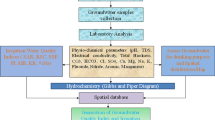
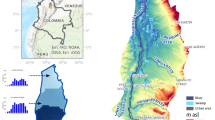
Abstract
The role of groundwater in irrigation and drinking purposes and sustaining growth in economy is well-known. Groundwater is generally less susceptible to contamination and pollution when compared to surface water bodies. This paper is based on extensive investigations on the spatial and seasonal representative measurement of chemical parameters from 80 dug wells of Churu and adjoining Bikaner districts of Rajasthan, India. The region has dearth of water resources — both surface and sub-surface, with the main source of water being the dug wells. The application of hydro-statistical techniques and tools like Pearson’s correlation coefficient, relative activity of sodium ion (SAR), Wilcox diagram, Piper diagram and magnesium hazard indicate that the chemical parameters of the water of the study region is of very poor quality and not suitable for drinking and irrigation purposes. Wilcox diagram shows high sodium content, can destroy the soil structure rendering the soil and water unsuitable.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ameen, H.A. (2019) Spring water quality assessment using water quality index in villages of BarwariBala, Duhok, Kurdistan Region, Iraq. Appl. Water Sci., v.9, pp.176. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-019-1080-z.
Arulbalaji, P., Gurugnanam, B. (2017) Groundwater quality assessment using geospatial and statistical tools in Salem District, Tamil Nadu, India. Appl. Water Sci., v.7, pp.2737–2751. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-016-0501-5.
Bouslah, Soraya, Djemili, Lakhdar, Houichi, Larbi. (2017) Water quality index assessment of KoudiatMedouar Reservoir, northeast Algeria using weighted arithmetic index method. Jour. Water and Land Development, v.35. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1515/jwld-2017-0087.
Biswas, Brototi, Jain, Sanjay and Rawat, Sanchita (2018) Spatio-temporal analysis of groundwater levels and projection of future trend of Agra city, Uttar Pradesh, India. Arabian Jour. Geosci., v.11. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3577-4.
Baride, Mukund, Patil, Sanjaykumar and Golekar, Rushikesh (2014) Groundwater geochemistry of shallow and deep aquifers from Jalgaon district, northern Maharashtra (India). Internat. Jour. Advan. Geosci., v.2. pp.97–104. DOI:https://doi.org/10.14419/ijag.v2i2.3348.
Brown, R.M., McClelland, N.I., Deininger, R.A., Tozer, R.G. (1970) A water quality index—do we dare. Water Sew Works, v.117, pp.339–343.
Bora, M., Goswami, D.C. (2017) Water quality assessment in terms of water quality index (WQI): case study of the Kolong River, Assam, India. Appl. Water Sci., v.7, pp.3125–3135. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-016-0451-y.
Durga, D. Poudel, Timothy, W. Duex (2017) Vanishing Springs in Nepalese Mountains: Assessment of Water Sources, Farmers’ Perceptions, and Climate Change Adaptation. Mountain Res. Develop., v.37(1), pp.35–46.
Ganiyu, S., Olurin, O., Ojo, A., Badmus, B., Jegede, O. (2017) Quality assessment of spring and well waters: an approach using water quality index and multivariate statistical analysis. Afr. Rev. Phys., v.12, pp.47–64.
Horton, R.K. (1965) An index number system for rating water quality. Jour. Water Poll, Control Federation, v.37, pp.300–305.
IPCC (2007) Climate change 2007: impacts, adaptation and vulnerability. In: Parry ML, Canziani of, Palutik of JP, van der Linden PJ, Hanson CE (Eds.), Contribution of working group II to the fourth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge/New York.
Jat, M.K., Khare, D. and Garg, P.K. (2009) Urbanization and its impact on groundwater: a remote sensing and GIS-based assessment approach. The Environmentalist, v.29(1), pp.17–32. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10669-008-9176-2.
Jhariya, D.C., Shandilya, A.K. and Dewangan, R. (2012) Nitrate Pollution in the Groundwater around Sagar Town, Madhya Pradesh, India. International Conference on Chemical, Ecology and Environmental Sciences (ICEES’2012), Bangkok, pp.151–154.
Khan, R. and Jhariya, D.C. (2016) Land Use, Land Cover Change Detection Using Remote Sensing and Geographic Information System in Raipur Municipal Corporation Area, Chhattisgarh. SSARSC Internat. Jour. GeoScience and Geo Informatics. v.3(1), pp.1–4. http://www.ssarsc.org/volumes/ijgsgi/volume3/SSARSC-IJGSGI_1.pdf.
Kaviarasan, M., Geetha, P., Soman, K.P. (2016) GIS-based groundwater monitoring in Thiruvannamalai District, Tamil Nadu, India. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Soft Computing Systems, vol. 397, Springer, India, pp.685–700.
Nickson, R.T., McArthur, John, Shrestha, B., Kyaw-Myint, T.O. and Lowry, David (2005) Arsenic and other drinking water quality issues, Muzaffargarh District, Pakistan. Appl. Geochem., v.20, pp.55–68. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2004.06.004.
Paliwal, K.V. (1972) Irrigation with Saline Water. Water Technology Centre, Indian Agriculture Research Institute, New Delhi, 198 p.
Ramesh, K. and Elango, L. (2011) Groundwater quality and its suitability for domestic and agricultural use in Tondiar river basin, Tamil Nadu, India. Environ. Monit. Assess., v.184, pp.3887–99. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-22313.
Rubia, K., Jhariya, D.C. and Singh, V.K. (2015) Urbanization and its impact on Groundwater: An Overview. Workshop on Groundwater issues and challenges in Chhatt is garh state with special reference to its Conservation, Security and Quality. Central Groundwater Board, NCCR, Ministry of Water Resources, River Development & Ganga Rejuvenation. Govt. of India, pp.127–136.
Reza, R., Singh, G. (2010) Heavy metal contamination and its indexing approach for river water. Internat. Jour. Environ. Sci. Tech., v.7, pp.785–792.
Samantray, P., Mishra, B.K., Panda, C.R., Rout, S.P. (2009) Assessment of water quality index in Mahanadi and Atharabanki Rivers and Taldanda Canal in Paradip area, India. Jour. Hum. Ecol., v.26(3), pp.153–161.
Shigut, D.A., Liknew, G., Irge, D.D., Ahmad, T. (2017) Assessment of physico-chemical quality of borehole and spring water sources supplied to Robe Town, Oromia region, Ethiopia. Appl. Water Sci. v.7, pp.155–164.
Stamatis, Georgios, Alexakis, Dimitris, Gamvroula, D. and Migiros, G. (2011) Groundwater quality assessment in Oropos–Kalamos basin, Attica, Greece. Environ. Earth Sci., v.64, pp.973–988. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-0914-2.
Szabolcs I. and Darab, C. (1964) The influence of irrigation water of high sodium carbonate content of soils. In: Proceedings of 8th international congress of ISSS, Transaction II, pp.803–881.
Tiwari, A.K., Singh, A.K., Singh, A.K., Singh, M.P. (2015) Hydrogeochemical analysis and evaluation of surface water quality of Pratapgarh district, Uttar Pradesh, India. doi: https://doi.org/10.10007/s13201-015-0313-z
Todd, D.K. (1976) Groundwater Hydrology. John Wiley and sons Inc. New York.
Yisa, J., Tijani Oladejo, Jimoh and Oyibo, Ohiemi (2012) Underground water Assessment using Water Quality Index. Leonardo Jour. Sci., v.21, pp.33–42.
Acknowledgement
The authors are indebted to ICSSR for financial assistance through MRP entitled “Application of Geo-Informatics for Sustainable Development of Environmental Resources in a Semi-Arid Region of India”. The authors wish to thank Central Ground Water Board (CGWB) and State Ground Water Board, Rajasthan for ground water data received. The authors also wish to acknowledge the editors of the present journal for their timely and resourceful insights into the paper for making it more informative.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, J., Biswas, B. & Verghese, S. Assessment of Groundwater Quality for Drinking and Irrigation Purpose using Geospatial and Statistical techniques in a Semi-arid Region of Rajasthan, India. J Geol Soc India 97, 416–427 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-021-1699-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-021-1699-x