Abstract
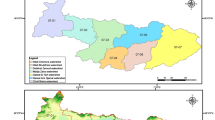
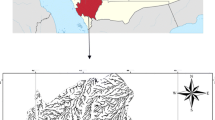
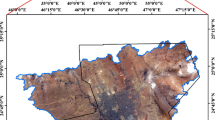
Water is extremely critical for human survival. It is therefore important to efficiently manage integrated water resources, which includes basins, watersheds, and wadies. In this study, the freely available data was used, which included a digital elevation model, soil and geological maps, satellite imageries, and daily precipitation records. Furthermore, remote sensing techniques and geographic information system were also integrated in this study. The linear and areal aspects, along with the longitudinal profile were also included, and the hydrologic soil groups (HSGs), land use/land cover (LULC), and curve number (CN) were identified for the main basin of the Riyadh capital. The morphometric analysis indicated that the total area of the main basin was 8500 km2, with 40 watersheds and the highest stream order as eighth. The drainage density of the main basin was 1.57 km/km2. Impermeable surface constituted most of the basin area, as group D was the most prevalently found HSG, constituting 71% of the total basin area. Additionally, the main basin had a highly steep slope, with varying elevations. Furthermore, four types of LULC were identified in the basin namely urban-based, barren land, cultivated land, and ways. The CN for every cell of the main basin ranged from 64 to 98, and the basin weighted CN was found to be 92. The potential direct runoff ranged from 10 to 59 mm. More than 70% of the total area was found to be vulnerable to high and very high runoffs (> 35 mm). These values confirmed the occurrence of flood events, particularly in urban areas and cultivated lands.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas, A., Amjath-Babu, T., Kächele, H., Müller, K. (2016) Participatory adaptation to climate extremes: an assessment of households’ willingness to contribute labor for flood risk mitigation in Pakistan. Jour. Water and Climate Change, v.7, pp.621–636.
Abdullah, M., Feagin, R., Musawi, L. (2017) The use of spatial empirical models to estimate soil erosion in arid ecosystems. Environ. Monit. Assess., v.189, pp.1–17.
Ahmad, I., Verma, V., Verma, M.K. (2015) Application of curve number method for estimation of runoff potential in GIS environment. Paper presented at the 2nd International Conference on Geological and Civil Engineering
Aina, Y.A., Merwe, J., Alshuwaikhat, H.M. (2008) Urban spatial growth and land use change in Riyadh: Comparing spectral angle mapping and band ratioing techniques. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the Academic Track of the 2008 Free and Open Source Software for Geospatial (FOSS4G) Conference, incorporating the GISSA 2008 Conference, Cape Town, South Africa
Ajmal, M., Kim, T-W. (2014) Quantifying excess stormwater using SCS-CN-based rainfall runoff models and different curve number determination methods. Jour. Irrigat. Drainage Engg., v.141, pp.1–12.
Ajmal, M., Waseem, M, Ahn, J-H., Kim, T-W. (2016) Runoff estimation using the nrcs slope-adjusted curve number in mountainous watersheds. Jour. Irrigat. Drainage Engg., v.142, pp.1–12.
Ali, S.A., Alhamed, M., Ali, U. (2016) Morphometric Analysis of Abdan Basin, Almahfid Basement Rock, Yemen: using Remote Sensing and GIS. Internat. Jour. Advan. Remote Sensing and GIS, v.5, pp.1605–1617.
Ali, U., Ali, S.A. (2014) Analysis of drainage morphometry and watershed prioritization of Romushi-Sasar catchment, Kashmir valley, India using remote sensing and GIS technology. Jour. Advan. Res., v.2, pp.5–23.
Anaba, L.A., Banadda, N., Kiggundu, N., Wanyama, J., Engel, B., Moriasi, D. (2017) Application of SWAT to assess the effects of land use change in the Murchison Bay catchment in Uganda. Computational Water, Energy, Environ. Engg., v.6, pp.24–40.
Angelakis, A. (2016) Evolution of rainwater harvesting and use in Crete, Hellas, through the millennia. Water Sci. Tech.: Water Supply v.16, pp.1624–1638.
Archer, D., Fowler, H. (2015) Characterising flash flood response to intense rainfall and impacts using historical information and gauged data in Britain. Jour. Flood Risk Managmt., v.11, pp.S121–S133.
Ashwan, M.S.A., Salam, A.A., Mouselhy, M.A. (2012) Population growth, structure and distribution in Saudi Arabia. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Rev., v.1, pp.33–46.
Asode, A.N., Sreenivasa, A., Lakkundi, T. (2016) Quantitative morphometric analysis in the hard rock Hirehalla sub-basin, Bellary and Davanagere districts, Karnataka, India using RS and GIS. Arabian Jour. Geosci., v.9, pp.1–14.
Bagyaraj, M., Gurugnanam, B., Nagar, A. (2011) Significance of morphometry studies, soil characteristics, erosion phenomena and landform processes using remote Sensing and GIS for Kodaikanal Hills, a global biodiversity hotpot in Western Ghats, Dindigul District, Tamil Nadu, South India. Res. Jour. Environ. Earth Sci., v.3, pp.221–233.
Bajabaa, S., Masoud, M., Al-Amri, N. (2014) Flash flood hazard mapping based on quantitative hydrology, geomorphology and GIS techniques (case study of Wadi Al Lith, Saudi Arabia). Arabian Jour. Geosci., v.7, pp.2469–2481.
Bhagat, N. (2016) Estimation of SCS-CN for lower Mahi basin, Gujarat, India. Internat. Jour. Advan. Engg. Res. Tech., v.4, pp.61–63.
Bhunia, G.S., Samanta, S., Pal, B. (2012) Quantitative analysis of relief characteristics using space technology. Internat. Jour. Phys. Social Sci., v.2, pp.350–365.
Bindu, G., Neelakantan, R., Reghunath, R. (2012) Remote sensing cum GIS based assessment of morphometric characteristics of Chittar basin in district Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala, South India. Nature, Environ. Pollution Tech., v.11, pp.729–736.
Biswas, A., Das Majumdar, D., Banerjee, S. (2014) Morphometry governs the dynamics of a drainage basin: Analysis and implications Geography Jour., v.2014, pp.1–14.
Biswas, S., Sudhakar, S., Desai, V. (1999) Prioritization of sub-watersheds based on morphometric analysis of drainage basin, district Midnapore, West Bengal. Jour Indian Soc. Remote Sens., v.27, pp.155–166.
Chavda, D.B., Makwana, J.J., Parmar, H.V., Kunapara, A.N., Prajapati, G.V. (2016) Estimation of runoff for Ozat catchment using RS and GIS based SCS-CN method. Curr. World Environ., v.11, pp.212–217.
Clarke, J.I. (1966) Morphometry from Maps. Essays in Geomorphology. Elsevier Publ. Co., New York.
Coates, D.R. (1958) Quantitative geomorphology of small drainage basins of southern Indiana. (Report No.10) Columbia University, department of geology).
Cronshey R. (1986) Urban hydrology for small watersheds TR-55. Retrieved from United States Department of Agriculture: https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/Internet/FSE_DOCUMENTS/stelprdb1044171.pdf.
Dale, M., Clarke, J., Harris, H. (2016) Urban flood prediction and warning-challenges and solutions. Proc. Water Environ. Feder., pp.2237–2242.
Deng, L., McCabe, M.F., Stenchikov, G., Evans, J.P., Kucera, P.A. (2015) Simulation of flash-flood-producing storm events in Saudi Arabia using the weather research and forecasting model. Jour. Hydrometeor., v.16, pp.615–630.
Dile, Y.T., Srinivasan, R. (2014) Evaluation of CFSR climate data for hydrologic prediction in data?scarce watersheds: an application in the Blue Nile River basin. JAWRA Jour. Amer. Water Resour. Assoc., v.50, pp.1226–1241.
Durán-Barroso, P., González, J., Valdés, J.B. (2016) Improvement of the integration of soil moisture accounting into the NRCS-CN model. Jour. Hydrol., v.542, pp.809–819.
Dutta, S., Roy, S. (2012) Determination of erosion surfaces and stages of evolution of Sangra drainage basin in Giridih district, Jharkhand, India. Internat. Jour. Geomatics Geosci., v.3, pp.63–73.
Ebrahimian, M. (2012) Application of NRCS-curve number method for runoff estimation in a mountainous watershed. Caspian Jour. Environ. Sci., v.10, pp.103–114.
Ebrahimian, M., See, L.F., Ismail, M.H., Malek, I.A. (2009) Application of natural resources conservation service-curve number method for runoff estimation with GIS in the Kardeh watershed, Iran. European Jour. Scient. Res., v.34, pp.575–590.
Elfeki, A., Masoud, M., Niyazi, B. (2017) Integrated rainfall-runoff and flood inundation modeling for flash flood risk assessment under data scarcity in arid regions: Wadi Fatimah basin case study. Saudi Arabia Natural Hazards, v.85, pp.87–109.
Fisher, P., Comber, A.J., Wadsworth, R. (2005) Land use and land cover: contradiction or complement. In: Fisher, P. (Ed.), Re-presenting GIS. Wiley, England, pp.85–98.
Fuka, D.R., Walter, M.T., MacAlister, C., Degaetano, A.T., Steenhuis, T.S., Easton, Z.M. (2014) Using the Climate Forecast System Reanalysis as weather input data for watershed models. Hydrolog. Proces., v.28, pp.5613–5623.
Gabale, S.M., Pawar, N.R. (2015) Quantitative morphometric analysis of AmbilOdha (Rivulet) in Pune, Maharashtra, India. IOSR Jour. Environ. Sci., Toxicol. Food Tech., v.9, pp.41–48.
Gajbhiye, S., Mishra, S., Pandey, A. (2014) Relationship between SCS-CN and sediment yield. Applied Water Sci., v.4, pp.363–370.
Ghaffarian Hoseini, A., Tookey, J., Ghaffarian Hoseini, A., Yusoff S.M., Hassan, N.B. (2016) State of the art of rainwater harvesting systems towards promoting green built environments: A review. Desalination and Water Treatment, v.57, pp.95–104.
Gravelius, H. (1914). Grundrifi der Gesamten Gewcisserkunde. Band I: Flufikunde (Compendium of Hydrology, vol. I. Rivers in German). Goschen, Berlin, Germany.
Hajam, R.A., Hamid, A., Bhat, S. (2013) Application of morphometric analysis for geo-hydrological studies using geo-spatial technology-A case study of Vishav drainage basin. Hydrology: Curr. Res., v.4, pp.1–12.
Harish, N., Hemalatha, T., Babu, C.M. (2016) Sensitivity of curve number and initial abstraction coefficient on SCS-CN method of runoff estimation in an ungauged watershed intergrated with RS & GIS. PARIPEX-Indian Jour. Res., v.4, pp.50–52.
Hawkins RH, Hjelmfelt Jr AT, Zevenbergen AW (1985) Runoff probability, storm depth, and curve numbers. Jour. Irrigat. Drainage Engg., v.111, pp.330–340.
Hoedjes, J.C. et al. (2014) A conceptual flash flood early warning system for Africa, based on terrestrial microwave links and flash flood guidance. ISPRS Internat. Jour. Geo-Information, v.3, pp.584–598.
Hong, Y., Adler, R.F., Hossain, F., Curtis, S., Huffman, G.J. (2007) A first approach to global runoff simulation using satellite rainfall estimation. Water Resour. Res., v.43, pp.1–8.
Horton, R.E. (1932) Drainage basin characteristics. Eos, Trans. Amer. Geophys. Union, v.13, pp.350–361.
Horton, R.E. (1945) Erosional development of streams and their drainage basins; hydrophysical approach to quantitative morphology. Geol. Soc. Amer. Bull., no.56, pp.275–370.
Jaber, H.S., Mansor, S., Pradhan, B., Ahmad, N. (2016) Rainfall-runoff modelling and water balance analysis for Al-Hindiyah barrage, Iraq using remote sensing and GIS. Geocarto Internat., v.32, pp.1407–1420.
Kalam, M., Ramesh, M. (2015) Morphometric analysis of Milli watershed area in Zaheerabad. Internat. Jour., v.3, pp.97–101.
Kaliraj, S., Chandrasekar, N., Magesh, N. (2015) Morphometric analysis of the River Thamirabarani sub-basin in Kanyakumari district, South west coast of Tamil Nadu, India, using remote sensing and GIS. Environ. Earth Sci., v.73, pp.7375–7401.
Kant, S., Meshram, S., Dohare, R., Singh, S. (2015) Morphometric analysis of Sonar sub-basin using SRTM data and geographical information system (GIS). African Jour. Agricul. Res., v.10, pp.1401–1406.
Karagiorgos, K., Thaler, T., Hübl, J., Maris, F., Fuchs, S. (2016) Multi-vulnerability analysis for flash flood risk management. Natural Hazards, v.82, pp.63–87.
Khan, A.N. (2011) Analysis of flood causes and associated socio-economic damages in the Hindukush region Natural hazards, v.59, pp.1239–1260.
Kumar, N. (2013) Morphometric analysis of river catchments using remote sensing and GIS (a case study of the Sukri River, Rajasthan) Internat. Jour. Sci. Res. Publ., v.3, pp.1–6.
Lal, M. et al. (2016) Evaluation of the Soil Conservation Service curve number methodology using data from agricultural plots. Hydrogeol. Jour., v.25, pp.151–167.
Lee, R.S., Traver, R.G., Welker, A.L. (2016) Evaluation of soil class proxies for hydrologic performance of in situ bioinfiltration systems. Jour. Sustain. Water Built Environ., v.2, pp.1–10.
Li, R., Rui, X., Zhu, A-X., Liu, J., Band, L.E., Song, X. (2015) Increasing detail of distributed runoff modeling using fuzzy logic in curve number. Environ. Earth Sci., v.73, pp.3197–3205.
Mack, B., Leinenkugel, P., Kuenzer, C., Dech, S. (2017) A semi-automated approach for the generation of a new land use and land cover product for Germany based on Landsat time-series and Lucas in-situ data. Remote Sensing Lett., v.8, pp.244–253.
Magesh, N., Jitheshlal, K., Chandrasekar, N., Jini, K. (2013) Geographical information system-based morphometric analysis of Bharathapuzha river basin, Kerala, India. Applied Water Sci., v.3, pp.467–477.
Mahmood, S., Mayo, S.M. (2016) Exploring underlying causes and assessing damages of 2010 flash flood in the upper zone of Panjkora River. Natural Hazards, v.83, pp.1213–1227.
Mahmood, S., Ullah, S. (2016) Assessment of 2010 flash flood causes and associated damages in Dir Valley, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Pakistan. Internat. Jour. Disaster Risk Reduction, v.16, pp.215–223.
Mahmoud, S.H., Gan, T.Y. (2018a) Impact of anthropogenic climate change and human activities on environment and ecosystem services in arid regions. Sci. Total Environ., v.633, pp.1329–1344.
Mahmoud, S.H., Gan, T.Y. (2018b) Long-term impact of rapid urbanization on urban climate and human thermal comfort in hot-arid environment. Building and Environ., v.142, pp.83–100.
Mahmoud, S.H., Gan, T.Y. (2018c) Multi-criteria approach to develop flood susceptibility maps in arid regions of Middle East. Jour. Cleaner Production, v.196, pp.216–229.
Mahmoud SH, Gan TY (2018d) Urbanization and climate change implications in flood risk management: Developing an efficient decision support system for flood susceptibility mapping. Sci. Total Environ., v.636, pp.152–167.
Mahmoud, S.H., Gan, T.Y. (2019) Irrigation water management in arid regions of Middle East: Assessing spatio-temporal variation of actual evapotranspiration through remote sensing techniques and meteorological data. Agricul. Water Managmt., v.212, pp.35–47.
Masseroni, D., Cislaghi, A., Camici, S., Massari, C., Brocca, L. (2016) A reliable rainfall-runoff model for flood forecasting: review and application to a semi-urbanized watershed at high flood risk in Italy. Hydrol. Res., v.48, pp.726–740.
Miller VC (1953) A quantitative geomorphic study of drainage basin characteristics in the Clinch Mountain area, Virginia and Tennessee. (Report No. 3), Columbia University, department of geology.
Mishra, S., Jain, M., Babu, P.S., Venugopal, K., Kaliappan, S. (2008) Comparison of AMC-dependent CN-conversion formulae Water Resour. Managmt., v.22, pp.1409–1420.
Mishra S.K., Singh, V. (2013) SCS-CN Method. In: Soil Conservation Service Curve Number (SCS-CN) Methodology, Vol.42. Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht, pp.84–146.
Mistry, A., Lodha, P., Prakash, I., Mehmood, K. (2017) Estimation of direct runoff for Purna river sub-bsin, using SCS-CN method, Dangs district, Gujarat. Internat. Jour. Advan. Engg. Res. Develop., v.4, pp.581–593.
Moon, G-W., Ajmal, M., Ahn, J-H., Kim, T-W. (2016) Investigating practical alternatives to the NRCS-CN method for direct runoff estimation using slope-adjusted curve numbers. KSCE Jour. Civil Engg., v.20, pp.3022–3030.
Nongkynrih, J.M., Husain, Z. (2011) Morphometric analysis of the Manas river basin using earth observation data and geographical information system. Internat. Jour. Geomatics Geosci., v.2, pp.647–654.
Nonglait, TL., Tiwari, B. (2016) Application of SCS-CN method for estimation of runoff in a humid microwatershed. Internat. Jour. Curr. Agricul. Sci., v.6, pp.121–127.
NRCS (2007) National Engineering Handbook: Part 630-Hydrology, USDA Soil Conservation Service. Washington, DC, USA, Available online at https://directives.sc.egov.usda.gov/viewerFS.aspx?hid=21422.
NRCS (2009) National Engineering Handbook: Part 630-Hydrology, USDA Soil Conservation Service. Washington, DC, USA, Available online at https://directives.sc.egov.usda.gov/viewerFS.aspx?hid=21422
Oliveira, P., Nearing, M., Hawkins, R., Stone, J., Rodrigues, D., Panachuki, E., Wendland, E. (2016) Curve number estimation from Brazilian Cerrado rainfall and runoff data. Jour. Soil Water Conserv., v.71, pp.420–429.
Pandey, P.K., Das, S. (2016) Morphometric analysis of Usri River basin, Chhotanagpur Plateau, India, using remote sensing and GIS. Arabian Jour. Geosci., v.9, pp.1–13.
Pareta, K., Pareta, U. (2011) Quantitative morphometric analysis of a watershed of Yamuna basin, India using ASTER (DEM) data and GIS. Internat. Jour. Geomatics Geosci., v.2, pp.248.
Pareta, K., Pareta, U. (2012) Quantitative geomorphological analysis of a watershed of Ravi River basin, HP India. Internat. Jour. Remote Sensing and GIS, v.1, pp.47–62.
Patel, G.R., Trivedi, M.M. (2016) Prediction and validation of runoff through RS and GIS-based distributed SCS-CN method. Advan. Life Sci., v.5, pp.4965–4977.
Patil, J., Sarangi, A., Singh, A., Ahmad, T. (2008) Evaluation of modified CN methods for watershed runoff estimation using a GIS-based interface. Biosystems Engg., v.100, pp.137–146.
Pitt, R. (1999) Small storm hydrology and why it is important for the design of stormwater control practices. Jour. Water Managmt. Model., v.7, pp.61–91.
Qhtani, A.M., Al Fassam, A.N. (2011) Ar Riyadh Geospatial urban information system and metropolitan development strategy for Ar Riyadh. Paper presented at the ESRI international user conference
Radwan, F., Alazba, A., Mossad, A. (2017) Watershed morphometric analysis of Wadi Baish Dam catchment area using integrated GIS-based approach. Arabian Jour. Geosci., v.10, pp.256.
Radwan, F., Alazba, A.A., Mossad, A. (2018) Estimating potential direct runoff for ungauged urban watersheds based on RST and GIS Arabian Jour. Geosci., v.11, pp.748. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-4067-4.
Radwan, F., Alazba, A.A., Mossad, A. (2019) Flood risk assessment and mapping using AHP in arid and semiarid regions. Acta Geophysica, v.67, pp.215–229. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-018-0233-z
Radwan, F., Alazba, A.A., Mossad, A. (2020) Analyzing the geomorphometric characteristics of semiarid urban watersheds based on an integrated GIS-based approach, Model, Earth Systems Environ., doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-020-00802-0
Rahman, M.T., Aldosary, A.S., Nahiduzzaman, K.M., Reza, I. (2016) Vulnerability of flash flooding in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Natural Hazards, v.84, pp.1807–1830
Rai, P.K., Mohan, K., Mishra, S., Ahmad, A., Mishra, V.N. (2014) A GIS-based approach in drainage morphometric analysis of Kanhar River Basin, India. Applied Water Sci, v.7, pp.217–232.
Rajeevan, M. (2017) Past and future trends of hydroclimatic intensity over the Indian Monsoon region. Jour. Geophys. Res., Atmospheres, v.122, pp.896–909.
Ranjan, R. (2017) Flood disaster management. In: Sharma N (ed) River System Analysis and Management. Springer, Singapore, pp.371–417.
Rao NK, Latha SP, Kumar AP, Krishna HM (2010) Morphometric analysis of Gostani river basin in Andhra Pradesh state, India using spatial information technology. Internat. Jour. Geomatics Geosci., v.1, pp.179.
Ryu, J., Jung, Y., Kong, D.S., Park, B.K., Kim, Y.S., Engel, B.A., Lim, K.J. (2016) Approach of Land Cover based Asymptotic Curve Number Regression Equation to Estimate Runoff. Irrigation and Drainage, v.65, pp.94–104.
Sartori A, Hawkins RH, Genovez AM (2011) Reference curve numbers and behavior for sugarcane on highly weathered tropical soils. Jour. Irrigat. Drainage Engg., v.137, pp.705–711.
Scheidegger, A.E. (1965) The algebra of stream-order numbers. USGS Prof. Paper, pp.187–189.
Schumm, S.A. (1956) Evolution of drainage systems and slopes in badlands at perth amboy, New Jersey. Geol. Soc. Amer. Bull., v.67, pp.597–646.
Shadeed, S., Almasri, M. (2010) Application of GIS-based SCS-CN method in West Bank catchments. Palestine Water Sci. Engg, v.3, pp.1–13.
Shah, M., Bhagat, N. (2017) Estimation of weighted SCS-CN: Case of Narmada river basin, India. Internat. Jour. Scient. Res., v.5, pp.687–688
Shi Q (2014) Flood Hazard assessment along the western regions of Saudi Arabia using GIS-based Morphometry and remote sensing techniques (doctoral dissertation). King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST).
Shreve, R.L. (1967) Infinite topologically random channel networks. Jour. Geol., v.75, pp.178–186.
Singh, L.K., Jha, M.K., Chowdary, V. (2017) Multi-criteria analysis and GIS modeling for identifying prospective water harvesting and artificial recharge sites for sustainable water supply. Jour. Cleaner Product., v.142, pp.1436–1456.
Sobhani, G. (1976) A review of selected small watershed design methods for possible adoption to Iranian conditions. M.S. Thesis, Utah State University, Logan, UT, USA.
Špitalar, M., Gourley, J.J., Lutoff, C., Kirstetter, P-E., Brilly, M., Carr, N. (2014) Analysis of flash flood parameters and human impacts in the US from 2006 to 2012 Journal of Hydrology 519:863–870.
Starosolszky, O., Melder, O. (2014) Hydrology of Disasters: Proceedings of the World Meteorological Organization Technical Conference Held in Geneva, November 1988. 1st edn. Routledge, London. doi:https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315073583.
Strahler, A.N. (1957) Quantitative analysis of watershed geomorphology. Eos, Trans. Amer. Geophys. Union, v.38, pp.913–920.
Strahler AN (1964) Quantitative geomorphology of drainage basins and channel networks, section 4-II. In: Chow VT (Ed.), Handbook of applied hydrology. McGraw Hill, New York, pp.39–76.
Tirkey, A.S., Ghosh, M., Pandey, A., Shekhar, S. (2017) Assessment of climate extremes and its long term spatial variability over the Jharkhand state of India. Egyptian Jour Remote Sensing and Space Sci., v.21, pp.49–63.
Waikar, M., Nilawar, A.P. (2014) Morphometric analysis of a drainage basin using geographical information system: a case study Internat. Jour. Multidiscip. Curr. Res., v.2, pp.179–184.
Walia D, Mipun BS (2010) Hydrological behavior of Umshing River, East Khasi Hills, Meghalaya. Acta Geophysica, v.58, pp.908–921 doi:https://doi.org/10.2478/s11600-010-0018-5
Wang, F., Ge, Q., Yu, Q., Wang, H., Xu, X. (2017) Impacts of land-use and land-cover changes on river runoff in Yellow River basin for period of 1956–2012 Chinese Geographical Science 27:13–24
Withanage, N., Dayawansa, N., De Silva, R. (2015) Morphometric analysis of the Gal Oya River basin using spatial data derived from GIS. Tropical Agric. Res., v.26, pp.175–188.
Zavoiance, I. (1985) Morphometry of drainage basins (Developments in water science) Publisher: Elsevier Science, v.20, pp.104–105
Zhang, Q., Luo, G., Li, L., Zhang, M., Lv, N., Wang, X. (2017) An analysis of oasis evolution based on land use and land cover change: A case study in the Sangong River Basin on the northern slope of the Tianshan Mountains. Jour. Geograph. Sci., v.27, pp.223–239.
Acknowledgements
The work was financially supported by King Saud University, vice deanship of research chairs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Radwan, F., Alazba, A.A. Integrated Hydrologic Study of the Arid and Semi-arid Regions using RST and GIS in the Riyadh Metropolitan Area, Saudi Arabia. J Geol Soc India 97, 539–554 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-021-1720-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-021-1720-4