Abstract
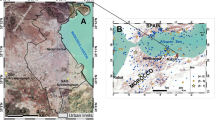
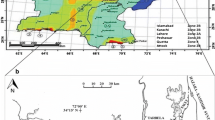
Northeast India is a seismically active region, with frequent major earthquakes. The impact of seismicity can be assessed by using the values fundamental resonant frequency (F0) and the site amplification factor (A0) to derive the seismic vulnerability index (Kg). In 2011, a network of 65 stations was installed in the Cachar fold belt, Assam to continuously record data for a continuous period of eleven months. In this study, the horizontal-to-vertical spectral ratio (H/V) method is employed to identify the resonant frequencies and site amplification factors using ambient noise data to assess the seismic hazard potential in the Cachar fold belt. The amplification factors ranged between 1.15 to 6, while the resonance frequencies varied between 0.25 to 5 Hz. The ambient noise interferometry is utilized to estimate surface waves between station pairs and invert the group velocity dispersion curves for the near-surface S-wave velocities. The S-wave velocity for the basement rocks varied between 600 to 1600 m/s. The S-wave velocities are in turn used to derive an empirical relationship between resonant frequency and alluvium thickness valid for the study region. It is found that stations located at regions with subsurface anticlines had a relatively high resonance frequency and low amplification factor, whereas receivers in synclinal locations and with a thick layer of alluvium sedimentary deposits have a substantially higher site amplification factor and lower resonant frequencies. Further, it is observed that regions with a substantial alluvium sediment cover and near the course of the Barak river are more seismically vulnerable and susceptible to natural hazards.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acerra, C., Havenith, H.B. and Zacharopoulos, S. (2004) Guidelines for the implementation of the H/V spectral ratio technique on ambient vibrations measurements, processing and interpretation (No. European Commission—EVG1-CT-2000-00026 SESAME). European Commission.
Akkaya, Ý. (2020) Availability of seismic vulnerability index (K g) in the assessment of building damage in Van, Eastern Turkey. Earthquake Engg. and Engineering Vibration, v.19(1), pp.189–204.
Bard, P. Y. (1999) Microtremor measurements: a tool for site effect estimation. The effects of surface geology on seismic motion. Jour. title, v.3, pp.1251–1279.
Behm, M., Leahy, G. M. and Snieder, R. (2014) Retrieval of local surface wave velocities from traffic noise—an example from the La Barge basin (Wyoming). Geophys. Prospect., v.62(2), pp.223–243.
Bensen, G. D., Ritzwoller, M. H., Barmin, M. P., Levshin, A. L., Lin, F., Moschetti, M. P., … & Yang, Y. (2007). Processing seismic ambient noise data to obtain reliable broad-band surface wave dispersion measurements. Geophys. Jour. Internat., v.169(3), pp.1239–1260.
Bonnefoy-Claudet, S., Baize, S., Bonilla, L. F., Berge-Thierry, C., Pasten, C., Campos, J., … & Verdugo, R. (2009) Site effect evaluation in the basin of Santiago de Chile using ambient noise measurements. Geophys. Jour. Internat., v.176(3), pp.925–937.
Census of India (2011) http://www.censusindia.gov.in/, accessed 30th June, 2019.
Chatterjee, S.M., Deb, A., Rao, C.V., Reddy, P.K., Sanyal, A. and Yadagiri, K. (2006) Triangle zone geometry in Cachar thrust-fold belt, India. In: SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2006 (pp. 1118–1122). Society of Exploration Geophysicists.
Chávez-García, F.J. and Luzón, F. (2005) On the correlation of seismic microtremors. Jour. Geophys. Res.: Solid Earth, v.110(11). doi:https://doi.org/10.1029/2005JB003671
Cox, B. R., Cheng, T., Vantassel, J. P. and Manuel, L. (2020). A statistical representation and frequency-domain window-rejection algorithm for single-station HVSR measurements. Geophys. Jour. Internat., v.221(3), pp.2170–2183.
Das, J.D., Dutta, T. and Saraf, A.K. (2007) Remote sensing and GIS application in change detection of the Barak river channel, NE India. Jour. Indian Soc. Remote Sensing, v.35(4), pp.301–312.
De Ridder, S., and Biondi, B.L. (2015) Ambient seismic noise tomography at Ekofisk: Geophys., v.80, pp.B167–B176.
Delgado, J., Casado, C.L., Estevez, A., Giner, J., Cuenca, A. and Molina, S. (2000) Mapping soft soils in the Segura river valley (SE Spain): a case study of microtremors as an exploration tool. Jour. Appl. Geophys., v.45(1), pp.19–32.
Dinesh, B.V., Nair, G.J., Prasad, A.G.V., Nakkeeran, P.V. and Radhakrishna, M.C. (2010). Estimation of sedimentary layer shear wave velocity using micro-tremor H/V ratio measurements for Bangalore city. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, v.30(11), pp.1377–1382.
Draganov, D., Campman, X., Thorbecke, J., Verdel, A. and Wapenaar, K. (2009) Reflection images from ambient seismic noise: Geophysics, v.74, pp.A63–A67.
Dziewonski, A., Bloch, S. and Landisman, M. (1969) A technique for analysis of transient seismic signals: Bull. Seismol. Soc. Amer., v.59, pp.427–444.
Fäh, D., Kind, F. and Giardini, D. (2001). A theoretical investigation of average H/V ratios. Geophys. Jour. Internat., v.145(2), pp.535–549.
Garain, S., Mitra, D., & Das, P. (2019). Detection of hydrocarbon microseepage-induced anomalies by spectral enhancements of Landsat 7 ETM+ images in part of Assam—Arakan Fold Belt, India. Jour. Petrol. Explorat. Prod. Tech., v.9(4), pp.2573–2582.
Geological Survey of India, Dasgupta, S., Narula, P.L., Acharyya, S.K. and Banerjee, J. (2000) Seismotectonic atlas of India and its environs. Geological Survey of India.
Haney, M.M., and Tsai, V.C. (2015) Nonperturbational surface-wave inversion: A Dix-type relation for surface waves. Geophysics, v.80, pp.EN167–EN177.
Haney, M.M. and Tsai, V.C. (2017) Perturbational and non-perturbational inversion of Rayleigh-wave velocities. Geophysics, v.82(3), pp.F15–F28.
Hanasoge, S. M., & Branicki, M. (2013) Interpreting cross-correlations of one-bit filtered seismic noise. Geophys. Jour. Internat., v.195(3), pp.1811–1830.
Ibs-von Seht, M. and Wohlenberg, J. (1999) Microtremor measurements used to map thickness of soft sediments. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Amer., v.89, pp.250–259.
Kayal, J. R. (2008). Microearthquake seismology and seismotectonics of South Asia. Springer Science & Business Media.
Kayal, J.R., Arefiev, S.S., Baruah, S., Hazarika, D., Gogoi, N., Gautam, J L., … & Tatevossian, R. (2012) Large and great earthquakes in the Shillong plateau-Assam valley area of Northeast India Region: Pop-up and transverse tectonics. Tectonophysics, v.532, pp.186–192.
Krischer, L., Megies, T., Barsch, R., Beyreuther, M., Lecocq, T., Caudron, C., and Wassermann, J. (2015). ObsPy: a bridge for seismology into the scientific Python ecosystem. Computational Science & Discovery, v.8(1), 014003.
Lachetl, C. and Bard, P.Y. (1994) Numerical and theoretical investigations on the possibilities and limitations of Nakamura’s technique. Jour. Phys. Earth, v.42(5), pp.377–397.
Lermo, J., and Chávez-García, F.J. (1993) Site effect evaluation using spectral ratios with only one station. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Amer., v.83(5), pp.1574–1594.
Lobkis, O. I., and Weaver, R.L. (2001) On the emergence of the Green’s function in the correlations of a diffuse field. Jour. Acoust. Soc. Amer., v.110, pp.3011–3017.
McNamara, D.E. and Buland, R.P. (2004) Ambient Noise Levels in the Continental United States. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Amer., v.94(4), pp.517–1527.
Martin, E. (2020) A Linear Algorithm for Ambient Seismic Noise Double Beamforming Without Cross-correlations.
Mazumder, S., Adhikari, K., Mitra, D.S., Mahapatra, S. and Pangtey, K.K.S. (2016) A neotectonic based geomorphic analysis using remote sensing data to delineate potential areas of hydrocarbon exploration: Cachar area, Assam. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.88(1), pp.87–97.
Molnar, S., Cassidy, J. F., Castellaro, S., Cornou, C., Crow, H., Hunter, J. A., … & Yong, A. (2018) Application of microtremor horizontal-to-vertical spectral ratio (MHVSR) analysis for site characterization: State of the art. Surveys in Geophysics. Geophysics, v.39(4), pp.613–631.
Mordret, A., M. Land’es, N. M. Shapiro, S. C. Singh, P. Roux, and O. I. Barkved, 2013, Near-surface study at the Valhall oil field from ambient noise surface wave tomography:Geophys. Jour. Internat., v.193, pp.1627–1643.
Mukhopadhyay, S. and Bormann, P. (2004). Low cost seismic microzonation using microtremor data: an example from Delhi, India. Jour. Asian Earth Sci., v.24(3), pp.271–280.
Mundepi, A.K. and Lindholm, C. (2009) Soft soil mapping using Horizontal to Vertical Spectral Ratio (HVSR) for seismic hazard assessment of Chandigarh city in himalayan foothills, North India. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.74(5), pp.551.
Nagamani, D., Sivaram, K., Rao, N.P., & Satyanarayana, H.V.S. (2020) Ambient noise and earthquake HVSR modelling for site characterization in southern mainland, Gujarat. Jour. Earth System Sci., v.129(1), pp.1–14.
Nakamura, Y. (1989) A method for dynamic characteristics estimation of subsurface using microtremor on the ground surface. Railway Technical Research Institute, Quarterly Reports, v.30(1).
Nakamura, Y. (1997, November) Seismic vulnerability indices for ground and structures using microtremor. In World Congress on Railway Research in Florence, Italy.
Nakamura, Y. (2000) Clear identification of fundamental idea of Nakamura’s technique and its applications: 12th World Conference on Earthquake and Engineering. New Zealand.
Nakamura Y. (2019) What is the Nakamura method?. Seismol. Res. Lett., v.90(4), pp.1437–1443.
Nakata, N., Chang, J.P., Lawrence, J.F. and Boue, P. (2015) Body wave extraction and tomography at Long Beach, California, with ambient-noise interferometry: Jour. Geophys. Res.: Solid Earth, v.120, pp.1159–1173.
Nath, S.K., Thingbaijam, K.K.S. and Raj, A. (2008) Earthquake hazard in Northeast India—A seismic microzonation approach with typical case studies from Sikkim Himalaya and Guwahati city. Jour. Earth System Sci., v.117(2), pp.809–831.
NEHRP (1997), Recommended Provisions For Seismic Regulations For New Buildings and Other Structures, FEMA-303, Prepared by the Building Seismic Safety Council for the Federal Emergency Management Agency, Washington, DC.
Nogoshi, M. and Igarashi, T. (1971) On the Amplitude Characteristics of Microtremor, Part II. Jour. Seismol. Soc. Japan, v.24, pp.26–40.
Obermann, A., Lupi, M., Mordret, A., Jakobsdottir, S.S. and Miller, S.A. (2016) 3D-ambient noise Rayleigh wave tomography of Snaefellsjokull volcano, Iceland: Jour. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res., v.317.
Peterson, J. (1993) Observation and modelling of seismic background noise. U.S. Geol. Surv. Tech. rept.
Parolai, S., Bormann, P., and Milkereit, C. (2002) New relationships between Vs, thickness of sediments, and resonance frequency calculated by the H/V ratio of seismic noise for the Cologne area (Germany). Bull. Seismol. Soc. Amer., v.92(6), pp.2521–2527.
Rickett, J. and Claerbout, J.F. (1999) Acoustic daylight imaging via spectral factorization: Helioseismology and reservoir monitoring: The Leading Edge, v.18, pp.957–960.
Rigo, A., Sokos, E., Lefils, V. and Briole, P. (2021) Seasonal variations in amplitudes and resonance frequencies of the HVSR amplification peaks linked to groundwater. Geophys. Jour. Internat., v.226(1), pp.1–13.
Saha, D., Bahguna, C.S., Prabhakarudu, J.N. and Baloni, C.L. (2008) Significance of gravity and magnetic data over thrust-fold area—A case study in the Cachar area of Surma sub-basin of Assam—Arakan Basin, Assam, India. In 7th Int. Conf. & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad, India (pp.145–151).
SESAME. (2004) Guidelines for the Implementation of the H/V Spectral Ratio Technique on Ambient Vibrations Measurements, Processing, and Interpretation. (No. WP12-Deliverable D23.12; p.62). European Commission — Research General Directorate.
Shapiro, N.M. and Campillo, M. (2004) Emergence of broad-band Rayleigh waves from correlations of the ambient seismic noise.: Geophys. Res. Lett., v.31, L07614.
Shapiro, N. M., Campillo, M., Stehly, L., & Ritzwoller, M. H. (2005). High-resolution surface-wave tomography from ambient seismic noise. Science, v.307(5715), pp.1615–1618.
Sivaram, K., Mahesh, P., & Rai, S.S. (2012). Stability assessment and quantitative evaluation of H/V spectral ratios for site response studies in Kumaon Himalaya, India using ambient noise recorded by a broadband seismograph network. Pure and Appl. Geophys., v.169(10), pp.1801–1820.
Snieder, R., 2004, Extracting the Green’s function from the correlation of coda waves: A derivation based on stationary phase: Phys. Rev. E, v.69, 046610.
Surve, G., & Mohan, G. (2010) Site response studies in Mumbai using (H/V) Nakamura technique. Natural Hazards, v.54(3), pp.783–795.
Sylvette, B. C., Cécile, C., Pierre-Yves, B., Fabrice, C., Peter, M., Jozef, K., & Fäh, D. (2006). H/V ratio: a tool for site effects evaluation. Results from 1-D noise simulations. Geophys. Jour. Internat., v.167(2), pp.827–837.
Vantassel, J. (2020) https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3666956, Zenodo. jpvantassel/hvsrpy: latest (Concept).
Walling, M. Y., & Mohanty, W. K. (2009) An overview on the seismic zonation and microzonation studies in India. Earth-Sci. Rev., v.96(1–2), pp.67–91.
Wapenaar, K. (2004) Retrieving the Elastodynamic Green’s Function of an Arbitrary Inhomogeneous Medium by Cross Correlation: Phys. Rev. Lett., v.93.
Yang, Y., & Ritzwoller, M. H. (2008) Characteristics of ambient seismic noise as a source for surface wave tomography. Geochem., Geophys., Geosyst., v.9(2).
Yao, H., X. Campman, M. V. de Hoop, and R. van der Hilst (2009) Estimation of surface wave Green’s functions from correlation of direct waves, coda waves, and ambient noise in SE Tibet: Phys. Earth Planet. Inter., v.77, pp.1–11.
Zigone, D., Y. Ben-Zion, M. Campillo, and P. Roux, 2015, Seismic Tomography of the Southern California Plate Boundary Region from Noise-Based Rayleigh and Love Waves: Pure and Applied Geophysics, 172, 1007–1032.
Acknowledgements
The “PAN IIT-ONGC” research project helped with funding and obtaining data for the study. We would like to express our gratitude to IIT Bombay and ONGC for allowing us to publish the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuldeep, Shekar, B., Mohan, G. et al. Assessment of Seismic Vulnerability using the Ambient Noise Recordings in Cachar Fold Belt, Assam. J Geol Soc India 98, 795–804 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-022-2070-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-022-2070-6