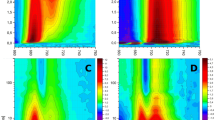
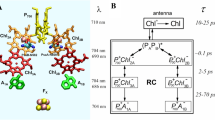
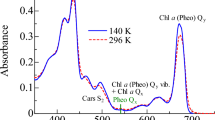
Abstract
This review analyzes new data on the mechanism of ultrafast reactions of primary charge separation in photosystem I (PS I) of cyanobacteria obtained in the last decade by methods of femtosecond absorption spectroscopy. Cyanobacterial PS I from many species harbours 96 chlorophyll a (Chl a) molecules, including six specialized Chls denoted Chl1A/Chl1B (dimer P700, or PAPB), Chl2A/Chl2B, and Chl3A/Chl3B arranged in two branches, which participate in electron transfer reactions. The current data indicate that the primary charge separation occurs in a symmetric exciplex, where the special pair P700 is electronically coupled to the symmetrically located monomers Chl2A and Chl2B, which can be considered together as a symmetric exciplex Chl2APAPBChl2B with the mixed excited (Chl2APAPBChl2B)* and two charge-transfer states P700+Chl2A− and P700+Chl2B−. The redistribution of electrons between the branches in favor of the A-branch occurs after reduction of the Chl2A and Chl2B monomers. The formation of charge-transfer states and the symmetry breaking mechanisms were clarified by measuring the electrochromic Stark shift of β-carotene and the absorption dynamics of PS I complexes with the genetically altered Chl2B or Chl2A monomers. The review gives a brief description of the main methods for analyzing data obtained using femtosecond absorption spectroscopy. The energy levels of excited and charge-transfer intermediates arising in the cyanobacterial PS I are critically analyzed.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adolphs J, Müh F, Madjet MEA et al (2010) Structure-based calculations of optical spectra of photosystem I suggest an asymmetric light-harvesting process. J Am Chem Soc 132:3331–3343. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja9072222
Akhtar P, Lambrev PH (2020) On the spectral properties and excitation dynamics of long-wavelength chlorophylls in higher-plant photosystem I. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1861:148274. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BBABIO.2020.148274
Akhtar P, Zhang C, Liu Z et al (2018) Excitation transfer and trapping kinetics in plant photosystem I probed by two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy. Photosynth Res 135:239–250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-017-0427-2
Akhtar P, Caspy I, Nowakowski PJ et al (2021) Two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy of a minimal photosystem I complex reveals the rate of primary charge separation. J Am Chem Soc 143:14601–14612. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.1c05010
Badshah SL, Sun J, Mula S et al (2018) Mutations in algal and cyanobacterial photosystem I that independently affect the yield of initial charge separation in the two electron transfer cofactor branches. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1859:42–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2017.10.003
Beauregard M, Martin I, Holzwarth AR (1991) Kinetic modelling of exciton migration in photosynthetic systems. (1) effects of pigment heterogeneity and antenna topography on exciton kinetics and charge separation yields. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1060:271–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0005-2728(05)80317-2
Beechen JM, Ameloot M (1985) Global and target analysis of complex decay phenomena. Instrum Sci Technol 14:379–402. https://doi.org/10.1080/10739148508543585
Berera R, van Grondelle R, Kennis JTM (2009) Ultrafast transient absorption spectroscopy: principles and application to photosynthetic systems. Photosynth Res 101:105–118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-009-9454-y
Brecht M, Radics V, Nieder JB et al (2008) Red antenna states of photosystem I from Synechocystis PCC 6803. Biochemistry 47:5536–5543. https://doi.org/10.1021/BI800121T/ASSET/IMAGES/BI800121T.SOCIAL.JPEG_V03
Brettel K (1997) Electron transfer and arrangement of the redox cofactors in photosystem I. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1318:322–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0005-2728(96)00112-0
Brettel K, Leibl W (2001) Electron transfer in photosystem I. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1507:100–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0005-2728(01)00202-X
Brüggemann B, Sznee K, Novoderezhkin V et al (2004) From structure to dynamics: modeling Exciton dynamics in the photosynthetic antenna PS1. J Phys Chem B 108:13536–13546. https://doi.org/10.1021/JP0401473
Byrdin M, Rimke I, Schlodder E et al (2000) Decay kinetics and quantum yields of fluorescence in photosystem I from Synechococcus elongatus with P700 in the reduced and oxidized state: are the kinetics of excited state decay trap-limited or transfer-limited? Biophys J 79:992–1007. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(00)76353-3
Byrdin M, Jordan P, Krauss N et al (2002) Light harvesting in photosystem I: modeling based on the 2.5-Å structure of photosystem I from Synechococcus elongatus. Biophys J 83:433–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(02)75181-3
Chauvet A, Dashdorj N, Golbeck JH et al (2012) Spectral resolution of the primary electron acceptor A0 in photosystem I. J Phys Chem B 116:3380–3386. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp211246a
Cheng Y-C, Mančal T, Engel GS et al (2007) Evidence for wavelike energy transfer through quantum coherence in photosynthetic systems. Nature 446:782–786. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05678
Chenu A, Scholes GD (2015) Coherence in energy transfer and photosynthesis. Annu Rev Phys Chem 66:69–96. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-physchem-040214-121713
Cherepanov DA, Krishtalik LI, Mulkidjanian AY (2001) Photosynthetic electron transfer controlled by protein relaxation: analysis by Langevin stochastic approach. Biophys J 80:1033–1049. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(01)76084-5
Cherepanov DA, Shelaev IV, Gostev FE et al (2017a) Mechanism of adiabatic primary electron transfer in photosystem I: femtosecond spectroscopy upon excitation of reaction center in the far-red edge of the Q Y band. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1858:895–905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2017.08.008
Cherepanov DA, Shelaev IV, Gostev FE et al (2017b) Excitation of photosystem i by 760 nm femtosecond laser pulses: transient absorption spectra and intermediates. J Phys B Atomic Mol Phys 50:174001. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6455/aa824b
Cherepanov DA, Milanovsky GE, Gopta OA et al (2018) Electron–phonon coupling in Cyanobacterial photosystem I. J Phys Chem B 122:7943–7955. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcb.8b03906
Cherepanov DA, Shelaev IV, Gostev FE et al (2020a) Symmetry breaking in photosystem I: ultrafast optical studies of variants near the accessory chlorophylls in the A- and B-branches of electron transfer cofactors. Photochem Photobiol Sci 20:1209–1227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43630-021-00094-y
Cherepanov DA, Brady NG, Shelaev IV et al (2020b) PSI-SMALP, a detergent-free Cyanobacterial photosystem I, reveals faster femtosecond photochemistry. Biophys J 118:337–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2019.11.3391
Cherepanov DA, Shelaev IV, Gostev FE et al (2020c) Generation of ion-radical chlorophyll states in the light-harvesting antenna and the reaction center of cyanobacterial photosystem I. Photosynth Res 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-020-00731-0
Cherepanov DA, Shelaev IV, Gostev FE et al (2020d) Evidence that chlorophyll f functions solely as an antenna pigment in far-red-light photosystem I from Fischerella thermalis PCC 7521. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2020.148184
Cherepanov DA, Shelaev IV, Gostev FE et al (2021) Primary charge separation within the structurally symmetric tetrameric Chl2APAPBChl2B chlorophyll exciplex in photosystem I. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 217:112154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2021.112154
Cohen RO, Shen G, Golbeck JH et al (2004) Evidence for asymmetric Electron transfer in Cyanobacterial photosystem I: analysis of a methionine-to-Leucine mutation of the ligand to the primary Electron acceptor A0. Biochemistry 43:4741–4754. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi035633f
Dashdorj N, Xu W, Martinsson P et al (2004) Electrochromic shift of chlorophyll absorption in photosystem I from Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803: a probe of optical and dielectric properties around the secondary electron acceptor. Biophys J 86:3121–3130. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(04)74360-X
Dashdorj N, Xu W, Cohen RO et al (2005) Asymmetric electron transfer in cyanobacterial photosystem I: charge separation and secondary electron transfer dynamics of mutations near the primary electron acceptor A0. Biophys J 88:1238–1249. https://doi.org/10.1529/biophysj.104.050963
Donato MD, Stahl AD, Van Stokkum IHM et al (2011) Cofactors involved in light-driven charge separation in photosystem I identified by subpicosecond infrared spectroscopy. Biochemistry 50:480–490. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi101565w
Esbensen KH, Geladi P (2009) Principal component analysis: concept, geometrical interpretation, mathematical background, algorithms, history, practice. In: Comprehensive Chemometrics. Elsevier, pp 211–226
Fromme P, Jordan P, Krauß N (2001) Structure of photosystem I. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1507:5–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0005-2728(01)00195-5
Fuller FD, Pan J, Gelzinis A et al (2014) Vibronic coherence in oxygenic photosynthesis. Nat Chem 6:706–711. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.2005
Giaimo JM, Gusev AV, Wasielewski MR (2002) Excited-state symmetry breaking in cofacial and linear dimers of a green perylenediimide chlorophyll analogue leading to ultrafast charge separation. J Am Chem Soc 124:8530–8531. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja026422l
Gibasiewicz K, Ramesh VM, Melkozernov AN et al (2001) Excitation dynamics in the core antenna of PS I from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii CC 2696 at room temperature. J Phys Chem B 105:11498–11506. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp012089g
Gibasiewicz K, Ramesh VM, Lin S et al (2003) Excitonic interactions in wild-type and mutant PSI reaction centers. Biophys J 85:2547–2559. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(03)74677-3
Giera W, Gibasiewicz K, Ramesh VM et al (2009) Electron transfer from A0̄ to A1 in photosystem i from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii occurs in both the a and B branch with 25-30-ps lifetime. Phys Chem Chem Phys 11:5186–5191. https://doi.org/10.1039/b822938d
Giera W, Ramesh VM, Webber AN et al (2010) Effect of the P700 pre-oxidation and point mutations near A0 on the reversibility of the primary charge separation in photosystem I from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1797:106–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2009.09.006
Giera W, Szewczyk S, McConnell MD et al (2018) Uphill energy transfer in photosystem I from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Time-resolved fluorescence measurements at 77 K. Photosynth Res 137:321–335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-018-0506-z
Gisriel C, Shen G, Kurashov V et al (2020) The structure of photosystem I acclimated to far-red light illuminates an ecologically important acclimation process in photosynthesis. Sci Adv 6:eaay6415. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aay6415
Gobets B, Van Grondelle R (2001) Energy transfer and trapping in photosystem I. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1507:80–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0005-2728(01)00203-1
Gobets B, Kennis JTM, Ihalainen JA et al (2001a) Excitation energy transfer in dimeric light harvesting complex I: a combined streak-camera/fluorescence upconversion study. J Phys Chem B 105:10132–10139. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp011901c
Gobets B, van Stokkum IH, Rögner M et al (2001b) Time-resolved fluorescence emission measurements of photosystem I particles of various cyanobacteria: a unified compartmental model. Biophys J 81:407–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(01)75709-8
Golbeck JH, Parrett KG, McDermott AE (1987) Photosystem I charge separation in the absence of center a and B. III. Biochemical characterization of a reaction center particle containing P-700 and FX. BBA - Bioenerg 893:149–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-2728(87)90034-X
Gorka M, Cherepanov DA, Semenov AY, Golbeck JH (2020) Control of electron transfer by protein dynamics in photosynthetic reaction centers. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 55:425–468. https://doi.org/10.1080/10409238.2020.1810623
Gorka M, Baldansuren A, Malnati A et al (2021a) Shedding light on primary donors in photosynthetic reaction centers. Front Microbiol 12:2776. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.735666
Gorka M, Charles P, Kalendra V et al (2021b) A dimeric chlorophyll electron acceptor differentiates type I from type II photosynthetic reaction centers. iScience 24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2021b.102719
Goyal A, Szewczyk S, Burdziński G et al (2022) Competition between intra-protein charge recombination and electron transfer outside photosystem I complexes used for photovoltaic applications. Photochem Photobiol Sci 21:319–336. https://doi.org/10.1007/S43630-022-00170-X/FIGURES/7
Guergova-Kuras M, Boudreaux B, Joliot A et al (2001) Evidence for two active branches for electron transfer in photosystem I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:4437–4442. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.081078898
Hastings G, Kleinherenbrink FAMM, Lin S et al (1994) Observation of the reduction and Reoxidation of the primary Electron acceptor in photosystem I. Biochemistry 33:3193–3200. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00177a008
Hastings G, Kleinherenbrink FAM, Lin S, Blankenship RE (2002) Time-resolved fluorescence and absorption spectroscopy of photosystem I. Biochemistry 33:3185–3192. https://doi.org/10.1021/BI00177A007
Heimdal J, Jensen KP, Devarajan A, Ryde U (2007) The role of axial ligands for the structure and function of chlorophylls. J Biol Inorg Chem 12:49–61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00775-006-0164-z
Herascu N, Hunter MS, Shafiei G et al (2016) Spectral hole burning in Cyanobacterial photosystem i with P700 in oxidized and neutral states. J Phys Chem B 120:10483–10495. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcb.6b07803
Holzwarth AR, Schatz G, Brock H, Bittersmann E (1993) Energy transfer and charge separation kinetics in photosystem I: part 1: picosecond transient absorption and fluorescence study of cyanobacterial photosystem I particles. Biophys J 64:1813–1826. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81552-2
Holzwarth AR, Müller MG, Niklas J, Lubitz W (2005) Charge recombination fluorescence in photosystem I reaction centers from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Phys Chem B 109:5903–5911. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp046299f
Holzwarth AR, Müller MG, Niklas J, Lubitz W (2006) Ultrafast transient absorption studies on photosystem I reaction centers from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. 2: mutations near the P700 reaction center chlorophylls provide new insight into the nature of the primary electron donor. Biophys J 90:552–565. https://doi.org/10.1529/biophysj.105.059824
Ihalainen JA, Rätsep M, Jensen PE et al (2003) Red spectral forms of chlorophylls in green plant PSI- a site-selective and high-pressure spectroscopy study. J Phys Chem B 107:9086–9093. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp034778t
Ihalainen JA, Van Stokkum IHM, Gibasiewicz K et al (2005) Kinetics of excitation trapping in intact photosystem I of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1706:267–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BBABIO.2004.11.007
Ishikita H, Knapp E-W (2003) Redox potential of quinones in both electron transfer branches of photosystem I. J Biol Chem 278:52002–52011. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M306434200
Ishikita H, Saenger W, Biesiadka J et al (2006a) How photosynthetic reaction centers control oxidation power in chlorophyll pairs P680, P700, and P870. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:9855–9860. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0601446103
Ishikita H, Stehlik D, Golbeck JH, Knapp E-W (2006b) Electrostatic influence of PsaC protein binding to the PsaA/PsaB heterodimer in photosystem I. Biophys J 90:1081–1089. https://doi.org/10.1529/biophysj.105.069781
Jordan P, Fromme P, Witt HT et al (2001) Three-dimensional structure of cyanobaoterial photosystem I at 2.5 Å resolution. Nature 411:909–917. https://doi.org/10.1038/35082000
Khyasudeen MF, Nowakowski PJ, Nguyen HL et al (2019) Studying the spectral diffusion dynamics of chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b using two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy. Chem Phys 527:110480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemphys.2019.110480
Kleinherenbrink FAM, Hastings G, Blankenship RE, Wittmershaus BP (1994) Delayed fluorescence from Fe-S type photosynthetic reaction centers at low redox potential. Biochemistry 33:3096–3105. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00176a044
Kramer T, Noack M, Reimers JR et al (2018) Energy flow in the photosystem I supercomplex: comparison of approximative theories with DM-HEOM. Chem Phys 515:262–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemphys.2018.05.028
Krishtalik LII (2008) The surface potential of solvent and the intraphase pre-existing potential. Russ J Electrochem 44:43–49. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193508010072
Kumazaki S, Ikegami I, Furusawa H et al (2001) Observation of the excited state of the primary Electron donor chlorophyll (P700) and the ultrafast charge separation in the spinach photosystem I reaction center. J Phys Chem B 105:1093–1099. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp003122m
Kurashov V, Gorka M, Milanovsky GE et al (2018) Critical evaluation of electron transfer kinetics in P700–FA/FB, P700–FX, and P700–A1 photosystem I core complexes in liquid and in trehalose glass. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1859:1288–1301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2018.09.367
Laible PD, Zipfel W, Owens TG (1994) Excited state dynamics in chlorophyll-based antennae: the role of transfer equilibrium. Biophys J 66:844–860. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80861-6
Lewandowski A, Waligora L, Galinski M (2009) Ferrocene as a reference redox couple for aprotic ionic liquids. Electroanalysis 21:2221–2227. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.200904669
Li Y, Van Der Est A, Lucas MG et al (2006) Directing electron transfer within photosystem I by breaking H-bonds in the cofactor branches. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:2144–2149. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0506537103
Madjet ME-A, Müh F, Renger T (2009) Deciphering the influence of short-range electronic couplings on optical properties of molecular dimers: application to “special pairs” in photosynthesis. J Phys Chem B 113:12603–12614. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp906009j
Malavath T, Caspy I, Netzer-El SY et al (2018) Structure and function of wild-type and subunit-depleted photosystem I in Synechocystis. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1859:645–654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2018.02.002
Malferrari M, Savitsky A, Lubitz W et al (2016) Protein immobilization capabilities of sucrose and Trehalose glasses: the effect of protein/sugar concentration unraveled by high-field EPR. J Phys Chem Lett 7:4871–4877. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.6b02449
Mazor Y, Nataf D, Toporik H, Nelson N (2014) Crystal structures of virus-like photosystem I complexes from the mesophilic cyanobacterium Synechocystis PCC 6803. Elife 3:e01496. https://doi.org/10.7554/elife.01496
Mazor Y, Borovikova A, Nelson N (2017) The structure of plant photosystem I super-complex at 2.8A resolution. Nat Plants 3:17014. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.07433
McMahon BH, Müller JD, Wraight CA, Nienhaus GU (1998) Electron transfer and protein dynamics in the photosynthetic reaction center. Biophys J 74:2567–2587. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(98)77964-0
Medvedev ES, Kotelnikov AI, Goryachev NS et al (2006) Protein dynamics control of electron transfer in reaction centers from Rps. Viridis. Mol Simul 32:735–750. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927020600880802
Melkozernov AN (2001) Excitation energy transfer in photosystem I from oxygenic organisms. Photosynth Res 70:129–153
Melkozernov AN, Lin S, Blankenship RE (2000a) Excitation dynamics and heterogeneity of energy equilibration in the Core antenna of photosystem I from the Cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Biochemistry 39:1489–1498. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi991644q
Melkozernov AN, Lin S, Blankenship RE (2000b) Femtosecond transient spectroscopy and Excitonic interactions in photosystem I. J Phys Chem B 104:1651–1656. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp993257w
Melkozernov AN, Lin S, Schmid VHR et al (2000c) Ultrafast excitation dynamics of low energy pigments in reconstituted peripheral light-harvesting complexes of photosystem I. FEBS Lett 471:89–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-5793(00)01370-3
Melkozernov AN, Lin S, Blankenship RE, Valkunas L (2001) Spectral inhomogeneity of photosystem I and its influence on excitation equilibration and trapping in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 at 77 K. Biophys J 81:1144–1154. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(01)75771-2
Melkozernov AN, Barber J, Blankenship RE (2006) Light harvesting in photosystem I supercomplexes. Biochemistry 45:331–345. https://doi.org/10.1021/BI051932O/ASSET/IMAGES/BI051932O.SOCIAL.JPEG_V03
Milanovsky GE, Ptushenko VV, Golbeck JH et al (2014) Molecular dynamics study of the primary charge separation reactions in photosystem I: effect of the replacement of the axial ligands to the electron acceptor A0. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1837:1472–1483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2014.03.001
Milanovsky GE, Petrova AA, Cherepanov DA, Semenov AY (2017) Kinetic modeling of electron transfer reactions in photosystem I complexes of various structures with substituted quinone acceptors. Photosynth Res 133:185–199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-017-0366-y
Milanovsky G, Gopta O, Petrova A et al (2019) Multiple pathways of charge recombination revealed by the temperature dependence of electron transfer kinetics in cyanobacterial photosystem I. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1860:601–610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2019.06.008
Molotokaite E, Remelli W, Casazza AP et al (2017) Trapping dynamics in photosystem I-light harvesting complex I of higher plants is governed by the competition between excited state diffusion from low energy states and photochemical charge separation. J Phys Chem B 121:9816–9830. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcb.7b07064
Müller MG, Niklas J, Lubitz W, Holzwarth AR (2003) Ultrafast transient absorption studies on photosystem I reaction centers from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. 1. A new interpretation of the energy trapping and early Electron transfer steps in photosystem I. Biophys J 85:3899–3922. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-3495(03)74804-8
Müller MG, Slavov C, Luthra R et al (2010) Independent initiation of primary electron transfer in the two branches of the photosystem I reaction center. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:4123–4128. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0905407107
Nadler W, Marcus RA (1987) Dynamical effects in electron transfer reactions. II. Numerical solution. J Chem Phys 86:3906–3924. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.451951
Nelson N (2013) Evolution of photosystem i and the control of global enthalpy in an oxidizing world. Photosynth Res 116:145–151. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-013-9902-6
Nürnberg DJ, Morton J, Santabarbara S et al (2018) Photochemistry beyond the red limit in chlorophyll f–containing photosystems. Science 360(80):1210–1213. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aar8313
Owens TG, Webbt SP, Mets L et al (1987) Antenna size dependence of fluorescence decay in the core antenna of photosystem I: estimates of charge separation and energy transfer rates. Proc Natl Acad Sci 84:1532–1536. https://doi.org/10.1073/PNAS.84.6.1532
Palazzo G, Mallardi A, Hochkoeppler A et al (2002) Electron transfer kinetics in photosynthetic reaction centers embedded in trehalose glasses: trapping of conformational substates at room temperature. Biophys J 82:558–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(02)75421-0
Pålsson L-OO, Flemming C, Gobets B et al (1998) Energy transfer and charge separation in photosystem I: P700 oxidation upon selective excitation of the long-wavelength antenna chlorophylls of Synechococcus elongatus. Biophys J 74:2611–2622. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(98)77967-6
Parrett KG, Mehari T, Warren PG, Golbeck JH (1989) Purification and properties of the intact P-700 and Fx-containing photosystem I core protein. Biochim Biophys Acta 973:324–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0005-2728(89)80439-6
Pawlowicz NP, Groot ML, Van Stokkum IHM et al (2007) Charge separation and energy transfer in the photosystem II core complex studied by femtosecond midinfrared spectroscopy. Biophys J 93:2732–2742. https://doi.org/10.1529/biophysj.107.105452
Pleskov YV (1987) Comments on “the absolute potential of a standard hydrogen electrode: a new estimate” by H. Reiss and a. Heller J Phys Chem 91:1691–1692. https://doi.org/10.1021/j100290a081
Proppe AH, Li YC, Aspuru-Guzik A et al (2020) Bioinspiration in light harvesting and catalysis. Nat Rev Mater 511(5):828–846. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41578-020-0222-0
Provencher SW (1976) An eigenfunction expansion method for the analysis of exponential decay curves. J Chem Phys 64:2772–2777. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.432601
Provencher SW (1982) CONTIN: a general purpose constrained regularization program for inverting noisy linear algebraic and integral equations. Comput Phys Commun 27:229–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/0010-4655(82)90174-6
Ptushenko VV, Cherepanov DA, Krishtalik LI, Semenov AY (2008) Semi-continuum electrostatic calculations of redox potentials in photosystem I. Photosynth Res 97:55–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-008-9309-y
Ramesh VM, Gibasiewicz K, Lin S et al (2004) Bidirectional electron transfer in photosystem I: accumulation of A0- in a-side or B-side mutants of the axial ligand to chlorophyll A0. Biochemistry 43:1369–1375. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi0354177
Ramesh VM, Gibasiewicz K, Lin S et al (2007) Replacement of the methionine axial ligand to the primary electron acceptor A0 slows the A0- reoxidation dynamics in photosystem I. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1767:151–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2006.12.013
Rätsep M, Johnson TW, Chitnis PR, Small GJ (2000) The red-absorbing chlorophyll a antenna states of photosystem I: a hole-burning study of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 and its mutants. J Phys Chem B 104:836–847. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp9929418
Renaud N, Powell D, Zarea M et al (2013) Quantum interferences and electron transfer in photosystem i. J Phys Chem A 117:5899–5908. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp308216y
Santabarbara S, Kuprov I, Fairclough WV et al (2005) Bidirectional electron transfer in photosystem I: determination of two distances between P700+ and A1- in spin-correlated radical pairs. Biochemistry 44:2119–2128. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi048445d
Santabarbara S, Kuprov I, Poluektov O et al (2010) Directionality of electron-transfer reactions in photosystem i of prokaryotes: universality of the bidirectional electron-transfer model. J Phys Chem B 114:15158–15171. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp1044018
Savikhin S, Jankowiak R (2014) Mechanism of primary charge separation in photosynthetic reaction centers. In: Golbeck J, van der Est A (eds) The biophysics of photosynthesis. Springer, New York, pp 193–240
Savikhin S, Xu W, Soukoulis V et al (1999) Ultrafast primary processes in photosystem I of the Cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Biophys J 76:3278–3288. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(99)77480-1
Savikhin S, Xu W, Chitnis PR, Struve WS (2000) Ultrafast primary processes in PS I from Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803: roles of P700 and A0. Biophys J 79:1573–1586. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(00)76408-3
Savikhin S, Xu W, Martinsson P et al (2001) Kinetics of charge separation and A0- → A1 Electron transfer in photosystem I reaction centers. Biochemistry 40:9282–9290. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi0104165
Searle GFW, Tamkivi R, Van Hoek A, Schaafsma TJ (1988) Temperature dependence of antennae chlorophyll fluorescence kinetics in photosystem I reaction Centre protein. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans 2 Mol Chem Phys:315–327. https://doi.org/10.1039/F29888400315
Segtnan VH, Šašić Š, Isaksson T, Ozaki Y (2001) Studies on the structure of water using two-dimensional near-infrared correlation spectroscopy and principal component analysis. Anal Chem 73:3153–3161. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac010102n
Shelaev IV, Gostev FE, Mamedov MD et al (2010) Femtosecond primary charge separation in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 photosystem I. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1797:1410–1420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2010.02.026
Shinkarev V (2006) Functional modeling of Electron transfer in photosynthetic reaction centers. Photosyst I Light PlastocyaninFerredoxin Oxidoreductase 611–637. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-4256-0_36
Shuvalov VA, Yakovlev AG, Vasilieva LG, Shkuropatov AY (2007) Primary charge separation between P700* and the primary Electron acceptor complex a-A0: A comparison with bacterial reaction centers. In: Golbeck JH (ed) Photosystem I. Springer, Netherlands, pp 291–300
Silori Y, Chawla S, De AK (2020) Unravelling the role of water in ultrafast excited-state relaxation dynamics within Nano-architectures of chlorophyll a. ChemPhysChem 21:1908–1917. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphc.202000487
Slavov C, Ballottari M, Morosinotto T et al (2008) Trap-limited charge separation kinetics in higher plant photosystem i complexes. Biophys J 94:3601–3612. https://doi.org/10.1529/BIOPHYSJ.107.117101
Smitienko OA, Feldman TB, Petrovskaya LE et al (2021) Comparative femtosecond spectroscopy of primary photoreactions of Exiguobacterium sibiricum rhodopsin and Halobacterium salinarum Bacteriorhodopsin. J Phys Chem B. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcb.0c07763
Steinbach PJ, Ionescu R, Robert Matthews C (2002) Analysis of kinetics using a hybrid maximum-entropy/nonlinear-least-squares method: application to protein folding. Biophys J 82:2244–2255. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(02)75570-7
Sumi H, Marcus RA (1986) Dynamical effects in electron transfer reactions. J Chem Phys 84:4894–4914. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.449978
Sun J, Hao S, Radle M et al (2014) Evidence that histidine forms a coordination bond to the A0A and A0B chlorophylls and a second H-bond to the A1A and A1B phylloquinones in M688HPsaA and M668HPsaB variants of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1837:1362–1375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2014.04.004
Torres RA, Lovell T, Noodleman L, Case DA (2003) Density functional and reduction potential calculations of Fe4S4 clusters. J Am Chem Soc 125:1923–1936. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0211104
Trissl HW (1993) (1993) long-wavelength absorbing antenna pigments and heterogeneous absorption bands concentrate excitons and increase absorption cross section. Photosynth Res 353(35):247–263. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00016556
Tzeng DY, Berns RS (2005) A review of principal component analysis and its applications to color technology. Color Res Appl 30:84–98
Van Stokkum IHM, Larsen DS, Van Grondelle R (2004) Global and target analysis of time-resolved spectra. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1657:82–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2004.04.011
Wall ME, Rechtsteiner A, Rocha LM (2005) Singular value decomposition and principal component analysis. A Pract Approach to Microarray Data Anal 91–109. https://doi.org/10.1007/0-306-47815-3_5
Warshel A, Sharma PK, Kato M, Parson WW (2006) Modeling electrostatic effects in proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta - Proteins Proteomics 1764:1647–1676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2006.08.007
White NTH, Beddard GS, Thorne JRG et al (1996) Primary charge separation and energy transfer in the photosystem i reaction center of higher plants. J Phys Chem 100:12086–12099. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp9604709
Yan YJ, Mukamel S (1990) Femtosecond pump-probe spectroscopy of polyatomic molecules in condensed phases. Phys Rev A 41:6485–6504. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.41.6485
Yang M, Damjanović A, Vaswani HM, Fleming GR (2003) Energy transfer in photosystem I of cyanobacteria Synechococcus elongatus: model study with structure-based semi-empirical Hamiltonian and experimental spectral density. Biophys J 85:140–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(03)74461-0
Yin S, Dahlbom MG, Canfield PJ et al (2007) Assignment of the Qy, absorption spectrum of photosystem-I from Thermosynechococcus elongatus based on CAM-B3LYP calculations at the PW91-optimized protein structure. J Phys Chem B 111:9923–9930. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp070030p
Zamzam N, Kaucikas M, Nürnberg DJ et al (2019) Femtosecond infrared spectroscopy of chlorophyll f-containing photosystem I. Phys Chem Chem Phys 21:1224–1234. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8cp05627g
Zazubovich V, Matsuzaki S, Johnson TW et al (2002) Red antenna states of photosystem I from cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus: a spectral hole burning study. Chem Phys 275:47–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-0104(01)00535-3
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Lomonosov Moscow State University Program of Development. Optical measurements were performed using core research facilities of FRCCP RAS (no. 1440743, 506694).
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation Grant RSF 22–24-00705.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Fedor E. Gostev, Ivan V. Shelaev, Mahir D. Mamedov, Arseniy V. Aybush, Alexey Yu. Semenov, Vladimir A. Shuvalov and Victor A. Nadtochenko. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Dmitry A. Cherepanov and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cherepanov, D.A., Semenov, A.Y., Mamedov, M.D. et al. Current state of the primary charge separation mechanism in photosystem I of cyanobacteria. Biophys Rev 14, 805–820 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12551-022-00983-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12551-022-00983-1