v.176(4), pp.1–22.
Malviya, V.P., Arima, M., Pati, J.K. and Kaneko, Y. (2006) Petrology and geochemistry of metamorphosed basaltic pillow lava and basaltic komatiite in the Mauranipur area: subduction related volcanism in the Archean Bundelkhand craton, Central India. Jour. Mineral. Petrol. Sci., v.101(4), pp.199–217.
Mondal, M.E.A., Goswami, J.N., Deomurari, M.P. and Sharma, K.K. (2002) Ion microprobe 207Pb/206Pb ages of zircons from the Bundelkhand massif, northern India: implications for crustal evolution of the Bundelkhand-Aravalli protocontinent. Precambrian Res., v.117(1–2), pp.85–100.
Morales, M.J., e Silva, R.C.F., Lobato, L.M., Gomes, S.D., Gomes, C.C. and Banks, D.A. (2016) Metal source and fluid-rock interaction in the Archean BIF-hosted Lamego gold mineralization: Microthermometric and LA-ICP-MS analyses of fluid inclusions in quartz veins, Rio das Velhas greenstone belt, Brazil. Ore Geol. Rev., v.72, pp.510–531.
Owona, S., Ondoa, J.M. and Ekodeck, G.E. (2013) Evidence of quartz, feldspar and amphibole crystal plastic deformations in the paleoproterozoic Nyong Complex Shear Zones under Amphibolite to Granulite conditions (west Central African Fold Belt, SW Cameroon). Jour. Geogr. Geol., v.5(3), pp.186.
Pal, N. and Mishra, B. (2003) Epigenetic nature of the BIF-hosted gold mineralization at Ajjanahalli, southern India: evidence from ore petrography and fluid inclusion studies. Gondwana Res., v.6(3), pp.531–540.
Passchier, C.W. and Trouw, R.A. (2005) Microtectonics: Springer Science & Business Media, 382p.
Pati, J.K., Patel, S.C., Pruseth, K.L., Malviya, V.P., Arima, M., Raju, S., and Prakash, K. (2007) Geology and geochemistry of giant quartz veins from the Bundelkhand Craton, central India and their implications. Jour. Earth Syst. Sci., v.116(6), pp.497–510.
Phillips, G.N., Groves, D.I. and Martyn, J.E. (1984) An epigenetic origin for Archean banded iron-formation-hosted gold deposits. Econ. Geol., v.79(1), pp.162–171.
Ramakrishnan, M. and Vaidyanadhan, R. (2008) Geology of India (Vol. 1). Geological Society of India, Bangalore, 556p.
Rao, J. M., Rao, G.P., Widdowson, M. and Kelley, S.P. (2005) Evolution of Proterozoic mafic dyke swarms of the Bundelkhand Granite Massif, central India. Curr. Sci., v.88(3), pp.502–506.
Saager, R., Oberthuer, T. and Tomschi, H.P. (1987) Geochemistry and mineralogy of banded iron- formation-hosted gold mineralization in the Gwanda greenstone belt, Zimbabwe. Econ. Geol., v.82(8), pp.2017–2032.
Saha, L., Pant, N. C., Pati, J. K., Upadhyay, D., Berndt, J., Bhattacharya, A. and Satynarayanan, M. (2011) Neoarchean high-pressure margarite-phengitic muscovite-chlorite corona mantled corundum in quartz-free high-Mg, Al phlogopite-chlorite schists from the Bundelkhand craton, north central India. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., v.161(4), pp.511–530.
Sarkar, S.C. and Gupta, A. (2012) Crustal evolution and metallogeny in India: Cambridge University Press, 912p.
Singh, P.K., Verma, S.K., Singh, V.K., Moreno, J.A., Oliveira, E.P. and Mehta, P. (2019) Geochemistry and petrogenesis of sanukitoids and high-K anatectic granites from the Bundelkhand Craton, India: Implications for late-Archean crustal evolution. Jour. Asian Earth Sci., v.174, pp.263–282.
Singh, P.K., Verma, S.K., Singh, V.K., Moreno, J.A., Oliveira, E.P., Li, X.H. and Prakash, D. (2021) Geochronology and petrogenesis of the TTG gneisses and granitoids from the Central Bundelkhand granite-greenstone terrane, Bundelkhand Craton, India: Implications for Archean crustal evolution and cratonization. Precambrian Res., v.359, pp.106210.
Singh, V.K. and Slabunov, A. (2015a) Geochemical characteristics of banded iron formation and metavolcanics of Babina greenstone belt of the Bundelkhand Craton, Central India. Jour. Econ. Geol. Georesource Manag., v. 10, pp.63–74.
Singh, V.K. and Slabunov, A. (2015b) The Central Bundelkhand Archaean greenstone complex, Bundelkhand craton, central India: geology, composition, and geochronology of supracrustal rocks. Int. Geol. Rev., v.57(11–12), pp.1349–1364.
Singh, V.K. and Slabunov, A. (2016) Two types of Archaean supracrustal belts in the Bundelkhand Craton, India: geology, geochemistry, age and implication for craton crustal evolution. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.88(5), pp.539–548.
Slabunov, A., Singh, V.K., Joshi, K.B. and Li, X. (2017) Paleoarchean zircons from quartzite of South Bundelkhand Supracrustal Complex: origin and implications for crustal evolution in Bundelkhand Craton, Central India. Curr. Sci., v.112(4), pp.794–801.
Slabunov, Á.I. and Singh, V.K. (2019) Meso-Neoarchaean crustal evolution of the Bundelkhand Craton, Indian Shield: new data from greenstone belts. Int. Geol. Rev., v.61(11), pp.1409–1428.
Steadman, J.A. and Large, R.R. (2016) Synsedimentary, diagenetic, and metamorphic pyrite, pyrrhotite, and marcasite at the Homestake BIF-hosted gold deposit, South Dakota, USA: Insights on Au-As ore genesis from textural and LA-ICP-MS trace element studies. Econ. Geol., v.111(7), pp.1731–1752.
Steadman, J.A., Large, R.R., Davidson, G.J., Bull, S.W., Thompson, J., Ireland, T.R. and Holden, P. (2014) Paragenesis and composition of ore minerals in the Randalls BIF-hosted gold deposits, Yilgarn Craton, Western Australia: Implications for the timing of deposit formation and constraints on gold sources. Precambrian Res., v.243, pp.110–132.
Stipp, M., StuÉnitz, H., Heilbronner, R. and Schmid, S.M. (2002) The eastern Tonale fault zone: a ‘natural laboratory’ for crystal plastic deformation of quartz over a temperature range from 250 to 700 °C. Jour. Struct. Geol., v.24(12), pp.1861–1884.
Trendall, A. (2013) Sedimentary rocks ∣ Banded Iron Formations. Reference Module in Earth Systems and Environmental Sciences, doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-409548-9.02985-7.
Vearncombe, J.R. (1993) Quartz vein morphology and implications for formation depth and classification of Archaean gold-vein deposits. Ore Geol. Rev., v.8(5), pp.407–424.
Verma, S.K., Verma S.P., Oliveira, E.P., Singh, V.K. and Moreno, J.A. (2016) LA-SF-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb geochronology of granitic rocks from the central Bundelkhand greenstone complex, Bundelkhand craton, India. Jour. Asian Earth Sci., v.118, pp.125–137.
Vielreicher, R.M., Groves, D.I., Ridley, J.R. and McNaughton, N.J. (1994) A replacement origin for the BIF-hosted gold deposit at Mt. Morgans, Yilgarn Block, WA. Ore Geol. Rev., v.9(4), pp.325–347.
Zoheir, B. and Akawy, A. (2009) Epigenetic BIF-hosted gold lodes at the Abu Marawat area, Eastern Desert, Egypt: integrated mineralogical, structural control and fluid inclusion studies. Appl. Earth Sci., v.118(2), pp.59–76.
Acknowledgements
AKS acknowledges the Start-up Research Grant (File No.SRG/2019/000424) from Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), Department of Science and Technology (DST), Govt. of India to carry out the research work. Laboratory support extended by Department of Geology, Banaras Hindu University is highly appreciable. NVCR thanks BHU for awarding him an Institution of Eminence (IOE) incentive grant. The authors acknowledge the anonymous reviewer for valuable suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sahoo, A.K., Krishnamurthi, R., Dinkar, G.K. et al. Gold-Sulfide Mineralization in Banded Iron Formation at Girar, Bundelkhand Craton, India: Inferences from Field Observations and Petrography. J Geol Soc India 99, 13–22 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-023-2262-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-023-2262-8