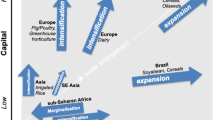
Abstract
There is growing concern that satisfying societal demand for food over coming decades will be increasingly challenging. Much of the debate centres on increasing food production which has always been–and remains–an important strategy to alleviate food insecurity. However, despite the fact that more than enough food is currently produced per capita to adequately feed the global population, about 925 million people remained food insecure in 2010. Meeting future demand will be further complicated by deleterious changes in climate and other environmental factors (collectively termed ‘global environmental change’, GEC). This paper lays out a case for a food systems approach to research the complex food security/GEC arena and provides a number of examples of how this can help. These include (i) providing a framework for structuring dialogues aimed at enhancing food security and identifying the range of actors and other interested parties who should be involved; (ii) integrating analyses of the full set of food system activities (i.e. producing, storing, processing, packaging, trading and consuming food) with those of the food security outcomes i.e. stability of food access, utilisation and availability, and all their nine elements (rather than only food production); (iii) helping to both assess the impacts of GEC on food systems and identify feedbacks to the earth system from food system activities; (iv) helping to identify intervention points for enhancing food security and analysing synergies and trade-offs between food security, ecosystem services and social welfare outcomes of different adaptation pathways; and (v) highlighting where new research is needed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adger, W. N. (2006). Vulnerability. Global Environmental Change, 16, 268–281.
Aggarwal, P. K., Joshi, P. K., Ingram, J. S. I., & Gupta, R. K. (2004). Adapting food systems of the Indo-Gangetic plains to global environmental change: Key information needs to improve policy formulation. Environmental Science & Policy, 7, 487–498.
Assimakopoulos, J. H., Kalivas, D. P., & Kollias, V. J. (2003). A GIS-based fuzzy classification for mapping the agricultural soils for N-fertilizers use. The Science of the Total Environment, 309(1–3), 19–33.
AusAID. (2004). Food security strategy (p. 16). Canberra: Commonwealth of Australia.
Bettazzi, F., Lucarelli, F., Palchetti, I., Berti, F., Marrazza, G., & Mascini, M. (2008). Disposable electrochemical DNA-array for PCR amplified detection of hazelnut allergens in foodstuffs. Analytica Chimica Acta, 614(1), 93–102.
Cash, D. W., Adger, W. N., Berkes, F., Garden, P., Lebel, L., Olsson, P., et al. (2006). Scale and cross-scale dynamics: Governance and Information in a Multilevel World. Ecology and Society, 11(2), 8.
CCAFS. (2009). Report 1: Climate change, agriculture and food security. A CGIAR challenge program, vol. 1 (p. 56). Rome and Paris: The Alliance of the CGIAR Centers and ESSP.
CCAFS Scenarios Team. (2010). Report on CCAFS Regional Scenarios Development for East Africa (p. 67). Copenhagen: CCAFS.
Challinor, A., Wheeler, T., Garforth, C., Craufurd, P., & Kassam, A. (2007). Assessing the vulnerability of food crop systems in Africa to climate change. Climatic Change, 83, 381–399.
CIBSE (2009). Energy efficiency in commercial kitchens (CIBSE Technical Memoranda 50). (pp. 64): Chartered Institution of Building Services Engineers.
Defra (2006). Food security and the UK: An evidence and analysis paper. Food Chain Analysis Group.
Dixit, A. (2003). Floods and vulnerability: Need to rethink flood management. Natural Hazards, 28(1), 155–179. doi:10.1023/a:1021134218121.
Dixon, J. (1999). A cultural economy model for studying food systems. Agriculture and Human Values, 16, 151–160.
Drimie, S., Arntzen, J., Dube, P., Ingram, J. S. I., Mano, R. T., Mataya, C., et al. (2011). Global environmental change and food systems in southern Africa: The dynamic challenges facing regional policy. Journal of Geography and Regional Planning, 4(4), 169–182.
Dupont, D. P., & Renzetti, S. (1998). Water use in the Canadian food processing industry. Canadian Journal of Agricultural Economics, 46, 1–10.
Eakin, H. (2010). What is vulnerable? In J. Ingram, P. Ericksen, & D. Liverman (Eds.), Security and global environmental change. London: Earthscan.
Edwards, J., Kleinschmit, J., Schoonover, H. (2009). Identifying our climate “foodprint”: Assessing and reducing the global warming impacts of food and agriculture in the U.S.: Institute for Agriculture and Trade Policy.
Environmental Investigation Agency (2010). Chilling facts: Supermarket Refrigeration Scandal Uncovered.
Ericksen, P. J. (2008a). Conceptualizing food systems for global environmental change research. Global Environmental Change, 18, 234–245.
Ericksen, P. J. (2008b). What is the vulnerability of a food system to global environmental change? Ecology and Society, 13(2).
Ericksen, P. J., Ingram, J. S. I., & Liverman, D. M. (2009). Food security and global environmental change: Emerging challenges. Environmental Science and Policy, 12(4), 373–377.
Ericksen, P. J., Stewart, B., Dixon, J., Barling, D., Loring, P., Anderson, M., et al. (2010). The value of a food system approach. In J. Ingram, P. Ericksen, & D. Liverman (Eds.), Security and global environmental change. London: Earthscan.
Ericksen, P. J., Stewart, B., Eriksen, S., Tschakert, P., Sabates-Wheeler, R., Hansen, J., et al. (2010). Adapting food systems. In J. Ingram, P. Ericksen, & D. Liverman (Eds.), Security and global environmental change. London: Earthscan.
ESF. (2009). European food systems in a changing world. Strasbourg: ESF-COST Forward Look Report.
EU (2011). Food security under threat: Global response needed. http://www.europarl.europa.eu/sides/getDoc.do?type=IM-PRESS&reference=20110216IPR13780&format=XML&language=EN. Accessed 17 February 2011.
FAO. (1996). Rome declaration and world food summit plan of action. Rome: FAO.
FAO. (2009). The State of Food Insecurity in the World (SOFI): Economic crises–impacts and lessons learned. Rome: FAO.
FAO (2010). The State of Food Insecurity in the World (SOFI): Addressing food insecurity in protracted crises. Rome.
Food Climate Research Network (2011). http://www.fcrn.org.uk/. Accessed 3 March 2011.
Foresight. (2011). The future of food and farming. Final project report. London: The Government Office for Science.
Fraser, E. D. G., Mabee, W., & Figge, F. (2005). A framework for assessing the vulnerability of food systems to future shocks. Futures, 37, 465–479.
GECAFS (2005). Science plan and implementation strategy. Earth System Science Partnership (IGBP, IHDP, WCRP, DIVERSITAS) Report No. 2 (pp. 36). Wallingford.
GECAFS (2006). A set of prototype Caribbean scenarios for research on global environmental change and regional food systems. (Vol. Report No. 2, pp. 62). Wallingford: GECAFS.
Gibson, C. C., Ostrom, E., & Ahn, T. K. (2000). The concept of scale and the human dimensions of global change: A survey. Ecological Economics, 32(2), 217–239.
Godfray, H. C. J., Beddington, J. R., Crute, I. R., Haddad, L., Lawrence, D., Muir, J. F., Pretty, J., Robinson, S., Thomas, S. M., Toulmin, C. (2010a). Food security: Feeding the world in 2050–Theme Issue September 2010.
Godfray, H. C. J., Beddington, J. R., Crute, I. R., Haddad, L., Lawrence, D., Muir, J. F., et al. (2010b). Food security: The challenge of feeding 9 billion people. Science, 327, 812–818.
Gregory, P. J., & Ingram, J. S. I. (2000). Global change and food and forest production: Future scientific challenges. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 82(1–3), 3–14.
Gregory, P. J., Ingram, J. S. I., Goudriaan, J., Hunt, T., Landsberg, J., Linder, S., et al. (1999). Managed production systems. In B. H. Walker, W. L. Steffen, J. Canadell, & J. S. I. Ingram (Eds.), The terrestrial biosphere and global change: Implications for natural and managed ecosystems (pp. 229–270). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Ingram, J. S. I. (2009). Food system concepts. In R. Rabbinge & A. Linneman (Eds.), ESF/COST forward look on European food systems in a changing world. Strasbourg: European Science Foundation.
Ingram, J. S. I., & Brklacich, M. (2002). Global Environmental Change and Food Systems (GECAFS). A new, interdisciplinary research project. Die Erde, 113, 427–435.
Ingram, J. S. I., Ericksen, P., & Liverman, D. (Eds.). (2010). Food security and global environmental change. London: Earthscan.
Ingram, J. S. I., Gregory, P. J., & Izac, A.-M. (2008). The role of agronomic research in climate change and food security policy. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 126, 4–12.
Ingram, J. S. I., & Izac, A.-M. (2010). Undertaking research at the regional level. In J. Ingram, P. Ericksen, & D. Liverman (Eds.), Security and global environmental change. London: Earthscan.
Ingram, J. S. I., Steffen, W. L., Canadell, J. (2007). Envisioning earth system science for societal needs: The development of Joint Projects and the Earth System Science Partnership (ESSP). GECAFS Working Paper 6 (pp. 10). Oxford: GECAFS.
IPCC. (2007). In M. Parry, O. Canziani, J. Palutikof, P. van der Linden, & C. Hanson (Eds.), Climate change 2007: Impacts, adaptation and vulnerability. Contribution of working group II to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Jat, M. L., Chandna, P., Gupta, R., Sharma, S. K., & Gill, M. A. (2006). Laser land leveling: A precursor technology for resource conservation. Rice-wheat consortium technical bulletin series 7 (p. 48). New Delhi: Rice-Wheat Consortium for the Indo-Gangetic Plains.
Kelepouris, T., Pramatari, K., & Doukidis, G. (2007). RFID-enabled traceability in the food supply chain. Industrial Management & Data Systems, 107(2), 183–200.
Kroyer, G. T. (1995). Impact of food processing on the environment—an overview. Lebensmittel-Wissenschaft und Technologie, 28(6), 547–552.
Liverman, D., & Ingram, J. (2010). Why regions? In J. Ingram, P. Ericksen, & D. Liverman (Eds.), Security and global environmental change. London: Earthscan.
Liverman, D., & Kapadia, K. (2010). Food systems and the global environment: An overview. In J. Ingram, P. Ericksen, & D. Liverman (Eds.), Security and global environmental change. London: Earthscan.
Lobell, D. B., Burke, M. B., Tebaldi, C., Mastrandrea, M. D., Falcon, W. P., & Naylor, R. L. (2008). Prioritizing climate change adaptation needs for food security in 2030. Science, 319(5863), 607–610. doi:10.1126/science.1152339.
Lobell, D. B., Schlenker, W., & Costa-Roberts, J. (2011). Climate trends and global crop production since 1980. Science, 1. doi:10.1126/science.1204531.
Lyutse, S. (2010). The one billion ton opportunity Cont’d–part IV: Diet and food waste. Switchboard: Natural resources defense council staff blog (vol. 2010): Natural Resources Defense Council.
MA (2005a). Scenarios, volume 2. In S. R. Carpenter, P. L. Pingali, E. M. Bennett, M. B. Zurek (Eds.), The millennium ecosystem assessment. Ecosystems and human well-being: Island Press
MA (2005b). Volume 1: Current state and trends. In Ecosystems and human well-being. Washington DC: Island Press
Maxwell, S., & Slater, R. (2003). Food policy old and new. Development Policy Review, 21(5–6), 531–553.
McMichael, P. (Ed.). (1994). The global restructuring of agro-food systems. New York: Cornell University Press.
Misselhorn, A., Eakin, H., Devereux, S., Drimie, S., Msangi, S., Simelton, E., et al. (2010). Vulnerability to what? In J. Ingram, P. Ericksen, & D. Liverman (Eds.), Security and global environmental change. London: Earthscan.
Pálsson, G., Avril, B., Crumley, C., Hackmann, H., Holm, P., Ingram, J., et al. (2011). Challenges of the anthropocene: Contributions from Social Sciences and Humanities for the Changing Human Condition. ESF/COST RESCUE–Task Force on “Science Questions”. Strasbourg: ESF.
Parfitt, J., Barthel, M., & Macnaughton, S. (2010). Food waste within food supply chains: Quantification and potential for change to 2050. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B, 365, 3065–3081. doi:10.1098/rstb.2010.0126.
Parry, M. L., Rosenzweig, C., & Livermore, M. (2005). Climate change, global food supply and risk of hunger. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society Biological Sciences, 360(1463), 2125–2138.
Rockström, J., Steffen, W., Noone, K., Persson, A. F., Stuart Chapin, I., Lambin, E. F., et al. (2009). A safe operating space for humanity. Nature, 461, 472–475.
Science (2010). Special issue 12 February 2010: Food Security.
Shaw, D. J. (2007). World food security: A history since 1945. New York: Palgrave MacMillan.
Sobal, J., Khan, L. K., & Bisogni, C. (1998). A conceptual model of the food and nutrition system. Social Science & Medicine, 47, 853–863.
Spedding, A. (2007). RuSource briefing 500: Food Miles.
Spring, Ú. O. (2009). Food as a new human and livelihood security challenge. In H. G. Brauch, J. Grin, C. Mesjasz, P. Kameri-Mbote, N. C. Behera, B. Chourou, & H. Krummenacher (Eds.), Facing global environmental change (vol. 4, pp. 471–500, Hexagon Series on Human and Environmental Security and Peace): Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Stamoulis, K., & Zezza, A. (2003). A conceptual framework for national agricultural, rural development, and food security strategies and policies. ESA Working Paper Number 03–17. Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization.
Termeer, C. J. A. M., Dewulf, A., & van Lieshout, M. (2010). Disentangling scale approaches in governance research: Comparing monocentric, multilevel, and adaptive governance. Ecology and Society, 15(4).
Tovey, H. (1997). Food, environmentalism and rural sociology: On the organic farming movement in Ireland. Sociologia Ruralis, 37(1), 21–37. doi:10.1111/1467-9523.00034.
U.S. Government (2010). Feed the future guide. Feed the Future Initiative, United States Government.
UNEP (2007). Global environment outlook 4: Environment for Development.
Wisconsin WIC Program (2007). Food security in the Wisconsin WIC population. Wisconsin Department of Health and Family Services.
Wood, S., Ericksen, P., Stewart, B., Thornton, P., & Anderson, M. (2010). Lessons learned from international assessments. In J. Ingram, P. Ericksen, & D. Liverman (Eds.), Security and global environmental change. London: Earthscan.
World Bank (2011). Food Price Watch April 2011. Poverty Reduction and Equity Group, Poverty Reduction and Economic Management (PREM) Network.
Acknowledgements
This paper is a contribution to the ESSP Joint Project “Global Environmental Change and Food Systems” (GECAFS). The author is very grateful to Dr Polly Ericksen for valuable comments on an earlier draft of this paper; to Anita Ghosh for help in sourcing references; to the Balaton Group for inspiring the discussion on food system interactions with planetary boundaries; to the many scientists and others who have contributed to GECAFS; to two anonymous reviewers; and to the UK’s Natural Environment Research Council for funding the GECAFS International Project Office.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ingram, J. A food systems approach to researching food security and its interactions with global environmental change. Food Sec. 3, 417–431 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12571-011-0149-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12571-011-0149-9