Abstract
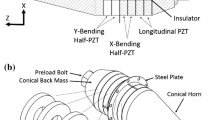
This paper proposes a dual-frequency surface texturing method that generates small, round, drop-shaped micro dimples on a cylindrical surface. To achieve this, two devices were developed: a 3D resonant elliptical vibration transducer and a non-resonant displacement amplifier. The 3D resonant elliptical vibration transducer operates at high frequency (≈18 kHz) and has three vibration modes: one longitudinal vibration mode and two bending vibration modes. The one-dimensional displacement amplifier operates at low frequency (≈155 Hz). Finite element analysis was used to develop 3D resonant elliptical vibration transducer. One dimensional displacement amplifier was designed on the basis of single parallel flexure hinge mechanism and its working principle was based on non-resonant transducer. The feasibility of the proposed method was examined by performing a surface texturing experiment on Al6061-T6 material specimen. The wettability of the micro-dimple structured surface was also examined by measuring the water contact angle.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xu, S., Kuriyagawa, T., Shimada, K., & Mizutani, M. (2017). Recent advances in ultrasonic-assisted machining for the fabrication of micro/nano-textured surfaces. Frontiers of Mechanical Engineering, 12, 33–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11465-017-0422-5
Zhang, J., Cui, T., Ge, C., Sui, Y., & Yang, H. (2016). Review of micro/nano machining by utilizing elliptical vibration cutting. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 106, 109–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2016.04.008
Bruzzone, A. A. G., Costa, H. L., Lonardo, P. M., & Lucca, D. A. (2008). Advances in engineered surfaces for functional performance. CIRP Annals-Manufucture Technology, 57, 750–769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2008.09.003
Kurniawan, R., & Ko, T. J. (2015). Friction reduction on cylindrical surfaces by texturing with a piezoelectric actuated tool holder. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 16, 861–868. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-015-0113-2
Guo, P., & Ehmann, K. F. (2011). Development of a new vibrator for elliptical vibration texturing, ASME 2011 Int. Manufacture Science Engineering Conference MSEC, 2011(1), 373–380. https://doi.org/10.1115/MSEC2011-50131
Vilhena, L. M., Sedlaček, M., Podgornik, B., Vižintin, J., Babnik, A., & Možina, J. (2009). Surface texturing by pulsed Nd:YAG laser. Tribology International, 42, 1496–1504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2009.06.003
Zhou, R., Cao, J., Wang, Q. J., Meng, F., Zimowski, K., & Xia, Z. C. (2011). Effect of EDT surface texturing on tribological behavior of aluminum sheet. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 211, 1643–1649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2011.05.004
Balasubramaniam, R., Krishnan, J., & Ramakrishnan, N. (2002). A study on the shape of the surface generated by abrasive jet machining. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 121, 102–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(01)01209-2
Wakuda, M., Yamauchi, Y., Kanzaki, S., & Yasuda, Y. (2003). Effect of surface texturing on friction reduction between ceramic and steel materials under lubricated sliding contact. Wear, 254, 356–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1648(03)00004-8
Byun, J. W., Shin, H. S., Kwon, M. H., Kim, B. H., & Chu, C. N. (2010). Surface texturing by micro ECM for friction reduction. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 11, 747–753. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-010-0088-y
Pettersson, U., & Jacobson, S. (2003). Influence of surface texture on boundary lubricated sliding contacts. Tribology International, 36, 857–864. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-679X(03)00104-X
Kurniawan, R., & Ko, T. J. (2013). A study of surface texturing using piezoelectric tool holder actuator on conventional CNC turning. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 14, 199–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-013-0028-8
Dornfeld, D., Min, S., & Takeuchi, Y. (2006). Recent advances in mechanical micromachining. CIRP Annal-Manufacturing Technology, 55, 745–768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2006.10.006
Greco, A., Raphaelson, S., Ehmann, K., Wang, Q. J., & Lin, C. (2009). Surface Texturing of tribological interfaces using the vibromechanical texturing method. Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering, 131, 061005. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4000418
Gandhi, R., Sebastian, D., Basu, S., Mann, J. B., Iglesias, P., & Saldana, C. (2016). Surfaces by vibration/modulation-assisted texturing for tribological applications. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 85, 909–920. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7968-3
Kurniawan, R., Ko, T. J., Ping, L. C., Kumaran, S. T., Kiswanto, G., Guo, P., & Ehmann, K. F. (2017). Development of a two-frequency, elliptical-vibration texturing device for surface texturing. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 31, 3465–3473. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-017-0635-x
Shamoto, E., & Moriwaki, T. (1999). Ultraprecision diamond cutting of hardened steel by applying elliptical vibration cutting. CIRP Annals–Manufacturing and Technology, 48, 441–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0007-8506(07)63222-3
Shamoto, E., Suzuki, N., Moriwaki, T., & Naoi, Y. (2002). Development of ultrasonic elliptical vibration controller for elliptical vibration cutting. CIRP Annals–Manufacturing and Technology, 51, 327–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0007-8506(07)61528-5
Nath, C., Rahman, M., & Neo, K. S. (2009). A study on ultrasonic elliptical vibration cutting of tungsten carbide. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 209, 4459–4464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2008.10.047
Shamoto, E., & Moriwaki, T. (1994). Study on elliptical vibration cutting. CIRP Ann- Manufacture Technology, 43, 35–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0007-8506(07)62158-1
Chen, T., Liu, S., Liu, W., & Wu, C. (2017). Study on a longitudinal-torsional ultrasonic vibration system with diagonal slits. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 9, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1177/1687814017706341
Tan, R., Zhao, X., Zou, X., & Sun, T. (2018). A novel ultrasonic elliptical vibration cutting device based on a sandwiched and symmetrical structure. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 97, 1397–1406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-2015-9
Guo, P., & Ehmann, K. F. (2013). Development of a tertiary motion generator for elliptical vibration texturing. Precision Engineering, 37, 364–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2012.10.005
Yang, Y., Gao, S., Chen, K., Pan, Y., & Guo, P. (2017). Vibration analysis and development of an ultrasonic elliptical vibration tool based on a portal frame structure. Precision Engineering, 50, 421–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2017.06.016
Yin, Z., Fu, Y., Xu, J., Li, H., Cao, Z., & Chen, Y. (2017). A novel single driven ultrasonic elliptical vibration cutting device. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 90, 3289–3300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9641-x
Yang, X., Liu, Y., Chen, W., & Liu, J. (2013). Longitudinal and bending hybrid linear ultrasonic motor using bending PZT elements. Ceramics International, 39, S691–S694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2012.10.163
Shuyu, L. (1995). Study on the multifrequency Langevin ultrasonic transducer. Ultrasonics, 33, 445–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/0041-624X(95)00051-4
Kurniawan, R., Ali, S., & Ko, T. J. (2018). Modal simulation analysis of novel 3D elliptical ultrasonic transducer. IOP Conference Series Material Science and Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/324/1/012063
Zhou Errata, X., Zuo, C., Liu, Q., & Lin, J. (2016). Surface generation of freeform surfaces in diamond turning by applying double-frequency elliptical vibration cutting. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 104, 45–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2015.11.012
Zhou, X., Zuo, C., Liu, Q., Wang, R., & Lin, J. (2016). Development of a double-frequency elliptical vibration cutting apparatus for freeform surface diamond machining. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8596-2
Kurniawan, R., Kiswanto, G., & Ko, T. J. (2017). Surface roughness of two-frequency elliptical vibration texturing (TFEVT) method for micro-dimple pattern process. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 116, 77–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2016.12.011
Zhu, Z., Zhou, X., Liu, Q., & Zhao, S. (2011). Multi-objective optimum design of fast tool servo based on improved differential evolution algorithm. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 25, 3141–3149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-011-0824-y
He, Y., Zou, P., Zhu, Z., Le Zhu, W., Yang, X., Cao, J., & Ehmann, K. F. (2018). Design and application of a flexure-based oscillation mechanism for surface texturing. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 32, 298–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2018.02.017
Etsion, I. (2004). Improving tribological performance of mechanical components by laser surface texturing. Tribology Letters, 17, 733–737. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-004-8081-1
Yan, H., Abdul Rashid, M. R. B., Khew, S. Y., Li, F., & Hong, M. (2018). Wettability transition of laser textured brass surfaces inside different mediums. Applied Surface Science, 427, 369–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.08.218
Hosseinabadi, H. N., Sajjady, S. A., & Amini, S. (2018). Creating micro textured surfaces for the improvement of surface wettability through ultrasonic vibration assisted turning. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 96, 2825–2839. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-1580-2
Lu, Y., Guo, P., Pei, P., & Ehmann, K. F. (2015). Experimental studies of wettability control on cylindrical surfaces by elliptical vibration texturing. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 76, 1807–1817. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-6384-4
Kurniawan, R., Ali, S., & Ko, T. J. (2020). Measurement of wettability on rhombohedral pattern fabricated by using 3D-UEVT. Measurement, 160, 107784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2020.107784
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) and funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT, and Future Planning (grant number NRF-2020 R1A2B5B02001755).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, S., Kurniawan, R. & Ko, T.J. Development of 3D Resonant Elliptical Vibration Transducer for Dual-Frequency Micro-Dimple Surface Texturing. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 22, 1365–1379 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-021-00551-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-021-00551-9