Abstract
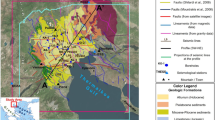
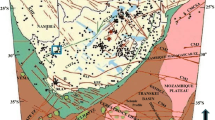
The Aravalli-Delhi fold belt (ADFB) in the NW Indian shield is associated with moderate level of seismicity, including the seismicity of the Delhi seismic zone (DSZ). Several studies have postulated northward extension of the ADFB beneath the alluvium cover of the Ganga basin and its existence beneath the Himalaya. However, subsurface disposition of the ADFB north of Delhi has not been mapped in detail. The results of a recent magnetotelluric study carried out along a profile between Kaithal and Bareilly across the inferred northward extension of the ADFB is presented to address this issue. The results reveal that the concealed ADFB consists of a collage of nearly vertical conductive and resistive blocks buried beneath about 1 to 1.3 km thick alluvial sediments. The boundaries of major inferred tectonic features, such as the western boundary of the Delhi-Haridwar ridge (DHR) and the Great Boundary Fault (GBF), as well as the locations of the Ganga and the Yamuna rivers coincide with such steep contacts. The results suggest the presence of some more concealed geological contacts/tectonic boundaries for which no corresponding surface tectonic features have been mapped. Such a configuration of nearly vertical conductive and resistive blocks has significant implications for the studies aimed at earthquake hazard assessment of the region, especially the DSZ. These results, in conjunction with the MT models available for the Garhwal Himalaya, also indicate continuation of these blocks beneath the Kumaun-Garhwal Himalaya (KGH). Thus, the crust of the KGH below the Main Himalayan Thrust should be highly heterogeneous spatially.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adilakshmi, L., Manglik, A., Thiagarajan, S. and Suresh, M. (2021) Crustal structure of the Indian plate underneath the alluvial plains of the central Ganga basin by broadband magnetotellurics. Tectonophysics, v.802, 228746.
Arora, B.R. (1993) Implications of electrical conductivity structures in the tectonic framework of Northwest India. Curr. Sci. v.64, pp.848–855.
Arora, B.R. and Mahashabde, M.V. (1987) A transverse conductive structure in the northwest Himalaya. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter., v.45, pp.119–127.
Becken, M. and Burkhardt, H. (2004) An ellipticity criterion in magnetotelluric tensor analysis. Geophys. Jour. Int., v.159, pp.69–82.
Booker, J.R. (2014) The Magnetotelluric Phase Tensor: A Critical Review. Surv. Geophys., v.35, pp.7–40.
Caldwell, T.G., Bibby, H.M. and Brown, C. (2004) The magnetotelluric phase tensor. Geophys. Jour. Int., v.158, pp.457–469.
Constable, S.C., Parker, R.L. and Constable, C.G. (1987) Occam’s inversion: a practical algorithm for generating smooth models from electromagnetic sounding data. Geophysics, v.52, pp.289–300.
Dal Zilio, L., Jolivet, R. and van Dinther, Y. (2020). Segmentation of the Main Himalayan Thrust illuminated by Bayesian inference of interseismic coupling. Geophys. Res. Lett., v.47, e2019GL086424.
Demudu Babu, M., Manglik, A., Thiagarajan, S. and Suresh, M. (2020) Electrical resistivity image of a basement ridge in the foreland central Ganga basin. Jour. Appl. Geophys., v.179, 104097.
Dwivedi, D., Chamoli, A. and Pandey, A.K. (2019) Crustal structure and lateral variations in Moho beneath the Delhi fold belt, NW India: Insight from gravity data modeling and inversion. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter., v.297, 106317.
Gahalaut, V. and Arora, B. (2012) Segmentation of seismicity along the Himalayan arc due to structural heterogeneities in the under-thrusting Indian plate and overriding Himalayan wedge. Episodes, v.35, pp.493–500.
Godin, L., La Roche, R.S., Waffle, L. and Harris, L.B. (2018) Influence of inherited Indian basement faults on the evolution of the Himalayan Orogen. Geol. Soc. London, Spec. Publ., v.481, pp.251–276.
Gokarn, S.G., Rao, C.K. and Singh, B.P. (1995) Crustal structure in southeast Rajasthan using magnetotelluric techniques. In: Gupta, K.R. and Sinha-Roy, S. (Eds.), Continental crust of northwestern and central India. Mem. Geol. Soc. India, no.31, pp.373–381.
Israil, M., Tyagi, D.K., Gupta, P.K. and Niwas, S. (2008) Magnetotelluric investigations for imaging electrical structure of Garhwal Himalayan corridor, Uttarakhand, India. Jour. Earth Syst. Sci., v.117, pp.189–200.
Kirkby, A.L., Zhang, F., Peacock, J., Hassan, R. and Duan, J. (2019) The MTPy software package for magnetotelluric data analysis and visualisation. Jour. Open Source Software, v.4(37), 1358. doi:https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.01358
Krieger, L. and Peacock, J. (2014) MTpy: A Python toolbox for magnetotellurics. Computers and Geosciences, v.72, pp.167–175.
Lilley, F.E.M., Singh, B.P., Arora, B.R., Srivastava, B.J., Prasad, S.N. and Sloane, M.N. (1981) A magnetometer array study in northwest India. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter., v.25, pp.232–240.
Mandal, P., Srinivas, D., Suresh, G. and Srinagesh, D. (2021) Modelling of crustal composition and Moho depths and their Implications toward seismogenesis in the Kumaon—Garhwal Himalaya. Scientific Reports, v.11, pp.1–13.
Manglik, A., Arora, T., Thiagarajan, S. and Mallick, A. (2009) Intraplate Stresses due to crustal heterogeneities along the Nagaur — Jhalawar transect, northwestern India. Curr. Sci, v.96, pp.838–843.
Manglik, A., Adilakshmi, L., Suresh, M. and Thiagarajan, S. (2015) Thick sedimentary sequence around Bahraich in the northern part of the central Ganga foreland basin. Tectonophysics, v.653, pp.33–40.
Manglik, A., Kandregula, R.S. and Pavankumar, G. (2022) Foreland basin geometry and disposition of major thrust faults as proxies for identification of segmentation along the Himalayan Arc. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.98, pp.57–61.
Pavankumar, G., Manglik, A., Demudu Babu, M. and Chakravarthi, N.N. (2021) Manetotelluric evidence for the presence of a deep electrical conductor in the vicinity of the Delhi Seismic Zone, India. Jour. Earth Syst. Sci., v.130, 79.
Rawat, G., Arora, B.R. and Gupta, P.K. (2014) Electrical resistivity cross-section across the Garhwal Himalaya: Proxy to fluid-seismicity linkage. Tectonophysics, v.637, pp.68–79.
Reuter, H.I., Nelson, A., Jarvis, A. (2007) An evaluation of void filling interpolation methods for SRTM data. International Jour. Geograph. Inform. Sci., v.21, pp.983–1008.
Rodi, W.L. and Mackie, R.L. (2001) Nonlinear conjugate gradients algorithm for 2-D magnetotelluric inversion. Geophysics, v.66, pp.174–187.
Roy, A.B. (1988) Stratigraphic and Tectonic Framework of the Aravalli Mountain Range. In: Roy, A.B. (Ed.), Precambrian of the Aravalli mountain, Rajasthan, India. Mem. Geol. Soc. India, no.7, pp.3–31.
Sastri, V.V., Bhandari, L.L., Raju, A.T.R. and Datta, A.K. (1971) Tectonic framework and subsurface stratigraphy of the Ganga basin. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.1(3), pp.222–233.
Sharma, R. (2010) Cratons and Fold Belts of India. Springer Berlin, Heidelberg. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-01459-8.
Shukla, A.K., Prakash, R., Singh, R.K., Mishra, P.S. and Bhatnagar, A.K. (2007) Seismotectonic implications of Delhi region through fault plane solutions of some recent earthquakes. Curr. Sci., v.93(12), pp.1848–1853.
Sinha-Roy, S., Malhotra, G. and Guha, D.B. (1995) A transect across Rajasthan Precambrian terrain in relation to geology, tectonics and crustal evolution of south-central Rajasthan. In: Gupta, K.R. and Sinha-Roy, S. (Eds.), Continental crust of northwestern and central India. Mem. Geol. Soc. India, no.31, pp.63–89.
Tewari, H.C., Dixit, M.M., Rao, N.M., Venkateswarlu, N. and Vijaya Rao, V. (1997) Crustal thickening under the Paleo/mesoproterozoic Delhi Fold Belt in NW India: evidence from deep reflection profiling. Geophys. Jour. Internat., v.129(3), pp.657–668.
Valdiya, K.S. (1976) Himalayan transverse faults and folds and their parallelism with the subsurface structures of the north Indian plains. Tectonophysics, v.32, pp.353–386.
Acknowledgements
The study has been carried out under an in-house project MLP6404-28(AM) of CSIR-National Geophysical Research Institute (CSIR-NGRI) with financial support from the projects MLP-FBR0003-28(AM) and SSP801-28(AM). DN acknowledges CSIR for a Research Associate Fellowship to him (Grant number: 31/0023(13135)/2021-EMR-1). Michael Becken is acknowledged for providing his distortion analysis code and Bernhard Friedrichs for the tsmp code. AM thanks Vineet Gahalaut for his comments on an initial version of the manuscript. The work has been approved by CSIR-NGRI for publication as contribution number NGRI/Lib/2022/Pub-89.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manglik, A., Suresh, M., Nagarjuna, D. et al. Subsurface Expressions of the Aravalli-Delhi Fold Belt in the Western Ganga Basin by Magnetotellurics. J Geol Soc India 98, 1721–1727 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-022-2242-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-022-2242-4