Abstract
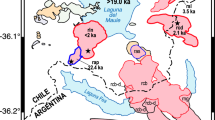
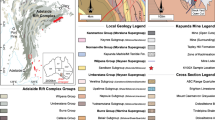
Single-phase CH4 and two-phase CH4-rich fluid inclusions were identified at Langdu skarn Cu deposit in Zhongdian area, southwest China. Microthermometric results confirm that the single-phase CH4 fluid inclusions are homogenized to liquid from -118.3ºC to -114.2ºC, and two-phase CH4-rich fluid inclusions partly homogenized from -87.5 ºC to -84.7 ºC. Laser Raman micospectroscopic analyses show that vapors of the fluid inclusions are dominant of CH4 with minor N2. The two-phase CH4-rich fluid inclusions allow the determination of the fluid temperature (300°C to 400°C) and pressure (1014 bars to 1484 bars) during mineralization, suggesting that ore formation took place at 3.8 to 4.8 km depth under lithostatic pressure. CH4 contained in the fluid inclusions most likely formed by the reaction 2C + 2H2O=CH4+CO2 between carbonaceous slate from Qugasi Formation and hydrothermal fluids either in situ or during migration. CH4 (and/or N2) will greatly expand the field of vapor/liquid immiscibility and will act as reducing agent which transforms SO4 2– to S2– that is essential anion for sulfide deposition. Numerous massive sulfide deposits (chalcopyrite and pyrrhotite) reflect that physical and chemical condition of hydrothermal fluid and significant change would be caused by CH4.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen, T., Burke, E.A.J. and Austrheim, H. (1989) Nitrogen bearing, aqueous fluid inclusions in some eclogites from the Western Gneiss Region of the Norwegian Caledonides. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., v.103, pp.153–165.
Brown, P.E. and Hagemann, S.G. (1995) MacFlincor and its application to fluids in Archaean lode-gold deposits. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, v.59, pp.3943–3952.
Bodnar, R.J. (1993) Revised equation and table for determining the freezing point depression of H2O-NaCl solutions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, v.57, pp.683–684.
Heinrich, C.A. (2007) Fluid-fluid interactions in magmatichydrothermal ore formation. Rev. Mineral. Geochem., v.65, pp.363–387.
Fan, H.R., Xie, Y.H., Wang, K.Y., et al. (2004) Methane-rich fluid inclusions in skarn near the giant REE-Nb-Fe deposit at Bayan Obo, Northern China. Ore Geol. Rev., v.25, pp.301–309.
Goldhaber, M.D. and Kaplan, I.R. (1980) Mechanisms of sulphur incorporation and isotope fractionation during early diagenesis in sediments of the Gulf of California. Marine Chemistry, v.9, pp.95–143.
Goodfellow, W.D. (1987) Anoxic stratified oceans as a source of sulphur in sediment-hosted stratiform Zn-Pb deposits (Selwyn Basin, Yukon, Canada). Chemical Geol., v.65, pp.359–382.
Hedenquist, J.W., Arribas, A. and Reynolds, T.J. (1998) Evolution of an intrusion centred hydrothermal system: far southeast-Lepanto porphyry and epithermal Cu-Au deposit. Econ. Geol., v.93, pp.373–404.
Heydari, E. and Moore, C.H. (1989) Burial diagenesis and thermochemical sulfate reduction, Smackover Formation, southeastern Mississippi salt basin. Geology, v.17, pp.1080–1084.
Hou, Z.Q., Qu, X.M., Zhou, J.R., et al. (2001) Collision-Orogenic processes of Yidun arc in the Sanjiang region: record of granites. Acta Geologica Sinica, v.75, pp.485–497(in Chinese).
Hou, Z.Q., Yang, Y.Q., Qu, X.M., et al. (2004) Tectonic evolution a mineralization system of the Yidun arc orogen in Sanjiang region, China. Acta Geologica Sinica, v.78, pp.110–120(in Chinese).
Taylor, J.R. and Richard, W. (1979) Forester. An Oxygen and Hydrogen Isotope Study of the Skaergaard Intrusion and its Country Rocks: a Description of a 55 M.Y. Old Fossil Hydrothermal System. Jour. Petrol., v.20, pp.355–419.
Huizenga, J.M., Gutzmer, J., Greyling, L.N., et al. (2006) Carbonic fluid inclusions in Paleoproterozoic carbonate-hosted Zn-Pb deposits in Griqualand West, South Africa. South Africa Jour. Geology, v.109, pp.55–62.
Jacobs, G.K. and Kerrick, D.M. (1981) Methane: An equation of state with application to the ternary system H2O-CO2-CH4. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, v.45, pp.607–614.
Liu, X.L., Li, W.C. and Yin, G.H. (2012) The metallogenic system of porphyry-skarn type Cu-Mo (Au) polymetallic deposits in Geza island arc of Yunnan Province. Geology in China, v.39, pp.1007–1022(in Chinese).
Li, Y.R., Fan, Y.H. and Meng, Q. (2009) The Langgdu skarn Cu deposit in northwest Yunnnan. Yunnan Geology, v.37, pp.137–142(in Chinese).
Lu, H.Z., Liu, Y., Wang, C., et al. (2004) Mineralization and fluid inclusion study of the Shizhuyuan W-Sn-Bi-Mo-F skarn deposit, Hunan Province, China. Econ. Geol., v.98, pp.955–974.
Meinert, L.D., Hefton, K.K., Mayes, D., et al. (1997) Geology, zonation, and fluid evolution of the Big Gossan Cu-Au skarn deposit, Ertsberg district, Irian Jaya. Econ. Geol., v. 92, pp.509–534.
Meinert, L.D., Hedenquist, J.W., Satoh, H., et al. (2003) Formation of anhydrous and hydrous skarn in Cu-Au ore deposits by magmatic fluids. Econ. Geol., v.98, pp.147–156.
Meinert, L.D. (1982) Skarn, manto, and breccia pipe formation in sedimentary rocks of the Cananea mining district, Sonora, Mexico. Econ. Geol., v.77, pp.919–949.
Machel, H.G. (1987) Some aspects of diagenetic sulphate–hydrocarbon redox reactions. In: J.D. Marshall (Ed.), Diagenesis of sedimentary sequences. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ., v.36, pp.15–28.
Naden, J. and Shepherd, T.J. (1989) Role of methane and carbon dioxide in gold deposition. Nature, v.342, pp.793–795.
Ramboz, C., Schnapper, D. and Dubessy, J. (1985) The evolution of H2O-CO2-CH4 bearing fluid in a wolframite vein: Reconstruction from fluid inclusion studies. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, v.49, pp.205–219.
Ren, T., Zhong, H., Zhang, X.C., et al. (2013) Mineralogical characteristics of skarns in the Langdu skarn copper deposit, Zhongdian,Yunnan province. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, v.33, pp.278–286(in Chinese).
Ren, T., Zhong, H., Zhu, W.G., et al.(2011) Geochemical characteristics of the Langdu high-K intermediate-acid intrusive rocks in the Zhongdian area, Northwest Yunnan. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, v.31, pp.43–54(in Chinese).
Roedder, E. (1984) Fluid inclusions. Rev. Mineral., v.12, pp.12–45.
Rui, Z.Y., Zhao, Y.M., Wang, L.S., et al. (2003) Role of volatile components in formation of skarn and porphyry deposits. Mineral Deposits, v.22, pp.141–150 (in Chinese).
Shi, G.U., Tropper, P., CUI,W., et al. (2005) Methane (CH4)-bears fluid inclusions in the Myanmar jadeitite. Geochemical Jour., v.39, pp.503–516.
Wang, T.G., Ni, P., Wang, G.G., et al. (2008) Identification and significance of methane-rich fluid inclusions in Changba Pb- Zn deposit, Gansu province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, v.24, pp.2105–2112(in Chinese).
Welhan, J.A. (1988) Origin of the methane in hydrothermal system. Chemical Geol,, v.71, pp.183–198.
Wilde, A.R., Layer, P., Meruagh, T., et al. (2001) The giant Muruntau gold deposit: Geologic geochronologic, and fluid inclusion constraints on ore genesis. Econ. Geol., v.96, pp.633–644.
Xu, J.H., Shan, L.H., Ding, R.F., et al. (2008) Carbonic fluid inclusion assemblages and their geological significance at the Tiemurte lead-zinc deposit, Altay. Acta Petrologica Sinica, v.24, pp.2094–2104(in Chinese).
Yang, Y.Q., Hou, Z.Q., Huang, D.H., et al. (2002) Collision orogenic process and magmatic metallogenic system in Zhongdian arc. Acta Geosci. Sinica, v.23, pp.17–24(in Chinese).
Zeng, P.S., Wang, H.P., Mo, X.X., et al. (2004) Tectonic setting and prospects of porphyry copper deposits in Zhongdian island arc belt. Acta Geosci. Sinica, v.25, pp.535–540(in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, T., Ma, M. Identification and significance of CH4-rich fluid inclusions in Langdu skarn Cu deposit, Yunnan Province, China. J Geol Soc India 86, 482–488 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-015-0336-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-015-0336-y